![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
blood serum concentration of a medication reached and maintained after repeated fixed doses
|
plateau
|
|
|
|
An Effect that is Intended or predicted physiological response
|
Thearapeutic Effects
|
|
|
|
Drugs will cause unintended secondary effects.
-May be harmless or cause injury -Often stop taking med's |
Side Effects
|
|
|
|
Something different alwaysis possible, opposite effect then what was intended.
Idiosyncratic Reaction |
Idiosyncratic Reaction
|
|
|
|
After prolonged intake of high doses of med's, or when drug accumulates in the body, b.c. of the impared metabolism or excretion.
|
Toxic Effects
|
|
|
|
greater effects of 2 drugs combined.
-May be desired: Diurectics & Vasodilaors to lower Bp -May be undesire:Alcohol & Narcotics |
Synergistic Effects
|
|
|
|
Drug Dose Response
|
After drug is administered it undergoes
-Absorption -Distrubution -Metabolism -Excretion |
|
|
|
-Easiest
-Slowest onset of action and more prolonged effect |
Oral Route
|
|
|
|
Sublingual Application
|
Placed under the tongue
|
|
|
|
Buccal Administration
|
Placing solid medication n mouth against the mucous memebrance of the cheek until it dissolves
|
|
|
|
Exposure to inital dose may cause an immunological response
Drug acts as an antigen which causes antibodies to be produced Allergic reaction |
Allergic reaction
|
|
|
|
Raised irregular shaped skin eruptions with varying sizing and shapes eruptions have reddened margins and pale centers.
|
Urticaria
|
|
|
|
Small raised vesicles that are usually reddened often distrubuted over the entire body
|
Rash
|
|
|
|
Itching of the skin accompanies most rashes.
|
Pruritus .
|
|
|
|
inflammation of mucous membrane lining nose causes swelling and clear watery discharge
|
Rhinitis
|
|
|
|
An application to mucous membrane
|
Topical
|
Ex: Eye gtts,Ear gtts, Nasal spray,Bladder and Rectal installation
|
|
|
Respiratory Tract
Large rich surface area for drug absorption. -Some are designed to have local effects *bronchodilators |
Inhallation
|
|
|
|
Parental Routes
|
Injecting Med's into body tissue.
ex;ID,IM,IV,SubQ |
|
|
|
injection into the dermis just under epidermis
|
Intradermal Route ID
|
|
|
|
injection Into the muscle
|
Intramuscular Route IM
|
|
|
|
injection into the vein
|
Intravenous Route IV
|
|
|
|
injection into the tissue below the dermis of the skin
|
Subcutaneous SUB-Q
|
|
|
|
Allergic Response
|
Common or Mild
Ex: Hives,eczema,rash,pruritus,rhinitis,urticaria,wheezing -Severe Ex:Anaphylactic Reaction |
|
|
|
severe sudden constriction of bronchioali muscles,edema of pharynx & larynx with severe wheezing and shortness of breathe
|
Anaphylactic Reaction
|
|
|
|
Alcohol and opiates are common forms that react to slow metabolism and cause a need for increased dosage.
|
Drug Tolerance
|
|
|
|
One drug modifies the action of another
-May potentiate or diminsh the action other drugs |
Drug Interaction
|
|
|
|
-For seizure treatment
-Administered by mouth or IV pushin large doses -Affects rhythms of the heart |
Dilantin
|
|
|
|
A substance used in the diagnosis treatment cure relief or prevention of diease.
|
Drug
|
|
|
|
Given by the manufacturer who irst developed the drug
ex:aspirin and Tetracycline HCl -may have different names |
Generic name
|
|
|
|
Brand Name or proprietary name under which a manufacturer markets a drug
|
Trade name
|
|
|
|
indicates the effect on the body system, systems relieved or desired effects.
-May belong to more than one ex: Aspirin-analagesic,antiinflammatory,anticlor,antipyretic Drug Classification |
Drug classification
|
ex: Aspirin-analagesic,antiinflammatory,anticlor,antipyretic
|
|
|
Does not create a function in a tissue or organ but rather alters physiological functions
-Alters body fluids,cell membrances or interacts with receptor sites. |
Drug
|
|
|
|
Study of how drugs enter the body, reach their site of action are metablized and exit the body
|
Pharmacokinetics
|
|
|
|
Passage of drug molecules into the blood
-most drugs enter systemic circulation to exert therapeutic effects except topicals |
Absorption
|
Factors-
-Route of admistion -Ability to dissolve -Conditions at site of absorption |
|
|
after drug is absprbed it is sent to the tissues and organs and ultimately to the specific site of action
|
Distrubition
|
Factors
-physical & chemical properties of drugs |
|
|
After drug reaches its site of action it is broken down into an inactive form that is more easily excreted aka Biotransformation
|
Metabolism
|
|
|
|
after metabolism drugs exit the body trhough the kidneys,liver,bowels,lungs & exocrine glands chemical makeup of drug determines the organ of excretion
|
Excretion
|
|
|
|
Time it takes for a medication to reach highest effective concentration
|
Peak
|
|
|
|
Time it takes after medication is administrated for it to produce a response
|
Onset
|
|
|
|
Minimum blood serum concentration of medication reached just before the next schedule dose.
Trough |
Trough
|
|
|
|
time during which the med's is present in concentration great enough to produce a response.
|
Duration
|
|
|
|
The 6 Rightsof Medication Administration
|
-Medication
-Dose -Client -Route -Time -Documentation |
|
|
|
A type of order that is carried out until MD cancels it or until the prescribed number of days elapse.
|
Standing Orders
|
|
|
|
MD may order drug on a when necessary basis. Nurse decides need
MD sets max intervals for time administration. PRN Orders |
PRN Orders
|
|
|
|
One time order
One dose eg; pre operative order Single Orders |
Single Orders
|
|
|
|
Single dose of medication to be given immediately and only once
|
Stat Orders
|
up to an hour to give the meds
|
|
|
Components of a Drug order
|
-Clients full name
-Date order is written -Drug name -Dosage -Route of administration -Time and frequency -Signature of MD or NP |
|
|
|
Injection technique
|
Nurse needs to know the volume to be administered.
-drug characteristics & viscosity -location of anatomical structures underlying injection site. |
|
|
|
Technique Failure
|
-Nerve or bone damage
no aspiration- vein or artery too large of volume-pain and local tissue damage |
|
|
|
Subcutaneous Site
|
-Vascular and easily accessible
-Sites require rotation -abdominal wall best for Heparin |
|
|
|
Heparin
|
Anticoagulant
-used to treat or prevent clots in the veins, arteries, lungs, or heart. -stops clots from forming or getting bigger. |
|
|
|
Sub Q Amount
|
only small doses 0.5 to 1ml of fluid
medication can collect within the tissue causing sterile abscess' hardened painful lumps under the skin. |
|
|
|
Sub Q Needle
|
25 guage - 5/8 inch needle
@ 45 degree but not always Obese pts pinch tissue and make sure needle is long enough. preferred need length 1/2 inch width of skin fold. |
|
|
|
Sub Q Sites
|
Abdomen
-Lateral upper arm -Deltoid Upper Back below Scapula -Ventrogluteal -Vastus Lateralis |
|
|
|
IM Amount
|
well developed client can tolerate 3 ml of fluid in large muscles
Child & Elderly - less than 2ml |
|
|
|
IM Sites
|
-Rectus Femoris
-Vastus Lateralis -Ventrogluteal-best site bc no vessels -Dorsogluteal Deltoid -small amounts only |
|
|
|
IM Factors
|
Assess site before injecting
-look for hardened lesions -free of infection -Bruising,abrasion -check underlying bones, nerves,major blood vessels |
|
|
|
Z track technique
|
-New needle after drawing up drug
-add 0.2 ml air lock -pull skin 1 to 1 1/2 in to side -apirate and inject -withdrawl needle -release skin & seal needle track |
|
|
|
Vistaril
|
AKA Hydroxyzine
Antihistamine -treat allergy symptoms, anxiety and tension |
|
|
|
ID Sites
|
used for allergy testing
-inner forearmor upper back |
|
|
|
ID Syringes
|
-come in sizes 1-50 ml
-2-3 ml for IM or SUBQ -More than 5ml for injection(uncommon) insulin -100units/1ml TB-1ml |
|
|
|
Parts of a Needle
|
-Hub
Must remain sterile -shaft -bevel |
|
|
|
Needle Size
|
according to size of pt.
-weight & tissue injected General -1 to 1 1/2 in -IM -3/8 to 5/8 in - Sub Q |
|
|
|
Needle Gauge
|
-Smaller the gauge the larger the needle diameter
*16 -18 blood products *19-23 IM depends on viscosity *25 SubQ *26 ID |
|
|
|
vacuum packed and will need to be inserted equal amounts of air before withrawled from container
|
Amples and Vials
|
|
|
|
Insulin
|
Mixed
NPH-Cloudy addition of a protein which slows absorption Regular-clear |
|
|
|
Insulin mixed
|
Must be given with in 5 mins of prep time bc binding will occur and reduce the effectiveness of the short acting insulin
Always draw up short acting insulin first so it will not become contaminated with long lasting insulin and slow down reaction time. |
|
|
|
Contraindications for Oral Route
|
Liver or Renal function
ability to swallow/cough/gag vomitting or nausea bowel inflammation |
|
|
|
Preparing medication
|
-One client at a time
-select correct med -compare label with MAR -check calcuation dose -double check with another nurse if needed -narcotics ( check Count) -take meds to client at correct time within 30mins before/after -2 identifiers, clients name and Identification number on MAR print out and ID Bracelet. ask pt to state name for 3rd identifier. -evaluate clients response to meds on onset peak and duration. |
|
|
|
pill crushing device
|
mortar and pestle
|
|
|
|
nasal instillation
|
effective for treating sinus infections
-severe nose bleeds are treating with packing and epinephrine to reduce blood flow |
|
|
|
-artificial tears and vasoconstrictors
ex Visine & Murine |
Eye Instillation
|
|
|
|
Intraocular Administration
|
medication delivered that resembles a contact lens
ex pilocarpine |
|
|
|
Nasal installation drops into the ethmoid or sphenoid sinus
|
lay supine and Tilt head back
use pillow or head over the edge of the bed |
|
|
|
Nasal installation drops into the frontal and maxillary sinus
|
lay lateral with head tilted to the side
use pillow or head over the edge of the bed |
|
|
|
POsition of body for ophthalmic installation
|
supine or sit back in chair with head hyperextended
|
|
|
|
Eye drops installation
|
-Have pt look at ceiling
dominant hand resting on clients forehead hold med dropper 1-2cm 1/ inch-3/4 inch from conj. sac -have pt closes eyes after -apply pressure from 30-60 sec (only for systemic effect) |
|
|
|
eye oinment installation
|
have pt look at ceiling
-apply ointment from inner to outer canthus -have pt close eye and rub lid lightly in circular motionswith cotton ball -if rubbing is not contraindicated |
|
|
|
vaginal installation
|
oval shaped suppositories foams,jellies or creams
|
|
|
|
Rectal installation
|
thinner and more bullet shaped suppositories
-promotes defecation or systemic effects -somes times enema used first then suppository |
|
|
|
albuterol
|
a beta-adrenergic agonist bronchodilator
|
|
|
|
-Lacks major nerves and blood vessels
-Rapid drug absorption -used in infants immunizations |
Vastus Lateralis
|
|
|
|
-Deep site away from major nerves andblood vessels
-less chance of contamination from incontinence -easily identified by bony prominent landmarks -perferred site for meds that are in larger volume |
Ventrogluteal
|
|
|
|
-Easily accessible but not well developed in all pt.
-small amounts of medications -not used in children or infants -recommended site for hepB and rabies. |
Deltoid
|
|
|
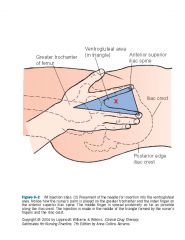
|
Intramuscular injection site
|
|
|
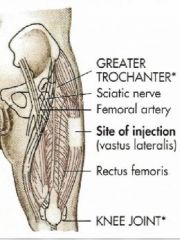
|
Vastus Lateralis injection
|
use mid third of injection of the thigh
|
|
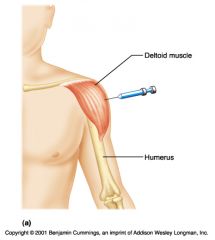
|
Deltoid injection
|
-1-2 inchs below acromion process(3 fingers below)
-not well developed in many adult, risk of potential injury -SMALL INJECTION VOLUME |
|
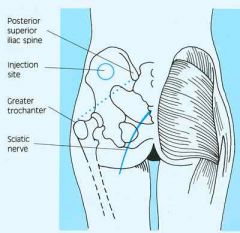
|
Do not use this site due to risk of hitting sciatic nerve.
|
|

