![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
growth hormone (somatotropin)
|
*growth of skeletal muscle, bone, cartilage
*increase protein synthesis stimulates lipolysis for ATP production *reduces glucose use for ATP production * increase release of stored glucose from liver *raises blood glucose level (diabetogenic effect) |
|
|
|
melanocyte stimulating hormone
|
peptide hormones produced by cells in the intermediate lobe of the pituitary gland.
fn- makes skin/hair darker |
|
|
|
thyroid stimulating hormone
|
*triggers thyroid hormone release from thyroid
*indirectly enhances basal metabolism of cells via thyroid activation |
|
|
|
oxytocin
|
Made in pituitary *stimulates uterine contraction (labor contractions)
*stimulates milk let-down reflex *pair bonding, mate-guarding, and social memory. |
|
|
|
antidiuretic hormone
|
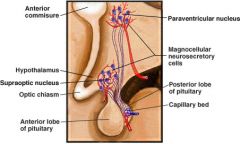
*stimulates water retention by renal collecting ducts in kidneys
*inhibits sweat glands in skin *stimulates vasoconstriction in skin (hence name "vasopressin") |
|
|
|
the major hormone secreted by the follicular cells of the thyroid gland and is involved in controlling the rate of metabolic processes in the body and influencing physical development.
|
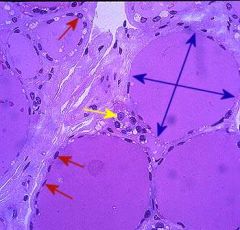
T4 thyroxin
|
produced in red arrows
|
|
|
T3 triiodothyronine
|
the most powerful thyroid hormone, and affects almost every process in the body, including body temperature, growth, and heart rate
|
|
|
|
A hormone produced by the thyroid gland that lowers the levels of calcium and phosphate in the blood and promotes the formation of bone. *parafollicular cells
|
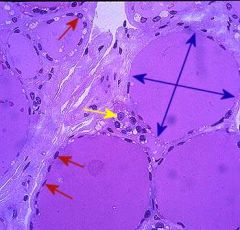
calcitonin
|
yellow arrow
|
|
|
The hormone involved in carbohydrate metabolism. Produced by the pancreas, it is released when the glucose level in the blood is low (hypoglycemia), causing the liver to convert stored glycogen into glucose and release it into the bloodstream.
|
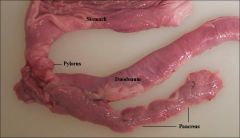
glucagon
|
|
|
Adrenal glands
|
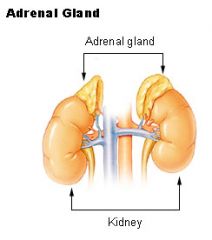
They are chiefly responsible for regulating the stress response through the synthesis of corticosteroids and catecholamines, including cortisol and adrenaline.
|
|
|
parathyroid hormone
|
increases calcium in the blood, produced in parathyroid glands
|
|
|
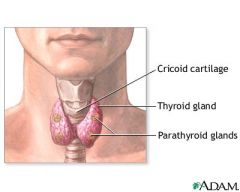
parathyroid gland
|
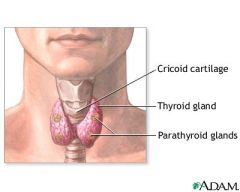
produces parathyroid hormone wich increases calcium
|
|
|
thyroid gland
|
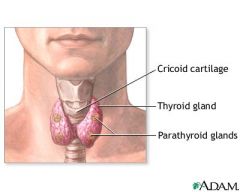
controls how quickly the body burns energy, makes proteins, and how sensitive the body should be to other hormones.
|
|
|
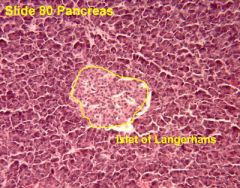
islets of langerhans
|
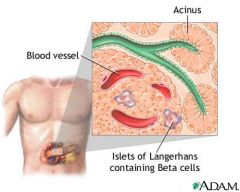
the insulin-producing tissue, the islets of Langerhans do more than that. They are groups of specialized cells in the pancreas that make and secrete hormones
|
|
|
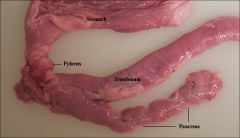
pancreas
|
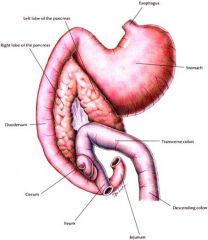
digestive - produces digestive enzymes
hormonal - islets of Langerhans produce insulin needed to control blood sugar levels |
|
|
|
Adrenocorticotropin hormone
|
*stimulates glucocorticoid (cortisol) secretion from adrenal cortex
* indirectly enhances "stress-response" via adrenal activation |
|
|
|
prolactin
|
*promotes milk production by mammary glands
|
|
|
|
Follicle-stimulating hormone
|
induces spermatogenesis in testes of males after onset of puberty
* induces 2o oocyte development in ovaries of females after onset of puberty * stimulates growth of ovarian follicles (granulosa cells) * stimulates estrogen production from ovaries |
|
|
|
Luteinizing hormone
|
enhances 2o oocyte maturation in ovaries
induces ovulation maintains corpus luteum for first two weeks after ovulation stimulates testosterone production from testes |
|
|
|
exophthalmos goiter
|
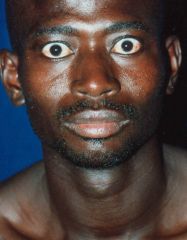
bulging of the eyes. Hyperthyroidism
|
|
|
|
goiter
|
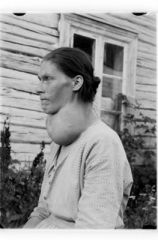
enlarged thyroid gland
|
|

