![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
174 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
adip/o
lip/o steat/o |
fat
|
|
|
derm/o
dermat/o cutane/o |
skin
|
|
|
erythr/o
|
red
|
|
|
4 signs of melanoma
|
asymmetry
border irregularity color diameter greater than 6mm |
|
|
hidr/o
|
sweat
|
|
|
hist/o
histi/o |
tissue
|
|
|
kerat/o
|
hard
|
|
|
leuk/o
|
white
|
|
|
melan/o
|
black
|
|
|
myc/o
|
fungus
|
|
|
onych/o
|
nail
|
|
|
plas/o
|
formation
|
|
|
purpur/o
|
purple
|
|
|
scler/o
|
hard
|
|
|
seb/o
|
sebum (oil)
|
|
|
squam/o
|
scale
|
|
|
trich/o
|
hair
|
|
|
xanth/o
|
yellow
|
|
|
xer/o
|
dry
|
|
|
subcutaneous layer
|
below dermis composed of loose connective tissue and adipose
|
|
|
connective tissue layer contains blood vessels & nerves
|
dermis
|
|
|
consists of several layers of stratified squamous
|
epidermis
|
|
|
cells are produced in _____ layer, moving older cells up towards surface
|
innermost basal
|
|
|
layers of packed dead cells accumulate in ________ layer
|
outermost squamous
|
|
|
trichorrexis
|
hair that is broken or split
|
|
|
seborrhea
|
overproduction of sebum
|
|
|
formation of sweat
|
hidropoises
|
|
|
any condition caused by a fungus
|
mycosis
|
|
|
abnormal softening of the nails
|
onychomalacia
|
|
|
onychomycosis
|
fungus infection of nails
|
|
|
steat/o
|
fat
|
|
|
steatis
|
inflammation of fat
|
|
|
partial/total absence of pigment in the skin
|
leukoderma
|
|
|
erythema/ erythroderma
|
red skin
|
|
|
xanthoma
|
yellow skin tumor
|
|
|
xeroderma
|
dry skin
|
|
|
xerosis
|
pathologically dry skin
|
|
|
cells covering externa and internal surfaces of the body
|
epithelium
|
|
|
thin outer layer of skin
|
epidermis
|
|
|
flat cell like epithelial cells comprising the outermost epidermis
|
squamous cell layer
|
|
|
deepest layer of epidermis
|
basal layer
|
|
|
cell in basal layer that gives color to the skin
|
melanocyte
|
|
|
dark brown to black pigment contained in melanocytes
|
melanin
|
|
|
dense fibrous CT layer of skin also known as corium
|
dermis
|
|
|
sebaceous glands
|
oil glands in skin
|
|
|
sebum
|
oily substsnce secreted by sebaceous glands
|
|
|
sudoriferous glands
|
sweat glands
|
|
|
protein substance in skin and CT
|
collagen
|
|
|
outgrowth of the skin composed of keratin
|
hair
|
|
|
outgrowth of the skin composed of keratin at the end of each finger and toe
|
nail
|
|
|
hard protein material found in epidermis hair and nails
|
keratin
|
|
|
sudoriferous glands are located in what layer
|
dermis
|
|
|
area of pathologically altered tissue (primary and secondary)
|
lesion
|
|
|
lesions arising from previously normal skin
|
primary lesions
|
|
|
flat discolored spot on the skin up to 1cm across
|
macule or macula
|
|
|
flat discolored area on the skin larger than 1cm
|
patch
|
|
|
solid mass on skin up to .5 cm in diameter
|
papule
|
|
|
solid mass greater than 1 cm in diameter and limited to the surface of the skin
|
plaque
|
|
|
solid mass greater than 1cm that extends deeper into epidermis
|
nodule
|
|
|
solid mass larger than 1-2 cm
|
tumor
|
|
|
area of localized skin edema
|
wheal
|
|
|
little bladder an elevated fluid filled sac within or under the epidermis up to .5 cm in diameter
|
vesicle
|
|
|
blister larger than .5 cm (second degree burn)
|
bulla
|
|
|
pus filled sac
|
pustule
|
|
|
lesions that result in changes in primary lesions
|
secondary lesions
|
|
|
erosion
|
loss of superficial dermis leaving an area of moisture but no bleeding
|
|
|
ulcer
|
open sore on skin or mucous membrane that can bleed and scar sometimes accompanied by infection
|
|
|
excpriation
|
scratch mark
|
|
|
fissure
|
linear crack in the skin
|
|
|
scale
|
think flake of exfoliated epidermis (dandruff)
|
|
|
crust
|
dried residue of serum puss or blood on the skin
|
|
|
vascular lesions
|
lesions of a blood vessel
|
|
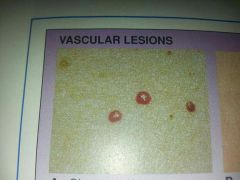
small round bright red blood vessel tumor on the skin often on the trunk of elderly
|
cherry angioma
|
|
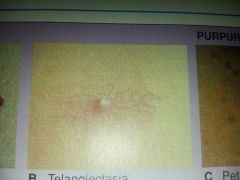
tiny red blood vessel lesion formed by the dilation of a group of blood vessels radiating from a central arteriole on face neck or chest
|
telangiectasia (spider angioma)
|
|
|
purpura lesions resulting from hemorrhages into the skin
|
purpuric lesions
|
|
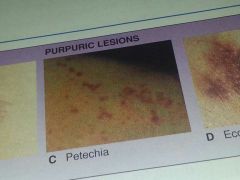
spot, reddish brown spots on skin that indicate a bleeding tendency, a small purpura
|
petechia
|
|

bruise, black and blue mark, large purpura
|
ecchymosis
|
|
|
cicatrix of the skin
|
mark left by healing of a sore or wound, replacement of destroyed tissue by fibrous tissue (scar)
|
|
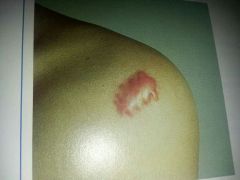
keloid
|
abnormal overgrowth of scar tissue that is thick and irregular
|
|
|
epidermal tumors
|
skin tumors arising from epidermis
|
|
|
mole
|
nevus
|
|
|
mole with precancerous changes
|
dysplastic nevus
|
|
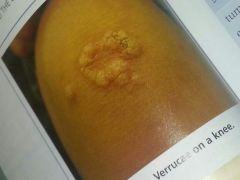
epidermal tumor caused by papilloma virus (wart)
|
verruca
|
|
|
alopecia
|
baldness
|
|
|
plug of sebum within opening of hair follicle
|
comedo (comedos, comedones)
|
|
|
closed comedo
|
comedo below skin surface with white center (whitehead)
|
|
|
open comedo
|
comedo open to skin surface with black center caused by presence of melanin (blackhead)
|
|
|
eruption
|
appearance of a skin lesion
|
|
|
erythema
|
redness of skin
|
|
|
pruritus
|
severe itching
|
|
|
rash
|
skin eruption (communicable disease)
|
|
|
skin pigmentation
|
skin color resulting from presence of melanin
|
|
|
depigmentation
|
loss of melanin pigmentat in skin
|
|
|
hypopigmentation
|
areas of skin lacking color bc of deficient amounts of melanin
|
|
|
hyperpigmentation
|
darkened areas of skin caused by excessive amounts of melanin
|
|
|
suppuration
|
production of purulent matter (pus)
|
|
|
urticaria
|
hives, eruption of wheals on skin accompanied by itching
|
|
|
xeroderma
|
dry skin
|
|
|
hereditary condition partial or total lack of melanin pigment
|
albinism
|
|
|
injury to body tissue caused by heat chemicals electricity radiation or gases
|
burn
|
|
|
first degree burn
|
burn involving only epidermis (erythema, hyperesthesia)
|
|
|
second degree burn
|
burn involving epidermis and dermis (erythema, hyperesthesia,vesications)
|
|
|
third degree burn
|
burn involving all layers of skin, destruction of epidermis&dermis damage or destruction to subcutaneous tissue
|
|
|
dermatitis
|
inflammation of skin
|
|
|
dermatosis
|
any disorder of the skin
|
|
|
exanthematous viral disease
|
eruption of skin caused by a viral disease
|
|
|
rubella
|
reddish, german measles
|
|
|
rubeola
|
reddish, 14 day measles
|
|
|
varicella
|
a tiny spot, chicken pox
|
|
|
used with dermatitis appearance of inflamed swollen papules and vesicles that crust & scale often with sensations of itching and burning
|
eczema
|
|
|
boil; painful nodule formed in skin by inflammation caused by staphylococcosis
|
furuncle
|
|
|
skin infection consisting of clusters of furuncles
|
carbuncle
|
|
|
localized collection of pus in cavity formed by inflammation of surrounding tissue, heals when drained
|
abscess
|
|
|
eating sore. death of tissue associated with loss of blood supply
|
gangrene
|
|
|
herpes simplex virus (type 1)
|
transient viral vesicles : cold sore
|
|
|
herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV2)
|
std ulcer like lesion of genital and anorectal skin, after infection lies dormant in skin and flares up
|
|
|
herpes zoster
|
viral disease affecting peripheral nerves , painful blisters spread over skin (shingles)
|
|
|
highly contagious bacterial skin inflammation marked by pustules that rupture and become crusted most often around mouth and nostrils
|
impetigo
|
|
|
keratoses
|
thickened area of epidermis
|
|
|
localized thickening of skin caused by excessive exposure to sunlight (precursor to cancer)
|
actinic (solar) keratoses
|
|
|
benign wart like tumors more common on elderly skin
|
seborrheic keratoses
|
|
|
chronic autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation of various parts of the body
|
lupus
|
|
|
cutaneous lupus
|
limited to the skin, characteristic rash
|
|
|
systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
|
more severe form of lupus involving skin joints and vital organs
|
|
|
malignant cutaneous neoplasm
|
skin cancer
|
|
|
squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
|
malignant tumor of the squamous epithelium
|
|
|
basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
|
malignant tumor of basal layer of epidermis (most common type of skin cancer)
|
|
|
malignant melanoma
|
malignant tumor composed of melanocytes
|
|
|
malignant tumor of walls of blood vessels, commonly seen in HIV/AIDS patients
|
kaposi sarcoma
|
|
|
onychia
|
inflammation of fingernail/toenail
|
|
|
paronychia
|
inflammation of nail fold
|
|
|
pediculosis
|
infestation of lice that causes itching and dermatitis
|
|
|
pediculosis capitis
|
head lice
|
|
|
pediculosis pubis
|
lice infects pubic region (crabs)
|
|
|
chronic recurrent skin disease marked by silvery scales covering red patches papules/plaques of skin result from overproduction& thickening of skin cells
|
psoriasis
|
|
|
contagious disease caused by a parasite that invades the skin causing intense itch
|
scabies
|
|
|
skin condition marked by hypersecretion of sebum from sebaceous glands
|
seborrhea
|
|
|
group of fungal skin diseases identified by body part affected including tinea corporis (body, ring worm) & tinea pedis (athletes foot)
|
tinea
|
|
|
condition caused by destruction of melanin white patches in skin
|
vitiligo
|
|
|
biopsy (Bx)
|
removal of small piece of tissue for microscopic pathological examination
|
|
|
excisional biopsy
|
removal of an entire lesion
|
|
|
incisional biopsy
|
removal of selected portion of lesion
|
|
|
shave biopsy
|
using surgical blade to shave tissue from epidermis and upper dermis
|
|
|
isolating and growing colonies of microorganisms to identify a pathogen & determine which drugs might be effective for combating infection it has caused
|
culture and sensitivity (C&S)
|
|
|
involves cutting a thin piece of tissue from a frozen specimen for immediate pathological examination
|
frozen section (FS)
|
|
|
test in which substance is applied to skin through a scratch
|
scratch test
|
|
|
test in which substance is applied topically to skin on a small piece of blotting paper or wet cloth
|
patch test
|
|
|
removal of tissue after it has been destroyed by chemical means
|
chemosurgery
|
|
|
technique for restoring wrinkled scarred or blemished skin by applying acid solution to peel away top layer of skin
|
chemical peel
|
|
|
destruction of tissue by freezing with application of an extremely cold chemical
|
cryosurgery
|
|
|
surgical removal of epidermis frozen by aerosol spray using wire brushes& emery papers to remove scars/tattoos/wrinkles
|
dermabrasion
|
|
|
scraping a wound using spoon like cutting instrument called curette used for debridement
|
curettage
|
|
|
use of electrical current to destroy tissue
|
electrosurgical procedures
|
|
|
use of an instrument heated by electric current to coagulate bleeding areas by burning the tissue
|
electrocautery
|
|
|
use of high frequency electric currents to destroy tissue by drying it, active electrode makes direct contact with skin lesion
|
electrodesiccation
|
|
|
to lighten; use of long high frequency electric sparks to destroy tissue, active electrode does not touch the skin
|
fulguration
|
|
|
incision and drainage of an infected skin lesion
|
incision and drainage (I&D)
|
|
|
surgery using laser in various dermatologic procedures to remove lesions scars tattoos
|
laser surgery
|
|
|
instrument that concentrates high frequencies of light into a small intense beam applied to body tissues to destroy lesions or for dissection
|
laser
|
|
|
technique used to excise tumors of the skin by removing fresh tissue layer by layer until a tumor free plane is reached
|
mohs surgery
|
|
|
transfer of skin from one body site to another to replace skin that has been lost due to burn or injury
|
skin grafting
|
|
|
graft transfer to a new position of the body of the same person
|
autograft
|
|
|
graft transfer between different species such as from animal to human
|
heterograft or xenograft
|
|
|
donor transfer between persons of the same species such as human to human
|
homograft or allograft
|
|
|
treatment of malignancies infections & other diseases with chemical agents that destroy selected chemicals or impair their ability to reproduce
|
chemotherapy
|
|
|
treatment of neoplastic disease using ionizing radiation to deter proliferation of malignant cells
|
radiation therapy
|
|
|
use of sclerosing agents in treating diseases
|
sclerotherapy
|
|
|
use of ultra violet light to promote healing of skin lesion
|
ultraviolet therapy
|
|
|
drug temporarily blocks transmission of nerve conduction to produce a loss of sensations
|
anesthetic
|
|
|
drug kills or inhibits growth of microorganisms
|
antibiotic
|
|
|
drug kills or prevents growth of fungi
|
antifungal
|
|
|
drug blocks effects of histamine in the body
|
antihistamine
|
|
|
regulating body substance released in excess during allergic reactions causing swelling and inflammation of tissues
|
histamine
|
|
|
antiinflammatory
|
drug reduces inflammation
|

