![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pulmonology
|
Aka pulmonary medicine. is diagnosis and treatment of diseases involving lower respiratory tract including lungs their airways and blood vessels in the chest wall
|
|
|
Pulmonologist
|
Medical doctors who treat respiratory disorders
|
|
|
Functions of the respiratory system
|
Primary Cardiovascular system transport oxygen and remove carbon dioxide. Secondary respiratory system includes warming air as it passes the body and assisting in the speech function
|
|
|
Anatomy of the upper and lower respiratory system
|
Upper track includes the nose pharnyx, larnyx and trachea. Lower track includes left and right bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli and the lungs
|
|
|
External respiration
|
Gas exchange between the body and the outside environment
|
|
|
Internal respiration
|
Just exchange at the cellular level between the blood and body tissue cells
|
|
|
Pneumomelanosis or pneumoconiosis
|
Condition of black lung cause my inhalation of black dust
|
|
|
Emphysema
|
Overexpansion and destruction of alveoli
|
|
|
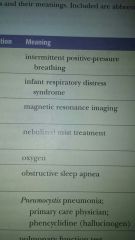
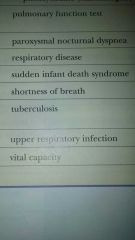
Dyspnea
|
Term for painful or difficult breathing
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
Abnormal breathing sound
- crackles - friction rub - rhonchi - Strider - wheezes |
- crackling or bubbling sounds when there is fluid in the alveoli aka rales
- drying, grating sound - snoring sounds - high pitched musical sound aka croup - continuous high pitched whistling sounds; asthma |
|
|
Acidosis
|
acidity of blood due to an accumulation of acids; abnormally high levels of carbon dioxide
|
|
|
acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
|
respiratory insufficiency marked by progressive hypoxia
|
|
|
Anoxia
|
Total absence of oxygen in body tissue
|
|
|
atelectasis
|
Collapse of lung tissue
|
|
|
Consolidation
|
Process of becoming solid
|
|
|
Coryza
|
Acute implementation of nasal passages aka a cold
|
|
|
Croup
|
Acute respiratory syndrome in children and infants; barking cough and stridor
|
|
|
Cystic fibrosis (CF)
|
Genetic disease by excessive secretions a thick mucus that do not drain
|
|
|
Empyema
|
Pus in body cavity especially in the pleural cavity ( pyothorax )
|
|
|
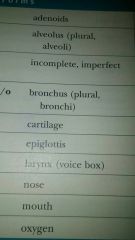
Epiglottitis
|
Life-threatening infection commonly in children
|
|
|
Epistaxis
|
Hemorrhage from the nose a que a nosebleed
|
|
|
Hypoxemia
|
Deficiency of oxygen in the blood
|
|
|
Hypoxia
|
Deficiency of oxygen in body tissues
|
|
|
Influenza
|
Acute contagious respiratory; fever
|
|
|
Lung cancer
|
Pulmonary malignancy. caused by smoking
|
|
|
Pertussis
|
Acute infectious disease characterized by "whoop" sounding cough ; whooping cough
|
|
|
Pleural effusion
|
Abnormal fluid in the pleural cavity. May contain blood (hemothorax), serum (hydrothorax) or pus (pyothorax)
|
|
|
pneumothorax
|
Collection of air in the pleural cavity causing collapse of a lung
|
|
|
Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
|
Unexpected death in infants aka crib death
|
|
|
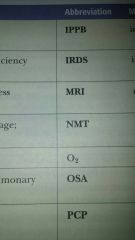
arterial blood gas (ABG)
|
Measurement of oxygen and carbon dioxide content of arterial blood
|
|
|
Bronchoscopy
|
Do you like domination of the interior bronchi using a bronchoscope
|
|
|
Chest x ray
|
Radiograph of the chest
|
|
|
computed tomography CT
|
Uses a narrow beam of x-rays that rotates in a full arc to produce cross sectional images (slices)
|
|
|
Magnetic Renaissance imaging MRI
|
electromagnetic energy to produce cross-sectional images
|
|
|
Pulmonary function test (PFTs)
- forced vital capacity (FVC) - forced expiration volume in 1 second (FEV1) - spirometry |
Capacity of the lungs
- amount of air forcefully exhaled from the lungs, deepest inhalation - first second - measurement, measures the breathing capacity of the lungs |
|
|
Postural drainage
|
Use of body positioning to assist removal of secretions of the lung
|
|
|
bronchodilators
|
Drugs used to increase air flow by dilating Airways; asthma
|
|
|
corticosteroids
|
Hormonal agents that reduce tissue edema
|
|
|
Nebulized mist treatment NMT
|
Fine spray that delivers medication directly to the lungs
|
|
|
Anesthesia
|
Insensitivity to pain especially as artificially induced by the administration of gases or the injection of drugs before surgical operations
|
|
|
Meatus
|
A passage or opening leading to the interior of the body or the passage leading into the ear
|
|
|
Metastatic
|
The spread of cancer to far away sites
|
|
|
Necropsy
|
Another term for autopsy; a postmortem examination to discover the cause of death or the extent of disease
|
|
|
Polyp
|
Swelling or tumor in mucus membrane
|
|
|
Snare
|
Device use to remove a polyp
|
|
|
phren/o is
|
Diaphragm
|
|
|
Carina
|
A keel-shaped structure; cartilage situated at the point where the trachea divides into two bronchi
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
aerophagia
|
Refers to swallowing air
|
|
|
anosmia
|
Is loss or impairment of sense of smell
|
|
|
apnea
|
Temporary cessation of breathing
|
|
|
* aspirate
|
Refers to using section to remove fluid from a body cavity
|
|
|
Asthma
|
A respiratory condition marked by current attacks of difficult or labored breathing accompanied by wheezing
|
|
|
atelectasis
|
Abnormal condition characterized by collapse of alveoli
|
|
|
catheter
|
A hollow flexible tube that can be inserted into a vessel or cavity of the body to withdraw or install fluids
|
|
|
Chondroma
|
A cartilaginous tumor
|
|
|
COPD
|
A group of respiratory disorders characterized by chronic bronchitis asthma and emphysema
|
|
|
Croup
|
Acute respiratory syndrome of childhood characterized by laryngeal obstruction and spasm, barking cough and stridor
|
|
|
Diagnosis
|
Refers to the use of scientific methods and medical skills to establish the cause and nature of a person's illness
|
|
|
Pharyngealplegia
|
Paralysis of pharyngeal muscles
|
|
|
pneumocystis
|
type of pneumonia seen in patients with AIDS and deliberated children
|
|
|
pneumothorax
|
Is presence of air in the pleural cavity
|
|
|
pyothorax
|
presence of pus in the chest
|
|
|
Rhinoplasty
|
refers to surgical repair or plastic surgery of the nose
|
|
|
TB
|
Infectious disease that produces small lesions or tubecles in the lungs
|
|
|
thoracentesis
|
Surgical puncture of the chest to remove fluid
|
|
|
tracheostomy
|
Surgical procedure that creates an opening through the neck into the trachea
|

