![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
79 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
cellular level
|
SMALLEST (simple) structural and functional unit of the body
|
|
|
|
tissue level
|
groups if cells that perform a specialized function
|
|
|
|
organ level
|
group of tissues that perform a specific function
|
|
|
|
system level
|
groups of organs that are interconnected or that have similar or interrelated functions
|
|
|
|
organism level
|
collection of body systems that makes up the MOST COMPLEX level-a living human being
|
|
|
|
-ac -al -ar -ary -eal -iac -ic -ior -ous -tic
|
pertaining to
|
|
|
|
anatomical position
|
standing straight upright facing forward, arms at the sides with palms forward, with the legs parallel and the feet slightly apart with the toes pointing forward
|
standing point position
|
|
|
superior
|
above another body structure or toward the head because the head is the most superior structure of the body
|
|
|
|
inferior
|
a position or direction meaning lower,below
|
|
|
|
posterior and dorsal
|
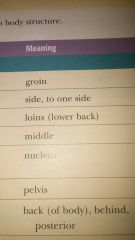
back of the body or back of any body structure
|
|
|
|
anterior and ventral
|
front of the body b or front of any body structure
|
|
|
|
medial
|
midline of the body a structure
|
|
|
|
lateral
|
the side or one side of the body
|
|
|
|
cephalad
|
direction towards the head
|
|
|
|
caudal
|
pertaining to the tail
|
|
|
|
proximal
|
near or nearest the point of attachment
|
|
|
|
distal
|
far or farthest from the point of attachment
|
|
|
|
abduction
|
movement away from the midline of the body
|
|
|
|
adduction
|
towards the midline of the body
|
|
|
|
median plane... aka
|
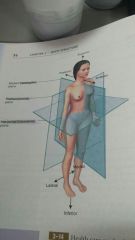
midsagittal
|
|
|
|
frontal plane... aka
|
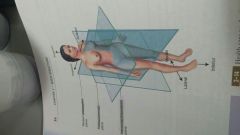
coronal
|
|
|
|
horizontal plane.... Aka
|
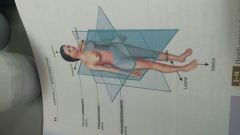
transverse
|
|
|
|
two major cavities are....
|
dorsal and ventral cavities. These cavities are hollow spaces that contain internal organs.
|
|
|
|
the larger division of the abdomino pelvic cavity consists of four quadrants....
|
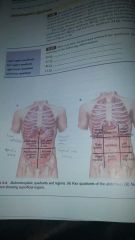
right upper quadrant (RUQ) right lower quadrant (RLQ) left upper quadrant (LUQ) left lower quadrant (LLQ)
|
|
|
|
abd stands for
|
abdomen
|
|
|
|
ant stands for
|
anterior
|
|
|
|
AP stands for
|
anteroposterior
|
|
|
|
Bx, bx stands for
|
biopsy
|
|
|
|
LAT, lat stands for
|
lateral
|
|
|
|
LLQ stands for
|
left lower quadrant
|
|
|
|
CT stands for
|
computed tomography
|
|
|
|
CXR stands for
|
chest x-ray, chest radiograph
|
|
|
|
MRI stands for
|
magnetic resonance imaging
|
|
|
|
LUQ stands for
|
left upper quadrant
|
|
|
|
RLQ stands for
|
right lower quadrant
|
|
|
|
RUQ stands for
|
right upper quadrant
|
|
|
|
U&L, U/L stands for
|
upper and lower
|
|
|
|
PET stands for
|
positron emission tomography
|
|
|
|
US stands for
|
ultrasound ; ultrasonography
|
|
|
|
SPECT stands for
|
single photon emission computed tomography
|
|
|
|
adhesion means
|
band if scar tissue
|
|
|
|
inflammation:
|
protective response
|
|
|
|
sepsis:
|
body's inflammatory response to infection
|
|
|
|
endoscopy:
|
visual examination of the interior organs... light instrument called an endoscope
|
|
|
|
fluoroscopy:
|
radiographic procedure that uses fluorescent screen to see the body part in motion
|
|
|
|
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
|
electromagnetic energy to produce cross-sectional images
|
|
|
|
nuclear scan
|
produces an image of an organ by recording concentration of a radiopharmaceutical
|
|
|
|
radiography:
|
captured shadow images on photographic film
|
|
|
|
radiopharmaceutical:
|
drug that contains radioactive substance which travels to an area or specific organ that will be scanned
|
|
|
|
scan:
|
recording and displaying an image
|
|
|
|
tomography:
|
Produces a film representing a detailed cross-section
|
|
|
|
computed tomography (CT):
|
Uses a narrow beam of x-rays that rotates in a full arc to produce cross sectional images (slices)
|
|
|
|
positron emission tomography (PET):
|
Combining computed tomography with Radiopharmaceutical
|
|
|
|
single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT):
|
Injection of a radioactive tracer and a specialized gamma camera
|
|
|
|
ultrasonography (US):
|
High frequency sound waves and are recorded to produce an image
|
|
|
|
droppler:
|
Audible sound of blood flowing through an artery
|
|
|
|
Anastomosis:
|
Connection between two
|
|
|
|
cauterize
|
Burning abnormal tissue
|
|
|
|
abdomin/o
|
abdomen
|
|
|
|
anter/o
|
Anterior, front
|
|
|
|
caud/o
|
tail
|
|
|
|
cephal/o
|
Head
|
|
|
|
cervic/o
|
neck; cervix uteri (neck of uterus)
|
|
|
|
chrondr/o
|
Cartilage
|
|
|
|
crani/o
|
cranium (skull)
|
|
|
|
cyt/o
|
cell
|
|
|
|
dist/o
|
far, farthest
|
|
|
|
dors/o
|
back of body
|
|
|
|
gastr/o
|
stomach
|
|
|
|
hist/o
|
tissue
|
|
|
|
ili/o
|
ilium (lateral, flaring portion of hip bone)
|
|
|
|
infer/o
|
lower or below
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
super-
|
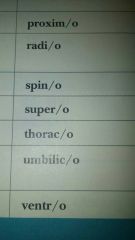
upper, above
|
|
|
|
trans-
|
through, across
|
|

