![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Alimentary Canal/Gastrointestinal Tract |
A continuous tube beginning with the mouth and ending at the anus. |
|
|
|
*What are the 3 main functions of the digestive system? Define each. |
Digestion ⇨ The process by which food is changed in the mouth, stomach, and intestines by chemical, mechanical, and physical action so the body can obsorb it. Absorption ⇨ The process by which nutrient material is taken into the bloodstream or lymph and travels to all cells of the body. Elimination ⇨ The process whereby the solid waste or end products of digestion at excreted. |
|
|
|
Gingivae |
Gums surrounding the necks of teeth |
|
|
|
Lingual Frenulum |
Connects the free part of the tongue to the underlying epithelium by a thin fold of mucous membrane which prevents extreme movement of the tongue |
|
|
|
Deciduous Teeth |
They are the temporary teeth 20 in total ⇨ 8 incisors, 4 canines or cuspids, 8 molars. |
Baby teeth or Milk teeth |
|
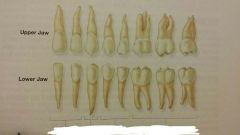
Permanent/Secondary Dentition Teeth *Name the teeth on the picture. |

They are the permanent teeth 32 in total ⇨ 8 incisors, 4 canines of cuspids, 8 premolars, 12 molars |
|
|
|
Incisors |
Have a sharp cutting edge adapted for biting into food |
4 front teeth in top and bottom |
|
|
Canine/Cuspid |
Larger and stronger than the incisors |
The one tooth on both top and bottom on either side of the front four. |
|
|
Premolars/Bicuspid |
Behind the canines |
|
|
|
Molars |
The largest teeth. Their crowns are adapted for grinding and pounding food. |
|
|

*Locate the Crown, Root and Neck and define. |

Crown ⇨ Projects above the gum Root ⇨ Embedded in the alveolus, jaw Neck ⇨ The constricted portion between the crown and root |
|
|
|
Pulp Cavity |
Contains the dental pulp |
|
|
|
Root Canal |
Narrow tunnel at the root or base of a tooth |
|
|
|
Apical Cavity |
Opening at the end of the root canal to allow blood vessels and nerves to enter |
|
|
|
Periodontal Ligament |
Binds the teeth to bony sockets in the jaw. |
|
|
|
Crementum |
A thin layer of bone covering the root, protecting the root and anchoring the peridontal ligament |
|
|
|
Dentin |
The bulk of the tooth |
|
|
|
Enamel |
Covers the exposed part of the crown and hardest, compact part of a tooth |
|
|
|
Gingival Sulcus |
A groove that surrounds the neck of the tooth. |
|
|
|
Pharynx |
The throat |
|
|
|
Nasopharynx |
The upper part of the pharynx above the soft plate |
|
|
|
Oropharynx |
Middle part of the pharynx between the palate and hyoid bone, has an opening to the oral cavity. |
|
|
|
Laryngopharynx |
Voice box |
|
|
|
Epiglottis |
Flap of tissue that blocks food from entering the airway |
|
|
|
Esophagus |
Muscular tube from the pharynx to the stomach |
|
|
|
Cardiac Sphincter/Lower Esophageal Sphincter |
The junction between the esophagus and stomach that relaxes to let food into the stomach |
|
|
|
Peristalsis |
Wave like, muscular contractions that carry food from the esophagus to the stomach |
|
|
|
Duodenum |
The first 12 inches of the small intestine beyond the stomach |
|
|
|
Jejunum |
8 feet of the small intestine after the duodenum |
|
|
|
Ileum |
Remaining 12 feet of the small intestine |
|
|
|
Cecum |
Pouch like structure forming the star of the large intestine and has the appendix attached to it |
|
|
|
Colon |
Bulk of the large intestine |
|
|
|
Anus |
Emd of the large intestine where the last is expelled from |
|
|
|
Parotid Salivary Glands |
Located just below the ears |
|
|
|
Submandibular Salivary Glands |
Located in the floor of the mouth |
|
|
|
Sublingual |
Located below the tongue |
|
|
|
Liver |
The largest glandular organ in the body located in the upper right part of the abdomen |
|
|
|
Gallbladder |
Small pear shaped sac under the liver |
|
|
|
Pancreas |
Large elongated gland situated behind the stomach and secretes pancreatic juice into the small intestine |
|
|
|
absorpt/o |
To take in |
|
|
|
aden/o |
Gland |
|
|
|
aliment/o |
Nourishment |
|
|
|
amyl/o |
Starch |
|
|
|
anabol/o |
Building up |
|
|
|
append/o appendic/o |
Appendix |
|
|
|
bil/i |
Gall, bile |
|
|
|
choledoch/o |
Common bile duct |
|
|
|
cirrh/o |
Orange-yellow |
|
|
|
col/o colon/o |
Colon |
|
|
|
cyst/o |
Bladder |
|
|
|
dent/o odont/o |
Tooth |
|
|
|
diverticul/o |
Diverticula |
|
|
|
duoden/o |
Duodenum |
|
|
|
enter/o |
Intestine |
|
|
|
esophag/o esophage/o |
Esophagus |
|
|
|
fibr/o |
Fiberous tissue |
|
|
|
gastr/o |
Stomach |
|
|
|
gingiv/o |
Gums |
|
|
|
gloss/o lingu/o |
Tongue |
|
|
|
glyc/o |
Sweet, sugar |
|
|
|
halit/o |
Breath |
|
|
|
hemat/o |
Blood |
|
|
|
hemorrh/o |
Vein liable to bleed |
|
|
|
hepat/o |
Liver |
|
|
|
herni/o |
Hernia |
|
|
|
ile/o |
Ileum |
|
|
|
labi/o |
Lip |
|
|
|
lapar/o |
Abdomen |
|
|
|
lip/o |
Fat |
|
|
|
pancreat/o |
Pancreas |
|
|
|
pept/o |
To digest |
|
|
|
pharyng/e pharyng/o |
Pharynx |
|
|
|
pil/o |
Hair |
|
|
|
prand/i |
Meal |
|
|
|
proct/o |
Anus and rectum |
|
|
|
pylor/o |
Pylorus, gatekeeper |
|
|
|
rect/o |
Rectum |
|
|
|
sial/o |
Saliva, salivary |
|
|
|
sigmoid/o |
Sigmoid |
|
|
|
splen/o |
Spleen |
|
|
|
stomat/o |
Mouth |
|
|
|
verm/i |
Worm |
|
|
|
Amylase |
Enzyme that breaks down starch *Ptyalin is salivary **Amylopsin is pancreatic |
|
|
|
Anorexia |
Lack of appetite, decreased desire for food |
|
|
|
Appendectomy |
Surgical excision of the appendix |
|
|
|
Appendicitis |
Inflammation of the appendix |
|
|
|
Ascites |
Significant accumulation of serous fluid in the peritoneal cavity |
|
|
|
Biliary |
Pertaining to bile |
|
|
|
Bilirubin |
Orange-colored bile pigment produced by separation hemoglobin into parts that are excreted by the liver cells |
|
|
|
Bowel |
Intestine |
|
|
|
Buccal |
*literally means pertaining to the cheek Relating to the cheek or mouth |
|
|
|
Catabolism |
*literally a casting down In metabolism a breaking of complex substances into more basic elements |
|
|
|
Celiac |
Pertaining to the abdomen |
|
|
|
Cheilosis |
Abnormal condition of the lip as seen in riboflavin and other B-complex deficiencies |
|
|
|
Cholecystectomy |
Surgical excision of the gallbladder |
|
|
|
Cholecystitis |
Inflammation of the gallbladder |
|
|
|
Choledochotomy |
Surgical incision of the common bile duct |
|
|
|
Chyle |
Milky fluid of intestinal digestion composed of lymph and emulsified fats |
|

