![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
295 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Ectomy |
Removal; excision |
Appendectomy |
|
|
centesis |
Surgical puncture Withdrawal of fluid |
Arthrocentesis |
|
|
Tripsy |
Crushing |
Lithotripsy |
|
|
Plasty |
Surgical repair |
Rhinoplasty |
|
|
Tome |
Surgical instrument to cut |
Osteotome |
|
|
Desis |
Binding, fixation |
Arthrodesis |
|
|
Lysis |
Destruction; separation; loosening |
Thrombolysis |
|
|
Pexy |
To bind or attach; fixation of an organ |
Mastopexy |
|
|
Stomy |
Opening or hole; forming an opening |
Tracheostomy |
|
|
Tomy |
Cutting or incision |
Tracheotomy |
|
|
Rrhaphy |
Suture |
|
|
|
Gram |
Recording; writing |
Electrocardiogram |
|
|
Scopy |
Visual examination tool |
Gastroscopy |
|
|
Scope |
Instrument for examining |
Esophagoscope |
|
|
Meter |
Instrument for measuring |
Pelvimeter |
|
|
Graph |
Instrument for recording |
|
|
|
Graphy |
Process of recording |
|
|
|
Metry |
Act of measuring |
|
|
|
Algia |
Pain |
-algia, -dynia |
|
|
Itis |
Inflammation |
Laryngitis |
|
|
Rrhage |
Bursting forth (of) |
-rrhage, -rrhagia hemorrhage menorrhagia |
|
|
Megaly |
Enlargement |
Cardiomegaly |
|
|
Cele |
Hernia; swelling |
Hepatocele |
|
|
Edema |
Swelling |
Lymphedema |
|
|
Pathy |
Disease |
Myopathy |
|
|
Rrhea |
Discharge; flow |
Diarrhea |
|
|
Oma |
Tumor |
Neuroma |
|
|
Plasia |
Formation, growth |
-plasia, -plasm |
|
|
Gen |
Forming, producing, origin |
-gen, -genisis |
|
|
Lith |
Stone; Calculus |
Lithography |
|
|
Osis |
Abnormal condition; increase |
Used primarily with blood cells |
|
|
Spasm |
Involuntary contraction, twitching |
|
|
|
Stenosis |
Narrowing; stricture |
|
|
|
-rrhexis |
Rupture |
|
|
|
-plegia |
Paralysis |
|
|
|
-ectasis |
Dilation; expansion |
|
|
|
Emesis |
Vomiting |
|
|
|
-emia |
Blood condition |
|
|
|
-iasis |
Abnormal condition |
Produced by something specific |
|
|
-ac,-al, -ar, -ary, -ic, -ile, -ous |
Adjective suffixes meaning pertaining to |
Pulmonary |
|
|
-esis, -ia, -ism |
Noun suffixes meaning condition |
Dysplasia |
|
|
-ician, -ist |
Noun suffixes mean specialist |
Pulmonologist |
|
|
-iatry |
Medicine; treatment |
Psychiatry |
|
|
diplo-, diplo- |
Double |
|
|
|
macro- |
Large |
|
|
|
homo-, homeo- |
Same |
|
|
|
mono-, uni- |
One |
|
|
|
Micro |
Small |
|
|
|
Circum-, peri- |
Around |
|
|
|
a-, an- |
Without, not |
|
|
|
super- |
Upper, above |
|
|
|
Post |
After,behind |
|
|
|
Pre- pro- |
Before, in front |
|
|
|
Primi- |
First |
|
|
|
Dia- trans- |
Through; across |
|
|
|
tonsillitis |
Root tonsil suffix itis |
Inflammation of tonsils |
|
|
Tonsilectomy |
Root tonsil suffix ectomy |
Excision of tonsil |
|
|
Rule 1 building medical words |
A word root links a suffix that begins with a vowel |
Append -ectomy excision of appendix |
|
|
Rule 2 building medical words |
A combining form (Root + o) links a suffix that begins with a consonant |
Colo o scope instrument for examining the colon |
|
|
Rule 3 building medical words |
A combining form (root + o) links a root to another root to form a compound word |
Gastro enter itis Inflammation of the stomach and intestine |
|
|
-Clasis |
To break, surgical fracture |
Osteoclasis |
|
|
Malacia |
Softening |
Chrondromalacia |
|
|
Penia |
Decrease, deficiency |
Erythropenia |
|
|
Phobia |
Fear |
Hemophobia |
|
|
Plegia |
Paralysis |
Hemiplegia |
|
|
Trophy |
Nourishment, development |
Dystrophy |
|
|
Anterior |
Front |
|
|
|
Anteroposterior |
Passing from front to back |
|
|
|
Inferior |
Below, lower, toward tail |
|
|
|
Scan |
Process of using a moving device to produce images |
|
|
|
Levels of organization |
Cell, tissue, organ, system, organism |
|
|
|
Adduction |
Toward midline |
|
|
|
Abduction |
Movement away from the midline |
|
|
|
Superior |
Above or higher |
|
|
|
Cephalic |
Toward the head |
|
|
|
Inferior |
Below, lower |
|
|
|
Caudal |
Toward the tail |
|
|
|
Anterior |
Front of body |
|
|
|
Ventral |
Toward the front |
|
|
|
Posterior |
Back of the body |
|
|
|
Dorsal |
Toward the Back |
|
|
|
Medial |
Toward the middle |
|
|
|
Lateral |
Toward the side |
|
|
|
External |
Outside |
|
|
|
Internal |
Inside |
|
|
|
Superficial |
On the surface |
|
|
|
Deep |
Away from the surface |
|
|
|
Proximal |
Near pointof attachment to trunk |
|
|
|
Distal |
Farther from the piont of attachment |
|
|
|
Parietal |
Outer wall of a cavity |
|
|
|
Visceral |
The organs within a cavity |
|
|
|
Median plane |
Vertical plane that crosses through the midline of the body that divides it into equal right and left sides. Midsagittal Plane |
|
|
|
Frontal plane |
Plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior |
|
|
|
Coronal plane |
Frontal Plane |
|
|
|
Horizontal plane |
Plague that accelerates the body into superior and inferior portions |
|
|
|
Transverse plane |
Horizontal plane |
|
|
|
Dorsal cavity |
Back of the body |
|
|
|
Ventral cavity |
Front of the body |
|
|
|
Cranial cavity |
Contains the brain |
|
|
|
Spinal cavity |
Contains the spinal cord |
|
|
|
Diaphragm |
A dome-shaped muscle separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities and plays an important role in breathing |
|
|
|
Thoracic cavity |
Contains the heart and lungs |
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic cavity |
Contains the abdominal and pelvic cavities |
|
|
|
Abdominal cavity |
Contains organs of the digestive and reproductive |
|
|
|
Pelvic cavity |
Contains organs of the digestive and reproductive systems |
|
|
|
Quadrant |
Used by clinicians to describe the site of a domino pelvic pain tumor or other abnormalities |
|
|
|
Region |
Nine regions are usually used in anatomical |
|
|
|
Region |
Nine regions are usually used in anatomical |
|
|
|
Right upper quadrant RUQ |
Contains the right lobe of the liver the gallbladder part of the pancreas and part of the small and large intestine |
|
|
|
Right lower quadrant RLQ |
Contains part of the small and large intestine the appendix the right ovary the right fallopian tube and the right ureter |
|
|
|
Left upper quadrant LUQ |
Contains the left lobe of the liver the stomach the spleen part of the pancreas and part of the small and large intestine |
|
|
|
Left lower quadrant LLQ |
Contains part of the small and large intestine the left ovary the left fallopian tube and the left ureter |
|
|
|
Right hypochondriac |
Upper right region located under the cartilage of the ribs |
|
|
|
Left hypochondriac |
Upper left region located under the cartilage of the ribs |
|
|
|
right lumbar |
Middle right region located near the waist |
|
|
|
Left lumbar |
Middle left region located near the |
|
|
|
Right iliac |
Lower right region located near the groin also called the right inguinal region |
|
|
|
Right inguinal region |
Same as right iliac |
|
|
|
Left iliac |
Lower left region located near the groin also called Left inguinal region |
|
|
|
Left inguinal |
Lower left region located near the groin same as left iliac |
|
|
|
Epigastric |
Middle region located above the stomach |
|
|
|
Umbilical |
Middle region located in the area of the umbilicus |
|
|
|
Hypogastric |
Lower middle region located below the stomach and umbilical |
|
|
|
Knee chest position |
Kneeling position with a buttocks elevated the head and chest are on the table and the arms are extended above the head and flexed at the elbow for rectal examination |
|
|
|
Lithotomy position |
Supine lying on the back position the legs sharply flexed at the knees and the feet are placed in stirrups use for vaginal examination |
|
|
|
Dorsal recumbent position |
Supine position the legs are sharply flakes at the knees of the feet are placed on the table used to examine the vagina and rectum |
|
|
|
Sims position |
Side lying position on the left left arm is placed behind the body the right arm is move forward and flexed at the elbow both legs are flexed at the knee but the right leg is sharply flex and position next to the left leg which is slightly flexed the position is used to examine the vagina and rectum to administer an enema |
|
|
|
Prone position |
Lie flat on the abdomen in the head turned slightly to the side the arms are extended above the head or alongside the body used to examine the back spine and lower extremities |
|
|
|
Fowler position |
Semi sitting position the head of the examination table is tilted to 45 to 60 degree angle with the patient's knees bent or not vent with a high and semi Fowler position to promote lung expansion used when patient has difficulty breathing |
|
|
|
Supine position |
Lie flat on the back with arms at the side used to examine chest heart abdomen extremities head and neck as well as certain neurological reflex testing |
|
|
|
Erect standing position |
Anatomical position |
|
|
|
Trendelenburg position |
The patient is lying flat on the back and the entire examination table is tilted with the head of the table down used for therapeutic treatments and drainage for thick respiratory secretions |
|
|
|
Abdomino |
Abdomen |
|
|
|
Caud/o |
Tail |
|
|
|
Cephal/o |
Head |
|
|
|
Cervic/o |
Neck, Neck of cervix |
|
|
|
Crani/o |
Skull |
|
|
|
Gastr/o |
Stomach |
|
|
|
ili/o |
Ilium |
|
|
|
Inguin/o |
Groin |
|
|
|
Lumb/o |
Loins |
|
|
|
Pelv/i |
Pelvis |
|
|
|
Pelv/o |
Pelvis |
|
|
|
Spin/o |
Spine |
|
|
|
Thorac/o |
Chest |
|
|
|
Umbilic/o |
Umbilicus |
|
|
|
Anter/o |
Anterior |
|
|
|
Dist/o |
Far |
|
|
|
Dors/o |
Back of the body |
|
|
|
Infer/o |
Lower, below |
|
|
|
Later/o |
Side, to one side |
|
|
|
Medi/o |
Middle |
|
|
|
Poster/o |
Back of the body, behind, posterior |
|
|
|
Proximo |
Bear, nearest |
|
|
|
Super/o |
Upper,above |
|
|
|
Ventr/o |
Belly,belly side |
|
|
|
Cyt/o |
Cell |
|
|
|
Hist/o |
Tissue |
|
|
|
Nucle/o |
Nucleus |
|
|
|
Radi/o |
Radiation, xray, radius |
|
|
|
-ad |
Toward |
|
|
|
-al |
Pertaining to |
|
|
|
-algia |
Pain |
|
|
|
-dynia |
Pain |
|
|
|
-gen |
Forming, producing, origin |
|
|
|
-genesis |
Forming, producing, origin |
|
|
|
-logist |
Specialist in the study of |
|
|
|
-logy |
Study of |
|
|
|
-lysis |
Separation, destruction, loosening |
|
|
|
-meter |
Instrument used to measure |
|
|
|
-plasia |
Formation, growth |
|
|
|
-toxic |
Poison |
|
|
|
bi- |
Two |
|
|
|
epi- |
Above, on |
|
|
|
infra- |
Below, under |
|
|
|
trans- |
Across,through |
|
|
|
Adhesion |
Band of scar tissue binding anatomical services that are normally separate from each other |
|
|
|
Inflammation |
Protective response of body tissues to irritation infection or allergy |
|
|
|
Sepsis |
Body's inflammatory response to infection in which there is fever elevated heart and respiratory rates and low blood pressure |
|
|
|
Endoscopy |
Visual examination of the interior of organs and Cavities with a specialized lighted instrument called endoscope |
|
|
|
Fluoroscopy |
Radiographic procedure that uses a fluorescent screen instead of a photographic plate to produce a visual image from x-rays that pass through the patient resulting in continuous Imaging of the motion of internal structures and immediate serial in images |
|
|
|
MRI |
Magnetic resonance imaging a technique that uses electromagnetic energy to produce multiplan are cross-sectional images of the body |
|
|
|
Nuclear scan |
Diagnostic technique that produces an image of an organ or area by recording the concentration of radiopharmaceutical substance called a tracer usually introduced into the body by ingestion inhalation or injection |
|
|
|
Radiography |
Production of captured shadow images on photographic film through the action of ionizing radiation passing through the body from an external source |
|
|
|
Radiopharmaceutical |
Drug that contains a radioactive substance which travels to an area or a specific organ that will be scanned |
|
|
|
Tomography |
Radiographic technique that produces a film representing a detailed cross-section of tissue structure at a predetermined depth |
|
|
|
CT |
Computed tomography scan a narrow beam of x-rays with a contrast medium or without a contrast medium that targets a specific organ or body area to produce multiple cross-sectional Imaging for detecting pathological conditions such as tumors or metastasis |
|
|
|
PET |
Positron emission tomography scan nuclear Imaging study that can bind CT with radiopharmaceuticals to produce a cross-sectional image of radioactive disbursements in a section of the body to reveal the areas where the radiopharmaceutical is being metabolized and where there is a deficiency in metabolism useful in evaluating Alzheimer disease and epilepsy |
|
|
|
SPECT single Photon emission computed tomography scan |
Nuclear Imaging study that scans organs after injection of a radioactive tracer and employs a specialized gamma camera that detects emitted radiation to produce a three-dimensional image from a composite of numerous views used to show how blood flows to an organ and helps determine how well the organ is functioning |
|
|
|
Ultrasonography |
Imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves that bounce off body tissues and are recorded to produce an image of an internal organ or tissue |
|
|
|
cutaneous |
Pertaining to the skin |
|
|
|
Lesion |
Wound, injury, or pathological change in body tissue |
|
|
|
Systemic |
Pertaining to a system or the whole body rather than a localized area |
|
|
|
Therapeutic |
Pertaining to treating, remedy 18, or cutting a disorder or disease |
|
|
|
Epidermis |
Outer layer of the skin |
|
|
|
Dermis |
Inner layer of the skin |
|
|
|
Cutane/o |
Skin |
|
|
|
Dermat/o |
Skin |
|
|
|
Derm/o |
Skin |
|
|
|
Sudor/o |
Sweat gland |
|
|
|
Hidr/o |
Sweat gland |
|
|
|
Subcutaneous tissue |
Layer below the dermis |
|
|
|
Sudoriferous |
Sweat gland |
|
|
|
Neur/o |
Nerve |
|
|
|
Arteriole |
Small artery |
|
|
|
Adipose tissue |
Fat tissue |
|
|
|
Pil/o |
Hair follicle |
|
|
|
Trich/o |
Hair follicle |
|
|
|
Seb/o |
Sebaceous gland oil |
|
|
|
Basal layer |
Located in the epidermis |
|
|
|
Adip/o |
Fat |
|
|
|
Lip/o |
Fat |
|
|
|
Steat/o |
Fat |
|
|
|
Cutane/o |
Skin |
|
|
|
Dermat/o |
Skin |
|
|
|
Derm/o |
Skin |
|
|
|
Cyan/o |
Blue |
|
|
|
Erythem/o |
Red |
|
|
|
Erythemat/o |
Red |
|
|
|
Erythr/o |
Red |
|
|
|
Hidro |
Sweat |
|
|
|
Sudor/o |
Sweat |
|
|
|
Ichthy/o |
Dry, scaly |
|
|
|
Kerat/o |
Horny tissue, hard, cornea |
|
|
|
Melan/o |
Black |
|
|
|
Myc/o |
Fungus |
|
|
|
Onych/o |
Nail |
|
|
|
Pil/o |
Hair |
|
|
|
Trich/o |
Hair |
|
|
|
Scler/o |
Hardening, white of the eye sclera |
|
|
|
Seb/o |
Sebum, sebaceous |
|
|
|
Squam/o |
Scale |
|
|
|
Therm/o |
Heat |
|
|
|
Xer/o |
Dry |
|
|
|
-phoresis |
Carryng, transmission |
|
|
|
-plasty |
Surgical repair |
|
|
|
-therapy |
Treatment |
|
|
|
Abrasion |
Scraping a rubbing a way of a surface such as a skin by friction |
|
|
|
Abscess |
Localized collection of pus at the site of an infection characteristically a staphylococcal infection originates in the hair follicle like a boil |
|
|
|
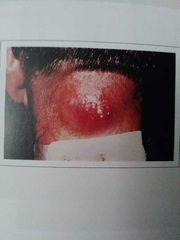
Furuncle |
Abscess that originates in a hair follicle also called a boil |
|
|
|
Carbuncle |
Cluster of furuncles in the subcutaneous tissue |
|
|
|
Acne |
Inflammatory disease of sebaceous follicles of the skin marked by blackheads papules and pustules |

|
|
|
Alopecia |
Absence or loss of hair especially on the head also known as baldness |
|
|
|
Gangrene |
Death of tissue usually resulting from loss of blood supply |
|
|
|
Hemorrhage |
External or internal loss of a large amount of blood in a short period |
|
|
|
Contusion |
Image of any size Under the Skin in which the skin is not broken also known as a bruise |
|
|
|
Ecchymosis |
Skin discoloration consisting of a large, are regularly for and hemorrhagic area with colors changing from Blue to Black to greenish brown or yellow also known as a bruise |

|
|
|
Petechia |
Minut pinpoint Hemorrhage a spot of the skin that is a smaller version of ecchymosis |
|
|
|
Hematoma |
Elevated localized collection of blood Trapped Under the Skin usually results from trauma |
|
|
|
Hirsutism |
Excessive growth of hair in unusual places places especially in women may be due to hypersecretion of testosterone |
|
|
|
Ichthyosis |
Genetic skin disorder in which the skin is dry and scaly resembling fish skin because of a defect in keratinization |

|
|
|
impetigo |
Bacterial skin infection characterized by isolated pustules that become crusted and rupture |
|
|
|
Keloid |
Overgrowth of scar tissue at the site of a skin injury especially a wound surgical incision or severe burn caused by excessive collagen formation during the healing process |
|
|
|
Psoriasis |
Chronic skin disease characterized by itchy red patches covered with silvery scales |

|
|
|
Scabies |
Contagious skin disease transmitted by the itch mite |
|
|
|
Skin lesions |
Areas of pathologically altered tissue caused by disease, injury, or a wound resulting from external factors or internal disease |
|
|
|
Tinea |
Fungal infection whose name commonly indicates the body part affected such as Tena Pettis ringworm I don't know |
|
|
|
Burn |
Tissue injury caused by contact with thermal chemical electrical or radioactive agent has first second and third degrees |
|
|
|
First degree burn |
Superficial Melbourne affecting the epidermis and characterized by redness and pain with no blistering or scar formation |
|
|
|
Second degree burn |
Partial thickness burn affecting the epidermis and part of the dermis characterized by redness, blistering or large Bola, and pain with little or no scarring |

|
|
|
Third degree burn |
Full-thickness severe burn characterized by destruction of the epidermis and dermis with damage to the subcutaneous layer, leaving the skin charred black or dry white and appearance with in sensitivity to touch |
|
|
|
Carcinoma |
Uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body malignant cells |
|
|
|
Melanoma |
Malignant tumor that originates in melanocytes and is considered the most dangerous type of skin cancer if not treated early becomes difficult to cure and can be fatal |
|
|
|
Comedo |
Discolored dry and sebum plugging and excretory duct of the skin also called blackhead |
|
|
|
Cyst |
Closed Sac or pouch in or under the skin with a definite wall that contains fluid semi fluid or solid material |
|
|
|
Pilonidal |
Growth of a hair in a dermoid cyst or in a sinus opening on the skin |
|
|
|
Sebaceous |
Cyst filled with sebum are fatty material from a sebaceous |
|
|
|
Eczema |
Redness of skin caused by swelling of the capillaries |

|
|
|
Ulcer |
Lesion of the skin or mucous membranes marked by inflammation necrosis and sloughing of damaged tissues |
|
|
|
Pressure ulcer |
Skin ulceration caused by prolonged pressure usually in a patient who is bedridden also known as decubitus ulcer or bedsore |

|
|
|
Verruca |
Rounded epidermal growth caused by a virus also called wart |
|
|
|
Urticaria |
Allergic reaction of the skin characterized by eruption of pale red elevated patches that are intensely itchy also called wheals or hives |

|
|
|
Vesicle |
Small blister like elevation on the skin containing a clear fluid large vesicles are called bullae |
|
|
|
Vitiligo |
Localized loss of skin pigmentation characterized by milk-white patches also called leucoderma |

|
|
|
Cryosurgery |
Use of sub-freezing temperature commonly with liquid nitrogen to destroy abnormal tissue cells such as unwanted cancerous or infected tissues |
|
|
|
Debridement |
Removal of foreign material damaged tissue or cellular debris from a wound or burn to prevent infection and promote healing |
|
|
|
Fulguration |
Tissue destruction by means of high-frequency electrical current also called Electro desiccation |
|
|
|
I&D |
Incision of a lesion such as an abscess followed by the draining of its contents |
|
|
|
Mohs surgery |
Surgical procedure used primarily to treat skin neoplasms in which tumor tissue fixed in place is removed layer-by-layer for microscopic examination until the entire tumor is removed |
|
|
|
Skin graft |
Surgical procedure to transplant healthy tissue by applying it to an injured site |
|
|
|
Allograft |
Transplantation of healthy tissue from one person to another person also called homograph |
|
|
|
Autograft |
Transplantation of healthy tissue from one site to another site on the same individual |
|
|
|
Synthetic |
Transplantation of artificial skin produced from collagen fibers arranged in a lattice pattern |
|
|
|
Xenograft |
Transplantation from a foreign donor dermis only usually a pig and transfer to human also called hero graft |
|
|
|
Skin resurfacing |
Procedure that repairs damaged skin, acne scars, fine or deep wrinkles, or tattoos or improve skin tone irregularities through the use of topical chemicals abrasion or laser |
|
|
|
Chemical peel |
Use of chemicals to remove outer layers of skin to treat acne scarring and general keratosis as well as for cosmetic purposes to remove fine wrinkles on the face also called chemabrasion |
|
|
|
Cutaneous laser |
Any of several laser treatments employed for cosmetic & plastic surgery |
|
|
|
Dermabrasion |
Removal of acne scars Navy tattoos or fine wrinkles on the skin through the use of sandpaper wire brushes are other abrasive materials on the epidermal layer |
|
|
|
Antibiotics |
Kill bacteria that cause skin infections |
|
|
|
Antifungals |
Kill fungi that infect the skin |
|
|
|
Antipruritics |
Reduce severe itching |
|
|
|
Corticosteroids |
Anti-inflammatory agents to treat skin inflammation |
|
|
|
Basal cell carcinoma |
Non-melanoma skin cancer that is malignant of the basal layer of the epidermis or hair follicles |

|
|
|
Squamous cell carcinoma |
Second most common form of non-melanoma skin cancer commonly caused by prolonged exposure to UV radiation |

|
|
|
Pleural pelvis |
Pelves |
|

