![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Earwax is produced by the __________ _________
|
ceruminous glands
|
|
|
The principle transducer on which most of the afferent axons of the cochlea synapse are the _____ ______ ______
|
inner hair cells
|
|
|
type I (bipolar axons) are found on the ________ _________ __________
|
inner hair cells
|
|
|
Inner hair cells consist of _____ row(s) of cells
|
1
|
|
|
Outer hair cells consist of ____ row(s) of cells
|
3
|
|
|
__________ afferent axons originate on the outer hair cells
|
type II
|
|
|
where do efferent axons of the inner cells synapse?
|
on the afferent axons
|
|
|
where do the efferent axons of the outer cells synapse?
|
directly on the outer hair cell
|
|
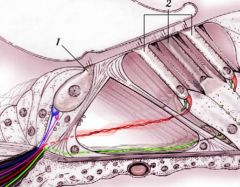
What is identified by 1? 2? Identify each of the colored fibers
|
1 = inner hair cell; 2 = outer hair cell; Afferent fibers: Blue = type I; Green = type II
Efferent fibers: Mauve = IHC; Red = OHC |
|
|
What is the center for sound localization in space?
|
Superior Olivary Complex
|
|
|
What are the three central auditory pathways that cross in the medulla?
|
Dorsal acoustic stria, medial olivocochlear bundle, intermediate acoustic stria
|
|
|
The central auditory pathways ascend from the medulla to the pons through what structure?
|
lateral lemniscus
|
|
|
Where do the central auditory pathways synapse in the cortex?
|
The transverse temporal gyrus
|
|
|
High pitched sounds are heard at the ________ of the cochlea
|
base
|
|
|
low pitched sounds are heard at the __________ of the cochlea
|
apex
|
|
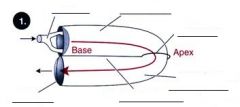
Fill in the blanks
|
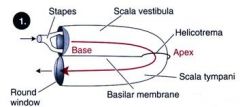
|
|
|
The scala tympani and scala vestibuli are filled with ___________
|
perilymph
|
|
|
The inner and outer hair cells of the cochlea are found in what structure?
|
Organ of Corti
|
|
|
The scala media is filled with ____________
|
endolymph
|
|
|
What initiates cochlear hair cell depolarization?
|
Traveling waves through the cochlea displace the basilar and tectorial membranes, bending the hair cells and depolarizing them.
|
|
|
depolarization of the cochlear hair cells is caused by a rapid influx of what ion?
|
K+
|
|
|
without the middle ear, only 2% of the energy of sound would get to the cochlea (True/False)
|
True
|
|
|
_____ conduction of sound requires an intact middle ear
|
air
|
|
|
During a Weber's test, if the patient has right cochlear damage, sound will lateralize to the _____ ear. If the patient has right middle ear obstruction, sound will lateralize to the ________ ear
|
left, right
|
|
|
How would you determine middle ear defects in a patient?
|
look for a lack of air conductance in the rhinne test
|
|
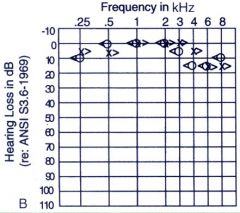
Interpret this patients hearing loss at 6kHz
|
Patient has hearing loss of +15db at 6kHz (normal)
|
|
|
What are the three types of hearing loss and what causes them?
|
Conductive (middle ear pathology), Sensory-neural (acoustic nerve or cochlear pathology), Central (CNS lesion)
|
|
|
The most common cause of adult onset hearing loss is ___________
|
otosclerosis
|
|
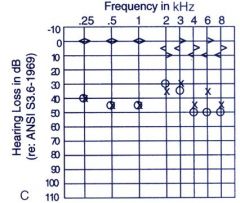
Interpret this patients hearing loss chart
|
Conductive hearing loss (bone conduction (sensory-neural) normal)
|
|
|
What condition, common in children, is associated with fluid in the middle ear? What is the treatment? Why does it often go undiagnosed? What are the results if untreated?
|
Serous Otitis Media, ear tubes, not painful, poor language aquisition and social development
|
|
|
What is tympanometry?
|
Objective measurement of ear impedance
|
|
|
What are the principal causes of sensory-neural hearing loss?
|
time (presbyacusis), ototoxic agents, noise-induced hearing loss
|
|
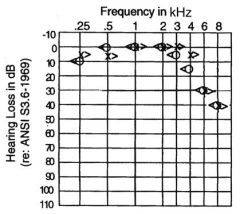
interpret this patients hearing loss chart
|
Presbyacusis, normal, age-related hearing loss
|
|
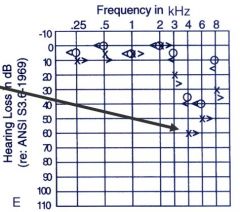
Interpret this patients hearing loss chart
|
Noise-induced hearing loss (note 4kHz notch)
|

