![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
fimbriae and pili are interchangeable terms (true/false)
|
true (wikipedia may tell you otherwise, but we'll go with Dugan for now)
|
|
|
____________ often carry genes for antibiotic resistance and toxin production.
|
plasmids
|
|
|
in bacteria, ____S + ____S subunits yield ____S ribosomes. In eukaryotes, ___S + ____S subunits yield ____S ribosomes (hint: these are numbers)
|
30; 50; 70; 40; 60; 80 (PROTIP: 'E'ukaryote = 'E'ven first digits, 4, 6, 8)
|
|
|
Medically, why is it useful that bacteria have differently structured ribosomes?
|
we can target antibiotics toward them
|
|
|
The peptidoglycan or murein layer is also known as what?
|
The cell wall
|
|
|
Endotoxin is unique to Gram-_______ bacteria. What is the shock-inducing counterpart in the other type?
|
negative; lipoteichoic acid
|
|
|
Murein layer is unique to bacteria (true/false)
|
true
|
|
|
What does lysozyme target?
|
peptidoglycans in the cell wall
|
|
|
Gram-_______ bacteria have an outer membrane. What is its function?
|
negative; protects cell from toxic material and forms periplasm which contains digestive enzymes
|
|
|
What are the three compnents of lipopolysaccharide?
|
O-specific side chain, core polysaccharide, Lipid A
|
|
|
Gram-________ has a thick murein layer
|
positive
|
|
|
Bacterial capsule is usually composed of ____________
|
polysaccharides
|
|
|
bacterial capsule: ___________ strains are referred to as smooth. __________ strains are referred to as rough
|
encapsulated; nonencapsulated
|
|
|
In the gram stain, gram-_______ show up purple, and gram-______ show up pink
|
positive; negative
|
|
|
Conjugation occurs through what structure formed by bacteria?
|
sex pili
|
|
|
What drives movement of flagella?
|
proton motive force
|
|
|
What is the function of common type bacterial pili?
|
attachment
|
|
|
What is chemotaxis?
|
the process by which bacteria direct their movement according to the chemical gradients in their environment
|
|
|
Counterclockwise rotation of flagella causes ___________. Clockwise rotation causes ___________
|
swimming (forward); tumbling (backward)
|
|
|
What induces sporulation and what type of bacteria will you find them in?
|
starvation; Bacillus and Clostridium
|
|
|
_____________: one organism lives at the expense of the other and may do harm (pathogen)
|
parastitism
|
|
|
_____________: one organism may benefit but neither is harmed (most normal flora organisms)
|
commensalism
|
|
|
______________: a mutually beneficial association (some normal flora organisms)
|
mutualism
|
|
|
What are the major groups of pathogenic bacteria?
|
Gram+, Gram-, Acid fast, Wall less, Intracellular
|
|
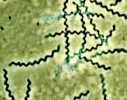
What is the morphology of this bacteria?
|
Spirochete
|
|
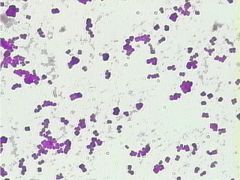
What is the morphology of this bacteria?
|
Coccus
|
|

What is the morphology of this bacteria?
|
Bacillus
|
|
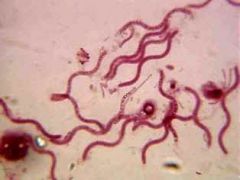
What is the morphology of this bacteria?
|
Spirillum
|
|

What is the morphology of this bacteria?
|
Vibrio
|
|

What is the morphology of this bacteria?
|
Fusiform bacillus
|
|
|
The electron transport chain drives H+ into or out of the cell?
|
out
|
|
|
What is the main source of electrons feeding the electron transport chain?
|
Reducing power (NADH)
|
|
|
Bacteria divide by ___________ __________
|
binary fission
|
|
|
What are the four phases of growth in bacteria?
|
lag, exponential(log), stationary, death(log)
|
|
|
If culture doubles every 30 minutes, how many cells would you have after 8 hours?
|
2^16
|
|
|
All bacteria are heterotrophic (true/false)
|
true
|
|
|
Some bacteria require only inorganic salts and nitrogen (true/false)
|
true (eg. E.coli)
|
|
|
What are fastidious bacteria?
|
Those that require a very enriched medium to grow
|
|
|
What are siderophores?
|
iron chelating compounds secreted by bacteria
|
|
|
What are the four steps of bacterial cell wall synthesis?
|
Bactoprenol phosphate transport ppg monomers across cell membrane
Autolysins break the glycosidic bonds of the ppg and peptide cross linkages Transglycosidase (TG) enzyme insert and link monomers into the new ppg Transpeptidase (TP) enzymes reform the peptide cross links |
|
|
Fosfomycin and cycloserine act in what compartment of the bacteria to block cell wall synthesis?
|
cytoplasm
|
|
|
Vancomycin and betalactams act in what compartment of the bacteria to block cell wall synthesis?
|
periplasm
|
|
|
What are the three points of attack for antibiotics targeting the bacterial ribosomal cycle?
|
initiating complex, 30S inhibitors, 50S inhibitors
|
|
|
What are the five ways bacteria resist antibiotics discussed by Dugan?
|
antibiotic degradation, antibiotic efflux pump, reduced antibiotic uptake, overproduction of antibiotic target, alteration of antibiotic target
|
|
|
Approximately how many genes does E. coli have?
|
2000-3000
|
|
|
Mutations are considered _________ gene transfer. Recombination is considered ___________ gene transfer
|
vertical; horizontal
|
|
|
__________: the process of gene transfer from one bacterial cell to another by means of a phage
|
transduction
|
|
|
_____________: carry both insertion sequences plus other genes and often carry a selective advantage
|
transposons
|

