![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Superior Mediastinum Boundary
|
plane connecting the cupola or the superior thoracic aperture
|
|
|
Inferior Mediastinum Boundary
|
diaphragm or inferior thoracic aperture
|
|
|
Anterior Mediastinum Boundary
|
sternum and costal cartilages
|
|
|
Posterior Mediastinum Boundary
|
T1 to T12 vertebrae and related ribs
|
|
|
Mediastinum Subdivisions
|
•Superior
•Inferior -anterior -middle -posterior |
|
|
Where does the Superior Mediastinum lie?
|
The superior mediastinum lies between the manubrium sterni and the upper four thoracic vertebrae .
|
|
|
Superior Mediastinum- Contents
|
–The lower ends of sternohyoid, sternothyroid and longus colli
–Thymic remnants –Internal thoracic arteries and veins –Brachiocephalic veins and the upper half of the superior vena cava –Aortic arch, the brachiocephalic, left common carotid and subclavian arteries and the left superior intercostal vein –Right and left vagiand phrenic nerves, the left recurrent laryngeal nerve, the cardiac nerves and the superficial part of the cardiac plexus |
|
|
Anterior Mediastinum -Contents
|
•Lymph nodes and vessels
•Small portion of thymus •Mediastinalbranches of the internal thoracic vessels •Sternopericardialligaments •Fat |
|
|
Middle Mediastinum -Contents
|
•It contains the:
–Pericardium –The heart and the ascending aorta –Lower half of the superior vena cava receiving the azygos venous arch posteriorly –Tracheal bifurcation and both main bronchi –Pulmonary trunk and right and left pulmonary arteries and veins –Right and left phrenic nerves accompanied by the pericardiacophrenic vessels –Deep part of the cardiac plexus –Tracheobronchial lymph nodes |
|
|
What is the broadest part of the inferior mediastinum?
|
•The middle mediastinum
|
|
|
Posterior Mediastinum -Contents
|
•Descending aorta & its branches
•Posterior intercostal VAN •Azygos, hemiazygos, accessory hemiazygos veins •Sympathetic trunks and splanchnic nerves |
|
|
Organs of the Superior mediastinum
|
Thymus
Trachea Esophagus Thoracic Duct |
|
|
Organs of Middle Inferior Mediastinum
|
Heart
Pericardium |
|
|
Organs of the Posterior Inferior Mediastinum
|
Esophagus
|
|
|
Arteries of the Superior Mediastinum
|
Aortic arch
Brachiocephalic trunk Left common carotid a. Left Subclavian a. |
|
|
Arteries of the Middle Inferior Mediastinum
|
Ascending Aorta
Pulimonary trunk and branches Pericardiophrenic aa and v.v. |
|
|
Arteries of the Posterior Inferior Mediastinum
|
Thoracic Aorta and branches
Thoracic Duct |
|
|
Veins and Lymph vessels of the Superior mediastinum
|
superior vena cava
Brachiocephalic v v Thoracic Duct |
|
|
Veins and Lymph vessels of Middle Inferior Mediastinum
|
superior vena cava
Azygos v. Pulmonary v v Pericardicophrenic aa. and v v |
|
|
Veins and Lymph vessels of Posterior Inferior Mediastinum
|
Azygos v.
Hemiazygos v. Thoracic duct |
|
|
Nerves of the Superior Mediastinum
|
Vagus nn.
Left recurrent laryngeal n. Cardiac nn. Phrenic nn. |
|
|
Nerves of the Middle Inferior Mediastinum
|
Phrenic nn.
|
|
|
Nerves of the Posterior Inferior Mediastinum
|
Vagus nn.
|
|
|
Descending aorta -thoracic portion
|
-visceral
-parietal |
|
|
Visceral Descending aorta -thoracic portion
|
esophageal
pericardial bronchial mediastinalaa. |
|
|
Parietal Descending aorta -thoracic portion
|
subcostal
superior phrenic posterior intercostal aa |
|
|
Veins in Thoracic Cavity
|
Superior vena cava
Pulmonary veins |
|
|
Superior vena cava
|
Brachiocephalic v v.
Azygos v. |
|
|
Azygos vein parts
|
a. Right superior intercostal vein
b.Hemiazygos v. c.Accessory hemiazygos v |
|
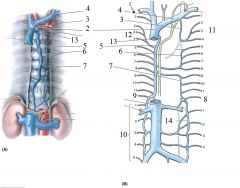
|
1- Posterior Inercostal Veins
2- Superior Vena Cava 3- Left Superior Intercostal Veins 4- Left Brachiocephalic Vein 5- Azygos Vein 6- Accessory Hemiazygos 7- Hemiazygos vein 8- L Subcostal v. 9- R Subcostal v 10- Lumbar vv. 11- L Superior Intercostal vv. 12- R Superior Intercosal vv. 13- Arch of Azygos v 14- Inferior Vena Cava |
|
|
Esophagus
|
•A muscular collapsible tube about 10 inches long
•Its abdominal portion is 1/2 inch long, enters stomach at its right side |
|
|
Esophagus Blood Supply
|
abdominal portion -left gastric a.
|
|
|
Esophagus Nerve Supply
|
vagus nerves and sympathetic nerves arising from T1-T4
|
|
|
Thymus Gland
|
•Flattened bilobed structure
•Continues to grow until puberty but thereafter undergoes involution •Has a pink lobulated appearance •Site of development of T lymphocytes |
|
|
Thymus Gland blood supply
|
inferior thyroid veins
internal thoracic |
|
|
Right vagus nerve
|
Enters thorax anterior to the right subclavian artery and gives off the right recurrent laryngeal nerve.
|
|
|
Left vagus nerve
|
descends in the neck posterior to the left CCA; gives off the left recurrent laryngeal nerve
|
|
|
Vagus Nerves
|
Both vagi breaks up into branches to form the pulmonary, cardiac, esophageal plexus; enters abdomen through esophageal opening
|
|
|
Phrenic Nerves
|
•Sole motor nerve supply to the diaphragm
•Sensory to central portion of diaphragm •Arise from ventral primary ramiof C3, C4, & C5 (motor branch of cervical plexus) •Descends down to superior and middle mediastinum •Pericardiacophrenic vessels run with it |
|
|
Thoracic Duct
|
•Largest lymphatic channel of the body
•Returns all lymph and chyle from all of the body below the diaphragm & the left half of the body above the diaphragm •Arises as an occasional dilatation called the cisterna chyli |
|
|
Cisterna Chyli
|
At the level of L2
receives the right & left lumbar trunks |
|
|
Thoracic Sympathetic Trunk
|
•Represents a major part of the sympathetic division of the ANS
•Thoracic chain ganglia are regions of synapse between the preganglionicand postganglionic neurons •Most laterally placed structure in mediastinum; runs downward on the heads of ribs •Leaves thorax next to T12 body passing |

