![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
79 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
adip/o, lip/o, steat/o
|
fat
(three combining forms) |
|
|
albin/o
|
white
|
|
|
caus/o
|
burn, burning
|
|
|
cauter/o
|
heat, burn
|
|
|
cutane/o, derm/o, dermat/o
|
skin
(three combining forms) |
|
|
derm/o, dermat/o
|
skin
|
|
|
diaphor/o
|
profuse sweating
|
|
|
erythem/o, erythemat/o
|
redness
|
|
|
hidr/o
|
sweat
|
|
|
ichthy/o
|
dry, scaly (fish-like)
|
|
|
leuk/o
|
white
|
|
|
lip/o
|
fat
|
|
|
melan/o
|
black
|
|
|
myc/o
|
fungus (fungi include yeasts, molds, and mushrooms)
|
|
|
onych/o, ungu/o
|
nail
(two combining forms) |
|
|
phyt/o
|
plant
|
|
|
pil/o
|
hair, hair follicle
|
|
|
py/o
|
pus
|
|
|
rhytid/o
|
wrinkle
|
|
|
seb/o
|
sebum (oily secretion from sebaceous glands)
|
|
|
squam/o
|
scale-like
|
|
|
steat/o
|
fat
|
|
|
trich/o
|
hair
|
|
|
ungu/o
|
nail
|
|
|
xanth/o
|
yellow
|
|
|
xer/o
|
dry
|
|
|
-algia
|
pain
|
|
|
-derma
|
skin
(suffix) |
|
|
-esis
|
condition, state of, action
|
|
|
-lysis
|
breakdown, separation, destruction, loosening
|
|
|
-ose
|
full of, pertaining to, sugar
|
|
|
-osis
|
condition (abnormal)
|
|
|
-ous
|
pertaining to
|
|
|
-plakia
|
plaque
|
|
|
-plasty
|
surgical repair
|
|
|
-rrhea
|
flow, discharge
|
|
|
Name three combining forms meaning fat.
|
adip/o
lip/o steat/o |
|
|
Name two combining forms meaning white.
|
albin/o
leuk/o |
|
|
Name two combining forms meaning skin.
|
cutane/o
derm/o, dermat/o |
|
|
Name two combing forms meaning nail.
|
onych/o
ungu/o |
|
|
Name two combining forms meaning hair.
|
pil/o
trich/o |
|
|
Name two combining forms meaning sweat.
|
hidr/o
diaphor/o |
|
|
Name two combining forms meaning redness.
|
erythem/o
erythemat/o |
|
|
What are the two types of sweat glands? What are the differences between them?
|
apocrine and eccrine
apocrine sweat glands are larger and found in the axilla and genital areas and are active only from puberty onward. |
|
|
The deepest region of the epidermis that gives rise to all the epidermal cells is called the ________.
|
basal layer
|
|
|
Structural proteins found in the skin and connective tissue are called ________.
|
collagen
|
|
|
The outermost layer of skin is called the __________, which is composed of flat, scale-like cells called _________ __________.
|
epidermis
squamous epithelium |
|
|
Hard protein material found in the epidermis, hair, and nails is called __________.
|
keratin
|
|
|
The outermost layer of the epidermis, which consists of flattened, keratinized cells is called the _________ _________.
|
stratum corneum
|
|
|
The innermost layer of the skin, containing fat tissue is called the ___________ _________.
|
subcutaneous layer
|
|
|
The oil-secreting gland in the dermis that is associated with hair follicles is called the _________ ________.
|
sebaceous gland
|
|
|
The oily substance secreted by sebaceous glands is called __________.
|
sebum
|
|
|
The half-moon shaped whitish area at the base of a nail is called the __________.
|
lunula
|
|
|
The soft tissue surrounding the nail border is called the ____________.
|
paronychium
|
|
|
What is the substance that gives pigment to skin? A person deficient in pigment and unable to produce this substance is called a(n) ________.
|
melanin
albino |
|
|
Comedones are commonly known as what?
|
blackheads
|
|
|
Nevi are commonly known as what?
|
moles
|
|
|
Alopecia is commonly known as what?
|
baldness
|
|
|
Pruritus is commonly known as what?
|
itching
|
|
|
Urticaria is commonly known as what?
|
hives
|
|
|
A decubitus ulcer is commonly known as what?
|
bedsore
|
|
|
Verrucae are commonly known as what?
|
warts
|
|
|
Tinea pedis is commonly known as what?
|
athlete's foot
|
|
|
What is an ecchymosis?
|
a bruise
|
|
|
Seborrheic dermatitis is commonly known as what?
|
dandruff
|
|
|
Vesicles are commonly known as what?
|
blisters
|
|
|
An exanthem is commonly known as what?
|
rash
|
|
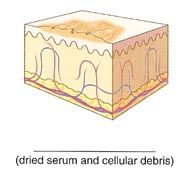
What is the medical name for a collection of dried serum and cellular debris, such as a scab.
|
crust
|
|
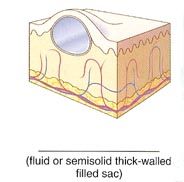
Name the cutaneous lesion characterized by a thick-walled, closed sac or pouch containing fluid or semisolid material.
|
cyst
|
|
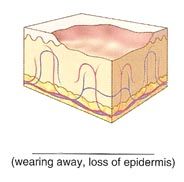
Name the cutaneous lesion characterized by the wearing away or loss of epidermis. An abrasion is an example of this type.
|
erosion
|
|
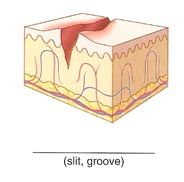
Name the cutaneous lesion characterized by a groove or crack-like sore.
|
fissure
|
|
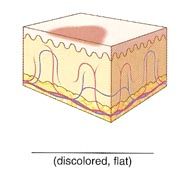
Name the cutaneous lesion characterized by a flat lesion measuring less than 1 cm in diameter. Freckles, tattoo marks, and flat moles are examples.
|
macule
|
|
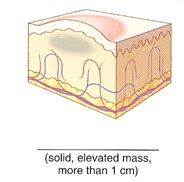
Name the cutaneous lesion characterized by solid, round or oval elevated lesion 1 cm or more in diameter.
|
nodule
|
|
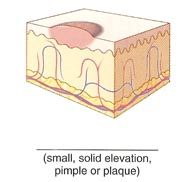
Name the cutaneous lesion characterized by a small (less than 1 cm in diameter), solid elevation of the skin. Pimples are an example of this type.
|
papule
|
|
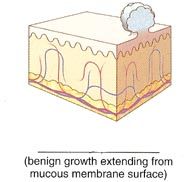
Name a cutaneous lesion characterized by growth extending from the surface of a mucous membrane and commonly found in the nose, sinuses, colon, urinary bladder, and uterus.
|
polyp
|
|
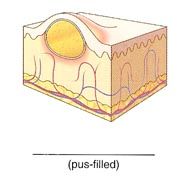
Name the cutaneous lesion characterized by a papule containing pus, such as an abscess.
|
pustule
|
|
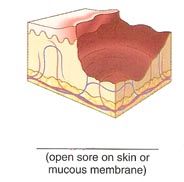
Name the cutaneous lesion characterized by an open sore on the skin or mucous membranes (deeper than an erosion). Bedsores are an example of this type.
|
ulcer
|
|
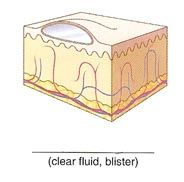
Name the cutaneous lesion characterized by a small collection of clear fluid (serum). Commonly called a blister.
|
vesicle
|
|
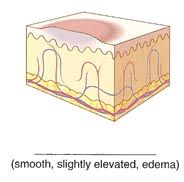
Name the cutaneous lesion characterized by smooth, edematous (swollen) papule or plaque that is redder or paler than the surrounding skin. They may be papular, as in a mosquito bite, or may involve a wide area, as in allergic reactions (hives).
|
wheal
|

