![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gravida |
The number of pregnancies a woman has had- primigravida: first time pregnant woman |
|
|
Para |
The number of children The number of births after 20 weeks not the number of fetuses. Alive or still born. (Contains full term birth, premature, abortion, living children) |
|
|
ECD/EDD |
Due date/ expected date of delivery |
|
|
LMP |
First day of Last menstrual period |
|
|
Doula |
For labor or postpartum. Has no nursing responsibilities, supports laboring women and her partner and offers individualized care and labor support |
|
|
CNM- certified nurse- midwife |
RN with advanced training in in labor, birth prenatal care, well woman care for women throughout the lifespan |
|
|
Perinatologist |
Obstetrician with advanced training in high risk obstetrics |
|
|
Obstetrician |
MD or DO with advanced training in obstetrics and gynecology care |
|
|
Family physician or GP( general practitioner) |
General practitioner, family MD, cares for the family unit, rarely attends women in birth( only in rural areas) |
|
|
Neonatologist( doctor for preemies) |
Pediatrician with advanced training in neonates, cares for extremely high risk babies from birth through discharge |
|
|
NNP |
Neonatal nurse practitioner- cares for sick and premature infants |
|
|
Level 1 hospital |
Community or rural hospital( cannot care for sick babies- transport to high risk center) |
|
|
Level 2 hospital |
Takes care of moderately I’ll neonates ( Wakemed and Duke regional) |
|
|
Level 3 hospital |
High risk, tertiary hospital, the highest of the high risk. (Duke, Wakemed Raleigh, unc) |
|
|
Birth center |
Sure of birth for very low risk women, usually attended by CNMS, RNs, and doulas for the birth |
|
|
Term gestation |
37-40 weeks |
|
|
Post term |
42 0/7 weeks and beyond |
|
|
Preterm |
Anything before 37 |
|
|
Fetal heart tones/rate (FHT) |
110-160 |
|
|
Leopold manuevers (4 types) |
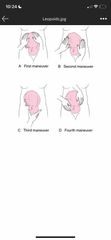
Use to locate fetal back, shoulders, presenting part |
|
|
Doptone |
Hand held ultrasonic device used to listen to fetal heart tones. Must be used with conductive gel |
|
|
Unit policy |
Hospital or unit specific guidelines that outlines the specifics of care or a procedure - first benchmark to which care is evaluated |
|
|
Standard of care |
What any reasonably prudent nurse would do I’m similar circumstances |
|
|
BOW- bag of water |
Sac of amniotic fluid(“my water broke” |
|
|
AROM- artificial rupture of membranes |
Provider breaking your water |
|
|
SROM- spontaneous rupture of membranes |
Water breaking on its own |
|
|
PROM |
Prelabor rupture of membranes is the spontaneous rupture of the amniotic sac and leakage of amniotic fluids beginning BEFORE the onset of labor at any gestational age( water breaking before labor) |
|
|
PPROM |
Preterm prelabor rupture (water breaking before 37 weeks) |
|
|
Dilation |
Cervix opens to accommodate the passage of the baby’s head into the vagina (10cm) |
|
|
Effacements |
Thinning and shortening of the cervix during the first stage of labor ( measures in percentages : 0-100%) |
|
|
Station |
Measurement of the baby in relation to the ischial spine.. the presenting part of the fetus through the birth canal 0- at the bottom of the pelvis +3- in the birth canal +5- crowning |
|
|
“Complete” dilation |
10cm.. marks the beginning of the second stage (labor) |
|
|
Placenta previa |
The placenta blocks the neck of the uterus thus interfering with normal delivery of baby |
|
|
Abruptio placenta |
The placenta detaches from the inner wall of the uterus before pregnant which can cause internal or external bleeding/ hemorrhage and cause the baby to lose oxygen and nutrients |
|
|
Frank/complete breech |
Baby’s feet are up by head and comes out butt first |
|
|
Footling breech |
Baby presenting one foot first |
|
|
Doubling footling breech |
Baby presenting both feet first |
|
|
VBAC |
Vaginal delivery after previous pregnancy was delivered by c-section ( vaginal birth after C-section ) |
|
|
Cesarean birth |
Birth of fetus by incision through the abdominal wall and uterus (cut along pelvic area and down abdomen) |
|
|
Primary c-section |
Mothers request to have C-section in absence of any indications of needing |
|
|
Repeat c-section |
Previous birth was c section so continue to have C-section |
|
|
Emergent c section |
Performed to immediately intervene to improve maternal or fetal outcome |
|
|
Emergency “crash” c-section |
Emergent c section set to deliver baby in 30 min |
|
|
Classic c-section |
Involves a long vertical incision being made in the midline of the abdomen, uterus is incised vertically |
|
|
Low transverse c-section |
Involves a transverse cut of the transverse at a lower point sometimes near the “bikini line” |
|
|
LGA |
Large for gestational age = bigger baby than expected (greater than 90th percentile) |
|
|
SGA |
Small for gestation age(less than 10th percentile) |
|
|
Meconium |
The baby’s first poop( excreting bilirubin) sticky, dark greenish brown almost black, viscid, sterile, odorless |
|
|
Apgar score |
Rapid assessment of newborn (1 min after birth and then 5min) Scores 0-10 appearance, pulse, grimace, activity/muscle tone, respirations |
|
|
IUPC |
Intrauterine pressure catheter- internal monitor placed between the baby and uterine wall (helps monitor contractions) |
|
|
Fetal scalp electrode (FSE) |
Measures fetal heart rate |
|
|
Failure to progress (FTP) |
Happens when labor slows and delays delivery of baby (cervix may not thin out or dilate for baby to move out of birth canal) |
|
|
External version |
A procedure used to turn a fetus from a breech position or side lying (transverse) position into a head down( vertex) position before labor begins (if done correctly, vaginal birth is possible) |
|
|
IUGR |
Intrauterine growth restriction( poor growth of baby while in the womb)- lack of nutrition from placenta |
|
|
HELLP syndrome |
Variant of preclamapsia that involves hepatic dysfunction characterized by hemolysis, elevated liver enzyme’s, low platelet count. Life- threatening complication of pregnancy, could occur during pregnancy or after birth |
|
|
DTR’s |
Deep tendon reflex, involuntary reaction of muscle being stretched |
|
|
Clonus |
Hyperactive reflexes at the ankle joint, dorsiflex pts foot and the foot keeps bouncing dorsiflex and plantar flex (almost like a tremor) |
|
|
Hemorrhage by definition of QBL for vaginal birth |
Quantitive blood loss-vaginal birth blood loss: 300-500 ml. C-section: 500-1000ml |
|
|
Laboring down |
Process of allowing the uterus to continue to contract without maternal pushing effort even though full dilation has been attained |
|
|
Prodromal labor (“false labor”) |
Labor that starts and stops before fully active labor begins. |
|
|
Latent (early) labor |
Cervix becomes soft and thing as it gets ready to dilate - start to have contractions that may be irregular and vary in length, frequency, and strength |
|
|
Active labor |
Cervix is dilated to 10cm, contractions become stronger, closer together and regular |
|
|
First stage of labor |
Early labor( cervix dilates and efface with mild and irregular contractions) and active labor |
|
|
Second stage of labor |
Birth of baby |
|
|
Third stage of labor |
Delivery of placenta |
|
|
Water birth |
Part of your labor, delivery or both, I’m a pool filled with warm water. Can take place in hospital, birthing center, or home |
|
|
Epidural |
Injection of a local anesthetic into the space outside the dura mater of the spinal cord in the lower back region to produce loss of sensation |
|
|
Spinal |
Administration of an anesthetic into the subarachnoid space via the lumbar area. Monitor closely for hypotension, impaired respirations, and indications of fetal distress following placement of spinal anesthesia. Admineristing a in bolus of 500 ml can help prevent adverse effects |
|
|
Local anesthesia |
A type of pain prevention used to numb a small site where pain is likely to occur without changing the patients awareness |
|
|
Episiotomy |
Surgical incision of the perineum at the end of the second stage of labor to enlarge the vaginal outlet, facilitate birth and avoid laceration of perineum |
|
|
Neonatal jaundice |
Liver condition that causes yellowing of newborn babies skin and eyes; premature livers- usually in preterm babies |
|
|
Acrocyanosis |
Peripheral cyanosis; bluish discoloration of the hands and feet in most newborns at birth that is a normal finding in the first 24hrs |
|
|
Engorgement of the breast |
When the breast feels nodular or lumpy (shifts in position during palpating ) |
|
|
Mastatitis of the breast |
Infection of the breast, usually confined to a milk duct. Characterized by influenza- like symptoms and redness and tenderness in the affected breast |
|
|
Abscess of the breast |
Painful buildup of pus in breast caused by an infection (mainly affects women who are breast feeding) |
|
|
Hamaturia |
Presence of blood or blood cells in urine |
|
|
Dysuria |
Painful or difficult urination |
|
|
Dysmenorrhea |
Pain during or shortly before menustration |
|
|
Dyspareunia |
Gentian pain associated with sexual intercourse, shortly before, during, or after intercourse |
|
|
Gestational diabeties |
Diabetes diagnosed during pregnancy that is not preexisting diabeties, carbohydrate |
|
|
Zygote |
Cell formed by the union of two reproductive cells or gametes( fertilization of the egg by the sperm) |
|
|
Embryo |
Conceptus from the second or third week of development until approximately the eight week after conception, when mineralization of the Skelton begins |
|
|
Blastocyst |
Stage on the development of a mammalian embryo, occurring after the morula stage, that consist of an outer layer, or trophoblast and a hollow sphere of cells enclosing of cavity |
|
|
Invitro fertilization |
Mature eggs are retrieved from ovaries and fertilized by sperm in a lab |

