![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
171 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
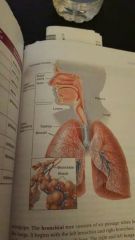
|
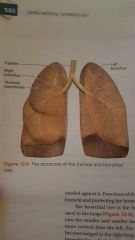
structures of upper and lower respiratory tracts |
|
|
space on either side of nasal septum |
nasal cavity |
|
|
region between mouth and esophagus |
pharynx (throat) |
|
|
voice box |
larynx |
|
|
tube that conducts air from larynx to bronchial tree |
trachea (windpipe) |
|
|
branches of bronchi |
bronchial tree |
|
|
organs of breathing |
lungs |
|
|
region of pharynx behind nasal cavity |
nasopharynx |
|
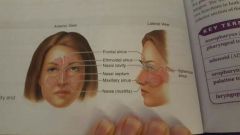
|
nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses |
|
|
lymphatic tissue on posterior wall of nasopharynx |
pharyngeal tonsils (adenoid) |
|
|
region of pharynx located near back of mouth |
oropharynx |
|
|
lymphatic tissue embedded in wall of oropharynx |
Palatine tonsils (tonsils) |
|
|
lower-most region of pharynx located near larynx |
laryngopharynx |
|
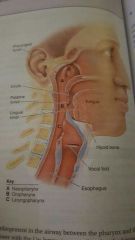
|
pharynx |
|
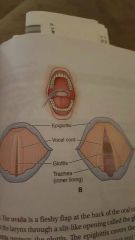
|
vocal cords with glottis closed and open |
|
|
fleshy flap at back of oral cavity that hangs above throat |
uvula |
|
|
slit-like opening where air enters larynx |
glottis |
|
|
flap of cartilage that guards glottis during swallowing |
epiglottis |
|
|
structures that vibrate in larynx to produce sound |
vocal cords |
|
|
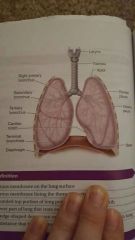
lungs |
|
|
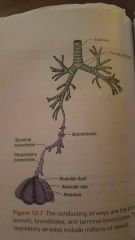
air pass from trachea to alveolus |
|
|
2 main branches (left and right) off trachea |
bronchi |
|
|
small subdivisions of bronchi |
bronchioles |
|
|
subdivision of bronchioles |
terminal bronchioles |
|
|
respiratory structures involved with air distribution |
conduction airway |
|
|
respiratory structures involved with gas exchange |
respiratory airway |
|
|
tiny air sacs in lungs where gases are exchanged between alveolar air and blood |
alveoli |
|
|
lungs |
|
|
serous membrane on lung surface |
visceral pleura |
|
|
serous membrane lining thoracic cavity |
parietal pleura |
|
|
rounded top portion of lung pointing toward first rib |
apex |
|
|
lower part of lung that rests on diaphragm |
base |
|
|
wedge-shaped depression on mediastinal surface of each lung |
hilum |
|
|
substance that helps to prevent alveoli from collapsing |
surfactant |
|
|
process of inhaling or inspiring |
inhalation |
|
|
process of exhaling or expiring |
exhalation |
|
|
chemical processes occurring in tissues for gas exchange |
respiration (breathing) |
|
|
breathing, respiration |
pulmonary ventilation |
|
|
curved muscle separates thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity |
diaphragm |
|
|
cough |
tussis |
|
|
normal breathing |
eupnea |
|

|
spirometer |
|
|
device that measures inhaled and exhaled air volumes |
spirometer |
|
|
evaluates and assesses lung function by measuring lung volume and capacities |
pulmonary function test (PFT) |
|
|
amount of air inhaled or exhaled in single breath |
tidal volume (tv) |
|
|
amount of air that can be forcefully breathed in after normal inhalation |
inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) |
|
|
amount of air that can be forcefully expired after normal exhalation |
expiratory reserve volume (ERV) |
|
|
amount of air that can be exhaled after deepest possible inhalation |
vital capacity (VC) |
|
|
amount of air remaining in lungs after complete exhalation |
residual volume (RV) |
|
|
total volume of air lungs can hold |
total lung capacity (TLC) |
|
|
locations for percussion |
|
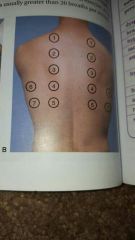
|
locations for auscultation |
|
|
listening to body sounds using stethoscope |
auscultation |
|
|
tapping on chest or back during auscultation to determine presence of normal air content in lungs |
percussion |
|
|
difficulty breathing |
dyspnea |
|
|
abnormally slow breathing |
bradypnea |
|
|
increased rate and depth of breathing |
hyperpnea |
|
|
rapid breathing |
tachypnea |
|
|
impaired or absent exchange of O2 and CO2 during breathing that results in suffocation |
asphyxia |
|
|
excessive inhalation and exhalation that leads to decreased CO2 levels |
hyperventilation |
|
|
decreased breathing rate that often results in increased levels of CO2 |
hypoventilation |
|
|
temporary absence of breathing |
apnea |
|
|
sudden temporary loss of breath |
reflex apnea (gasp) |
|
|
cessation of breathing during sleep that causes one to awaken and is associated with daytime sleepiness |
sleep apnea |
|
|
altering periods of apnea with breaths of same depth |
Biot respiration |
|
|
alternating pattern of apnea and deep, rapid breathing |
Cheyne-Strokes respiration |
|
|
rapid and deep respiration (air hunger) |
Kussmaul respiration |
|
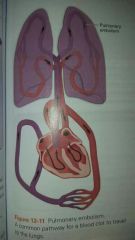
|
pulmonary embolism, common pathway for blood clot to travel to lungs |
|

|
o2 tent |
|
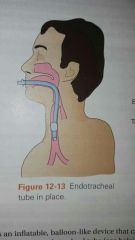
|
endotracheal tube |
|
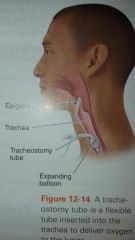
|
tracheostomy tube, a flexible tube inserted into trachea to deliver O2 to lungs |
|
|
blood clot lodged in pulmonary artery |
pulmonary embolism |
|
|
bluish color due to lack of O2 in blood |
cyanosis |
|
|
abnormal hissing or whistling respiratory sounds |
rales |
|
|
flexible tube placed in nostrils to deliver O2 |
nasal cannula |
|
|
supplying O2 via nasal cannula, Venturi mask, or O2 tent |
O2 therapy |
|
|
face mask that delivers O2 |
Venturi mask |
|
|
bag that manually pumped to deliver air or O2 |
resuscitation bag |
|
|
device for administering medicinal liquid in form of spray to be breathed through mouth or nose |
nebulizer (atomizer) |
|
|
structure that surrounds patient in bed to supply O2 |
O2 tent |
|
|
tube passed through mouth or nose to trachea |
endotracheal tube |
|
|
tube placed through hole in trachea |
tracheostomy tube |
|
|
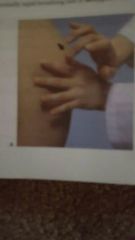
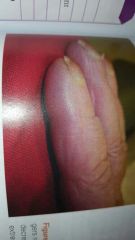
clubbing of fingers due to long term decreased O2 supply to extremities |
|
|
inherited disorder characterized by thick mucous secretions that block internal passages, including lungs |
cystic fibrous |
|
|
fluid or semifluid mucus mixture |
sputum (phlegm) |
|
|
coughed up and spit out |
expectorated |
|
|
inadequate O2 in tissues |
hypoxia |
|
|
fingertips that are rounded like a club as result of chronic inadequate O2 delivery to tissue |
clubbing of fingers |
|
|
Use of PEF meter to measure volume of air after forced expiration |
peak expiratory flow PEF test |
|
|
measurement of O2 in blood |
pulse oximetry |
|
|
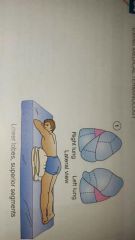
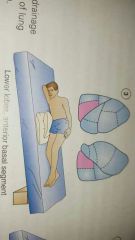
positioning body to allow gravity to drain mucus from areas of lungs |
postural drainage (PD) |
|
|
postural drainage for lower lobes |
|

|
postural drainage for upper lobes |
|
|
postural drainage for lower lobes |
|
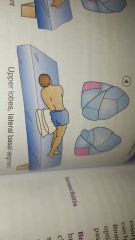
|
postural drainage for upper lobes |
|
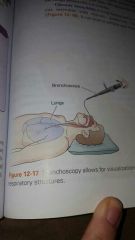
|
bronchoscopy |
|
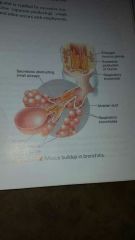
|
mucus buildup in bronchitis |
|
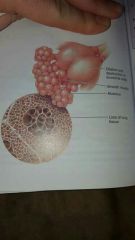
|
emphysema |
|
|
general term describing lung disease affecting bronchial tree |
Chronic Obstruction Pulmonary Disease (COPD) |
|
|
chronic dilation of airways |
bronchiectasis |
|
|
pertaining to mucus with pus |
mucopurulent |
|
|
coughing up blood or bloody mucus |
hemoptysis |
|
|
procedure for viewing inside of respiratory structures using bronchoscope |
bronchoscopy |
|
|
drugs that ease breathing by relaxing air passages |
bronchodilators |
|
|
inflammation of bronchial tubes |
bronchitis |
|
|
sudden and short lasting inflammation of bronchial tubes |
acute bronchitis |
|
|
long lasting inflammation of bronchial tubes |
chronic bronchitis |
|
|
abnormally rounded chest cavity |
barrel chest |
|
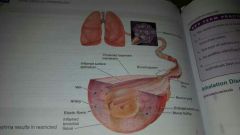
|
asthma results in restricted airways |
|
|
breathing disorder characterized by chest tightness and airway constriction |
asthma |
|
|
harsh rattling sound |
rhonchus |
|
|
audible whistling breath sound |
wheeze |
|
|
contraction of smooth muscle in walls of bronchi and broncholes, causing narrowing of bronchial tubes |
bronchospasm |
|
|
form of asthma with attacks of dyspnea and bronchial spasms |
bronchial asthma |
|
|
form of asthma with bronchialconstriction caused by exercise |
exercise induced asthma |
|

|
lung with silicosis |
|
|
disease caused by inhaling mineral or metallic dust over long period of time |
pneumoconiosis |
|
|
pneumoconiosis caused by inhalation of coal dust |
anthracosis |
|
|
pneumoconiosis caused by inhalation of asbestos fibers |
abestosis |
|
|
pneumoconiosis caused by inhalation of beryllium |
berylliosis |
|
|
pneumoconiosis caused by inhalation of silica dust |
silicosis |
|
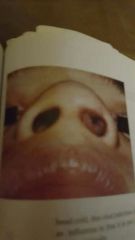
|
nasal polyp |
|
|
acute infection causing inflammation that affects upper respiratory structures |
upper respiratory infection (URI) |
|
|
any of many RNA viruses that cause upper respiratory tract infections |
rhinoviruses |
|
|
benign growth on nasal mucous membranes |
nasal polyp |
|
|
nasal inflammation resulting from allergy |
allergic rhinitis |
|
|
instrument for viewing nasal cavity |
nasal speculum |
|
|
inflammation of nasal cavity caused by infection |
acute rhinitis or nasal catarrh |
|
|
tear production |
lacrimation |
|
|
runny nose |
coryza |
|
|
inflammation of sinuses |
sinusitis |
|
|
inflammation of pharynx |
pharyngitis (sore throat) |
|
|
hoarseness |
dysphonia |
|
|
difficulty swallowing |
dysphagia |
|
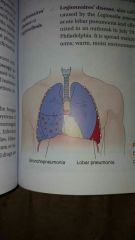
|
bronchopneumonia and lobar pneumonia |
|
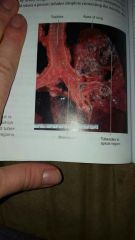
|
lung with TB |
|
|
larynx inflammation |
laryngitis |
|
|
loss of voice |
aphonia |
|
|
lighted instrument with short metal or plastic tube used for examination of larynx |
laryngoscope |
|
|
fungal infection of lung |
histoplasmosis |
|
|
seeping mass of cells and fluid |
exudate |
|
|
inflammation of lungs |
pneumonia |
|
|
inflammation of lungs that results from inhaling substance into lung field |
aspiration pneumonia |
|
|
inflammation of lungs affecting one or more lobes or part of a lobe |
lobar pneumonia |
|
|
tests to evaluate substances found in sputum |
sputum studies |
|
|
tests to identify microbes and the effectiveness of various antibiotics |
culture and sensitivity (C&S) studies |
|
|
lung inflammation caused by RSV |
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) pneumonia |
|
|
viral infection producing fever, sore throat, cough and muscle pain |
influenza |
|
|
mantoux test |
TB test |
|
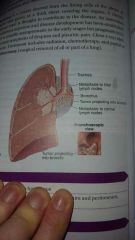
|
cancer of right lung, anterior view |
|
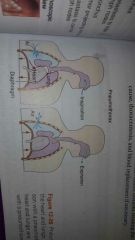
|
pneumothorax |
|
|
abnormal presence of air or gas in pleural cavity |
pneumothorax |
|
|
needle aspiration of pleural cavity through chest wall for fluid or air withdrawal |
thoracentesis |
|
|
blood in pleural cavity |
hemothorax |
|
|
low blood pH caused by CO2 retention (hypoventilation) |
respiratory acidosis |
|
|
increased blood pH due to elimination of too much CO2 (hyperventilation) |
respiratory alkalosis |
|
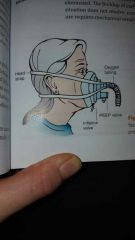
|
CPAP mask |
|
|
disorder marked by hypercapnia, acidemia, and severe hypoxia resulting in cyanosis |
adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) |
|
|
too much CO2 in blood |
hypercapnia |
|
|
abnormally low pH |
acidemia |
|
|
inadequate O2 in blood |
hypoxemia |
|
|
fluid accumulation in lungs causing breathing difficulty |
pulmonary edema |
|
|
positive pressure air delivered during expiration |
positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP) |
|
|
illness caused by ascent to high altitude resulting in shortage of O2 |
altitude sickness (mountain sickness) |
|
|
disorder marked by breathing difficulty and cyanosis in infant or newborn |
infant respiratory distress syndrome (IRDS) or (NRDS) or (HMD) |
|
|
NRDS |
neonatal respiratory distress syndrome |
|
|
HMD |
hyaline membrane disease |
|
|
respiratory system unable to meet O2 demand of body and CO2 levels increase |
respiratory failure |
|
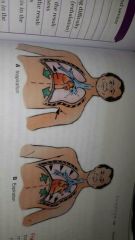
|
flail chest results from trauma to ribs |
|
|
fracture of ribs that causes paradoxical chest wall movement |
flail chest |
|
|
breathing that's contray to usual movements where lung deflates during inhalation and inflates during exhalation |
paradoxical respiration |

