![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
197 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Structural component of the nucleus, composed of nucleic acids and protein |
Chromatin |
|
|
Threadlike structures within the nucleus composed of DNA that carries hereditary information encoded in genes; formed by chromatin |
Chrimosome |
|
|
Molecule that holds genetic information capable of replicating and producing an exact copy whenever the cell divides |
Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
|
|
Muscular wall that divides the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity |
Diaphragm |
|
|
Sum of all physical and chemical changes that take place in a cell or an organism |
Metabolism |
|
|
Cellular structure that provides a specialized function, such as the nucleus , reproduction, golgi apparatus, and lysosomes |
Organelle |
|
|
The science of the structure of the human body |
Anatomy |
|
|
Deals with the functions of the body |
Physiology |
|
|
The basic functional and structural unit of the entire human being |
Cell |
|
|
Acts as a barrier that supports and protects the intracellular contents |
Cell membrane |
|
|
Jellylike matrix within cells that contain organelles |
Cytoplasm |
|
|
Control center of the cell that contains the genetic information |
Nucleus |
|
|
Tissue that covers surfaces of organs, lines cavities and canals, forms tubes and ducts, provides secreting portions of glands, and makes up the epidermis of skin |
Epithelial tissue |
|
|
Tissue that supports and connects other tissue and organs |
Connective tissue |
|
|
Tissue responsible for movement |
Muscular tissue |
|
|
Tissue that transmits electrical impulses and relays information |
Nervous tissue |
|
|
This plane separates the right and left halves |
Midsagittal plane |
|
|
This planes separates the anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) aspects |
Coronal (frontal) planes |
|
|
This plane separates the superior (upper) and inferior (lower) aspects |
Transverse (horizontal) planes |
|
|
This body cavity refers to the brain |
Cranial (dorsal) |
|
|
This body cavity refers to the spinal cord |
Spinal (dorsal) |
|
|
This body cavity refers to the heart, lungs, and associated structures |
Thoracic (ventral) |
|
|
This body cavity refers to the digestive, excretory, and reproductive organs and structures |
Abdominopelvic (ventral) |
|
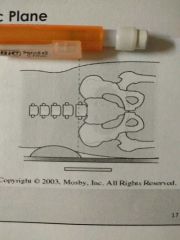
This plane transects the trunk at the top of the iliac crests |
Interiliac plane |
|
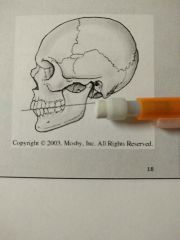
This plane is formed by the biting surfaces of the teeth |
Occlusal plane |
|
|
How many vertebrae are in the spine |
26 |
|
|
Cyt/o |
Cell |
|
|
Hist/o |
Tissue |
|
|
Kary/o |
Nucleus |
|
|
Nucle/o |
Nucleus |
|
|
Anter/o |
Anterior, front |
|
|
Caud/o |
Tail |
|
|
Cephal/o |
Head |
|
|
Dist/o |
Far, farthest |
|
|
Dors/o |
Back (of body) |
|
|
Infer/o |
Lower, below |
|
|
Later/o |
Side, to one side |
|
|
Medi/o |
Middle |
|
|
Poster/o |
Back, behind, posterior |
|
|
Proxim/o |
Near, nearest |
|
|
Ventr/o |
Belly side, belly |
|
|
Abdomin/o |
Abdomen |
|
|
Cervic/o |
neck |
|
|
Crani/o |
Cranium |
|
|
Gastr/o |
Stomach |
|
|
Ili/o |
Pertaining to the ilium |
|
|
Inguin/o |
groin |
|
|
Lumb/o |
Loins (lower back) |
|
|
Pelv/i or pelv/o |
pelvis |
|
|
Spin/o |
Spine |
|
|
Thorac/o |
Chest |
|
|
Umbilic/o |
Umbilicus, navel |
|
|
Albin/o |
White |
|
|
Leuk/o |
White |
|
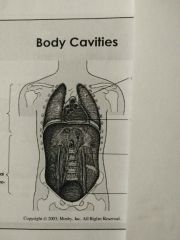
Identify the top body cavity |
Pleural cavity |
|
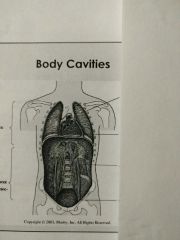
Identify the second body cavity |
Pericardial cavity |
|
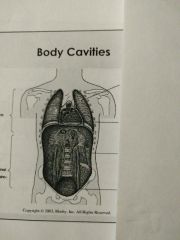
Identify the third body cavity |
Abdominal cavity |
|
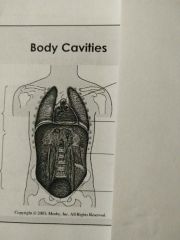
Identify the bottom body cavity |
Pelvic cavity |
|
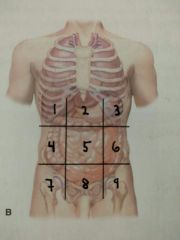
Identify quadrant 1 |
Right hypochondriac region |
|
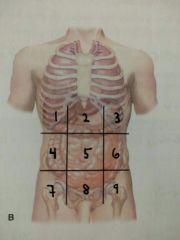
Identify quadrant 2 |
Epigastric region |
|
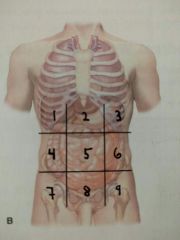
Identify quadrant 3 |
Left hypochondriac region |
|
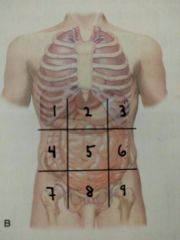
Identify quadrant 4 |
Right lumbar region |
|
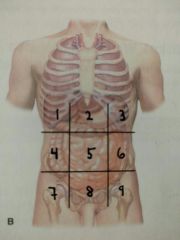
Identify quadrant 5 |
Umbilical region |
|
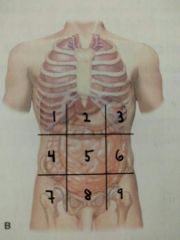
Identify quadrant 6 |
Left lumbar region |
|
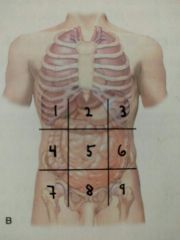
Identify quadrant 7 |
Right Inguinal / iliac region |
|
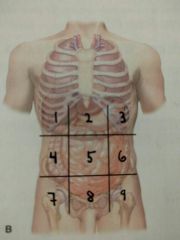
Identify quadrant 8 |
Hypogastric region |
|
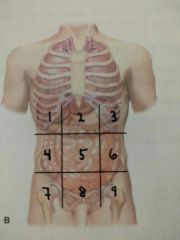
Identify region 9 |
Left inguinal / iliac region |
|
|
Abduction |
Movement away from the midsagital median plane of the body or one of its part |
|
|
Adduction |
Movement toward the midsagittal median plane of the body |
|
|
Medial |
Pertaining to the midline of the body or structure |
|
|
Lateral |
Pertaining to a side |
|
|
Superior (cephaloid) |
Toward the head or upper party of a structure |
|
|
Inferior (caudal) |
Away from the head, or toward the tail or lower part of a structure |
|
|
Proximal |
Nearer to the center (trunk of the body) or to the point of attachment to the body |
|
|
Distal |
Further from the center (trunk of the body) or from the point of attachment to the body |
|
|
Anterior (ventral) |
Front of the body |
|
|
Posterior (dorsal) |
Back of the body |
|
|
Parietal |
Pertaining of the outer wall of the body cavity |
|
|
Visceral |
Pertaining to the viscera, or internal organs, especially the abdominal organs |
|
|
Prone |
Lying if the abdomen, face down |
|
|
Supine |
Lying horizontally on the back, face up |
|
|
Inversion |
Toward inward or inside out |
|
|
Eversion |
Turning outward |
|
|
Palmar |
Pertaining to the palm of the hand |
|
|
Plantar |
Pertaining to the sole of the foot |
|
|
Superficial |
Toward the surface of the body (external) |
|
|
Deep |
Away from the surface of the body (internal) |
|
|
Chlor/o |
Green |
|
|
Chrom/o |
Color |
|
|
Cirrh/o |
Yellow |
|
|
Jaund/o |
Yellow |
|
|
Xanth/o |
Yellow |
|
|
Cyan/o |
Blue |
|
|
Erythr/o |
Red |
|
|
Melan/o |
Black |
|
|
Poli/o |
Gray |
|
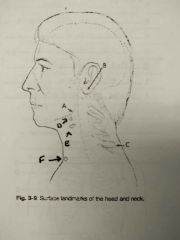
Identify A |
Gonion |
|
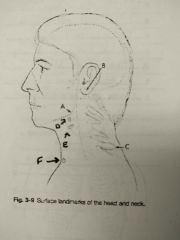
Identify B |
Mastoid tip |
|
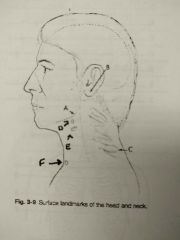
Identify C |
Vertebra prominens |
|
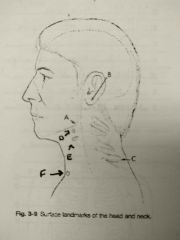
Identify D |
Hyoid bone |
|
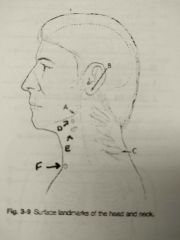
Identify E |
Thyroid cartilage |
|
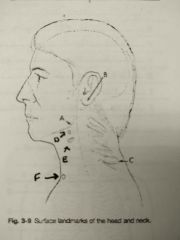
Identify F |
Jugular notch |
|
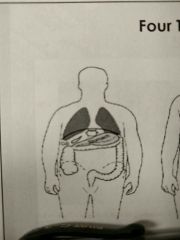
What body type is this |
Hypersthenic |
|
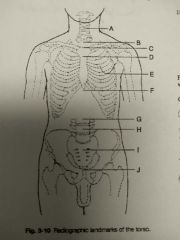
Identify A |
C5 and thyroid cartilage |
|
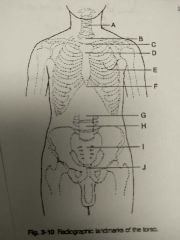
Identify B |
T1 |
|
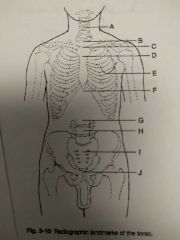
Identify C |
T2, T3, and jugular notch |
|
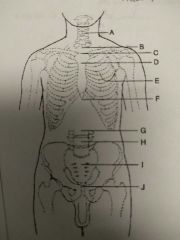
Identify D |
T4, T5 and sternal angle |
|
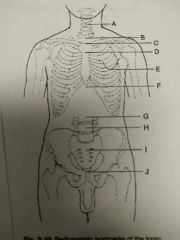
Identify E |
T7 and interior angle scapula |
|
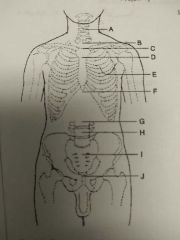
Identify F |
T9, T10 and xyphoid process |
|
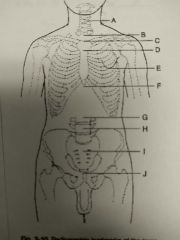
Identify G |
L2, L3 and interior coastal margin |
|
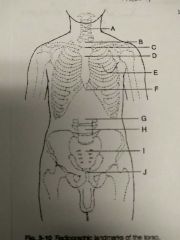
Identify H |
L4, L5 and iliac crest |
|
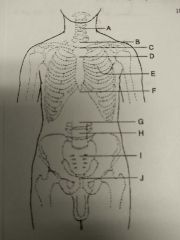
Identify I |
S1 and anterior superior Iliac spine |
|
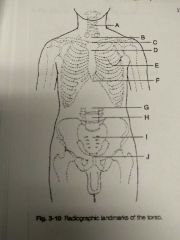
Identify J |
Coccyx, pubic symphysis and greater trocanters |
|
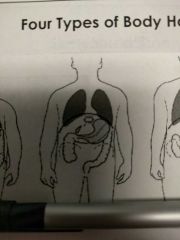
What body type is this |
Sthenic |
|
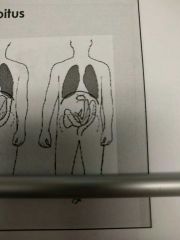
What body is this |
Asthenic |
|
|
Describe the outer layer of a bone |
Composed of compact bone |
|
|
Describe the inner portion of a bone |
Composed of spongy bone |
|
|
Covers all bony structures |
Periosteum |
|
|
Bone Tissue lining the medullary cavity |
Endosteum |
|
|
Knob like projections where muscles and tendons attach |
Tubercles, tuberosites |
|
|
Area on a bone where blood vessels and nerves enter and exit |
Foramina |
|
|
The opening on long bones in the periosteum where blood vessels and nerves enter and exit |
Nutrient foramen |
|
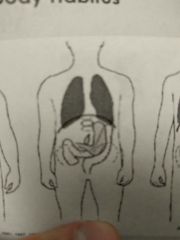
What body type is this |
Hyposthenic |
|
|
Osteology |
Study of bones |
|
|
Arthrology |
Study of joints |
|
|
Describes the development and formation of bones |
Ossification |
|
|
Describe bones that develop from fibrous membranes in the embryo. Produce flat bones such ad skull and sternum |
Intermembraneous ossification |
|
|
Describe bones that develop from hyaline cartilage in the embryo. Produces short, irregular, and long bones. Occurs from primary and secondary centers of ossification |
Endochondral ossification |
|
|
Process begins before birth and forms the long central shafts of bones |
Primary ossification |
|
|
Process after birth where separate bones begin to develop at the end of each long bone |
Secondary ossification |
|
|
Separate bone that develops at the end of each long bone |
Epiphysis |
|
|
Develops between the diaphysis and epiphysis as growth occurs |
Epiphyseal plate |
|
|
When does full ossification occur? |
21 years |
|
|
What are the five clarifications of bones |
Long, short, flat, irregular, sesamoid |
|
|
Joint classification based on the mobility of a joint |
Functional classification |
|
|
What are the three functional classifications? |
Synarthroses, amphiathroses, diarthroses |
|
|
Describers and immovable joint |
Synarthroses |
|
|
Describes a joint with limited movement |
Amphoarthroses |
|
|
Describes a freely moveable joint |
Diarthroses |
|
|
Joint classification based on types of tissues that unite or bind articulating bones |
Structural classification |
|
|
What are the three structural classifications? |
Fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial |
|
|
What is the connective / structural classification for syndesmosis |
Fibrous, amphiarthroses |
|
|
What is the connective / structural classification for suture |
Fibrous, synarthroses |
|
|
What is the connective / structural classification for gomphosis |
Fibrous, synarthroses |
|
|
What is the connective / structural classification for symphysis |
Cartilaginous, amphiarthroses |
|
|
What is the connective / structural classification for synchrondrosis |
Cartilaginous, synarthroses |
|
|
What is the connective / structural classification for gliding |
Synovial, diarthroses |
|
|
What is the connective / structural classification for hinge |
Synovial, diarthroses |
|
|
What is the connective / structural classification for Pivot |
Synovial, diarthroses |
|
|
What is the connective / structural classification for ellipsoid |
Synovial, diarthroses |
|
|
What is the connective / structural classification for saddle |
Synovial, diarthroses |
|
|
What is the connective / structural classification for ball and socket |
Synovial, diarthroses |
|
|
Bone marking - rounded process located at the end if an articular extremity |
Condyle |
|
|
Bone marking - ridge like process |
Crest |
|
|
Bone marking - projection located above condyle |
Epicondyle |
|
|
Bone marking - small smooth surfaced process |
Facet |
|
|
Bone marking - club-shaped process |
Malleolus |
|
|
Bone marking - sharp process |
Spine |
|
|
Bone marking - long pointed process |
Styloid |
|
|
Bone marking - deep groove |
Fissure |
|
|
Bone marking - hole in bone for transmission of blood vessels and nerves |
Foramen |
|
|
Bone marking - pit or hollow space |
Fossa |
|
|
Bone marking - shallow linear channel |
Groove |
|
|
Bone marking - tubelike passage running within a bone |
Meatus |
|
|
Bone marking - indentation into the border of a bone |
Notch |
|
|
Bone marking - cavity or hollow space |
Sinus |
|
|
Bone marking - furrow or trench depression |
Sulcus |
|
|
A fracture that does no break the skin |
Closed |
|
|
Serious fracture in which the bone projects through the skin |
Open |
|
|
Fracture in which the bone retains its normal alignment |
Non-displaced |
|
|
A serious fracture in which the bones are not in anatomic alignment |
Displaced |
|
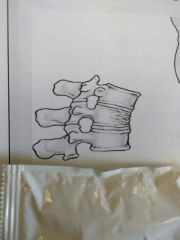
Identify this fracture |
Compression |
|
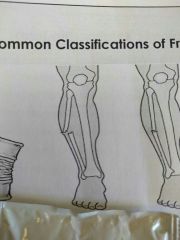
Identify this fracture |
Open/compound |
|
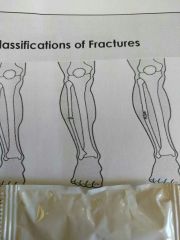
Identify this fracture |
Simple |
|
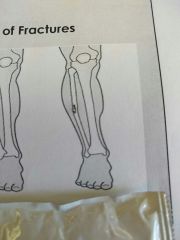
Identify this fracture |
Greenstick |
|
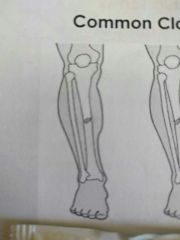
Identify this fracture |
Transverse |
|
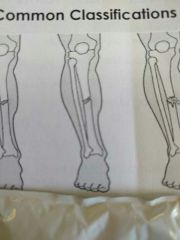
Identify this fracture |
Spiral / oblique |
|
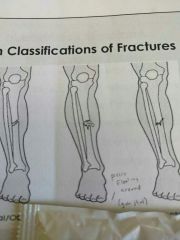
Identify this fracture |
Comminuted |
|
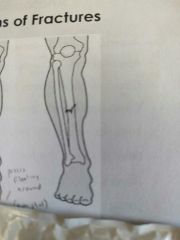
Identify this fracture |
Impacted |
|
|
Contralateral |
Refers to part or parts on the opposite side of the body |
|
|
Parietal |
Refers to the wall or lining of a body cavity |
|
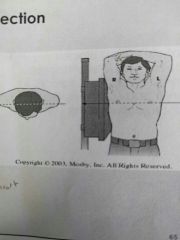
Identify the projection |
Lateral |
|

Identify the projection |
PA |
|

Identify the projection |
Ap |
|
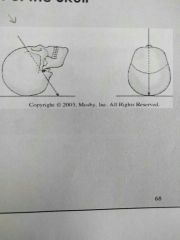
Identify the projection |
Ap axial |
|

Identify the projection |
Tangential projection |
|
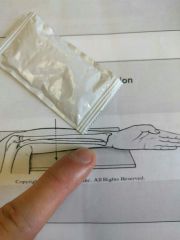
Identify the projection |
Lateromedial projection |
|
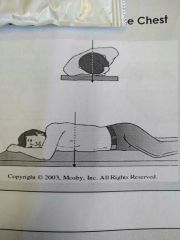
Identify the projection |
Pa oblique projection |
|

Identify the position |
Supine |
|

Identify the position |
Prone |
|

Identify the position |
Recumbent |
|
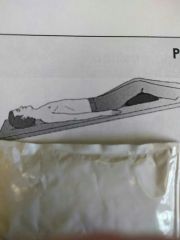
Identify the position |
Trendelenburg |
|
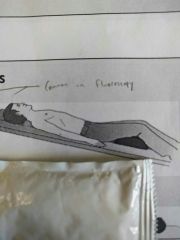
Identify the position |
Fowlers |
|

Identify the position |
Sims |
|
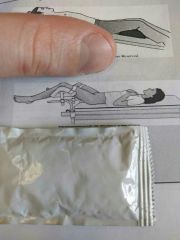
Identify the position |
Lithotomy |
|

Identify the position |
Left lateral |
|

Identify the position |
Right lateral |

