![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
91 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Urology
|
The study of disorders of the Urinary system
|
|
|
What are the warning signs of kidney disease
|
Burning or difficulty during urination
Increase in the frequency of urination, especially at night (nocturia) Passage of bloody appearing urine Puffiness around the eyes, or swelling of the hands and feet, especially in children Pain in the small of the back just below the ribs (not aggravated by movement) High blood pressure |
|
|
Nursing Management
|
General goal for kidney disorders is to preserve kidney function
One pound of weight gain = 500ml of retained fluid |
|
|
What is urgency
|
The desire to urinate
( about 250ml) The urine is then expelled from the bladder through the urethra |
|
|
How do urine move
|
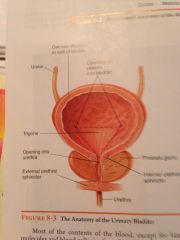
Urine moves steadily by peristalsis through the ureters into the urinary bladder
|
|
|
What is Micturition
|
The process of expelling urine from the urinary bladder, is also called urination or voiding
|
|
|
Where is the Retroperitoneal space
|
Behind the peritoneum outside the peritoneal cavity of the abdominal cavity
|
|
|
The kidneys also assist in what
|
Acid-base balance
Raise blood pressure by secreting the enzyme renin Produce the hormone erythropoietin |
|
|
What is Erythropoiesis
|
The production of red blood cells and their release by the red bone marrow
|
|
|
What are the functions of the Kidneys
|
* urine production and waste elimination
* erythropoietin secretion * Vitamin D metabolism * Excretion of excess potassium Bicarbonate production and acid secretion |
|
|
Where is urine made in the kidneys
|
In the nephrons
|
|
|
What is the glomerular filtration rate
( GFR) |
Is the amount of fluid filtered from the blood into the capsule per minute and an accurate measure of the functioning status of the kidneys
|
|
|
What is glomerular filtrate
|
The material filtered from the blood which contains water, electrolytes, glucose, various toxic substance, waste products
( urea and creatinine ) |
|
|
Assessment of the urinary system includes
|
Base-line data
Open-Ended questions Use laymen terms to help clients understand |
|
|
Assessment of high risk clients with renal disease with altered health status such as
|
Diabetes Mellitus
Pregnancy Hypertension Trauma Dehydration Fluid Retention |
|
|
What is Anuria
|
Cessation of urine production or urine output less< 100 ml/ day
|
|
|
What is Dysuria
|
Painful or difficult urination
|
|
|
What is Hematuria
|
Blood in the urine
|
|
|
What is Nocturia
|
Excessive urination at night
|
|
|
What is Oliguria
( scanty or decrease) |
Diminished capacity to form and excrete urine
( less than <500ml/ day) |
|
|
What is Polyuria
(Excessive) |
Excreting an abnormally large quantity of urine
|
|
|
What is Urgency
|
Feeling the need to urinate immediately
|
|
|
What to monitor client for
|
Edema
I &Os Vital Signs Palpate clients bladder for retention Weight Assess mucous membranes for moisture and the skin for dryness and uremic frost Evaluate urine for color, clarity, and odor Review diagnostic tests |
|
|
What are the changes with age
|
1. Nephrons decrease resulting in fluid over load
2. Glomerular filtration rate decrease resulting in toxic build up 3. Blood urea nitrogen increase 20% by age 70 The creatinine clearance test is better than the BUN of renal function in the elderly 4. Sodium-conserving ability is diminished So monitor fluids & electrolytes 5. Bladder capacity decrease, causing increased frequency of urination and nocturia ( Stress Incontinence) 6. Renal function increases when the client is lying down, sometimes causing a need to void shortly after going to bed 7. Bladder and perineal muscles weaken, resulting in inability to empty the bladder. This results in residual urine and predisposes the elderly to cystitis ( UTI) 8. Incidence of the stress incontinence increase in females 9. The prostate may enlarge, causing frequency or dribbling in males |
|
|
What are the upper UTIs
|
Pyelonephritis
Acute and Chronic Interstitial Nephritis Renal Abscess and Perirenal Abcess |
|
|
What is nuclear scans
|
When injected with dye to look at blood flow through kidneys
|
|
|
What is Endoscopic Procedures
|
Looking through urinary meatus at bladder
|
|
|
What is retrograde pyelography
|
It's the dye in veins to look for blood flow of the kidneys
|
|
|
What do renal function test evaluate
|
Ability of the kidneys to concentrate solute in urine
Specific gravity |
|
|
What are the signs and symptoms of elderly clients with UTIs
|
Change in mental status
Dehydration Hypernatremia |
|
|
What do you assess clients for with UTIs
|
Voiding patterns
Association of symptoms with sexual intercourse Contraceptive practices Personal hygiene |
|
|
How can we as nurses prevent UTIs
|
Avoid in dwelling catheters
Exercise proper care of catheters |
|
|
Signs & Symptoms of UTIs
|
Symptoms include
Pain and burning upon urination Frequency, Nocturia Incontinence Superapubic , pelvic, or back pain Hematuria or change in urine or urinary pattern Change in mental status |
|
|
How long is a urine specimen good for
|
1hour
|
|
|
How much urine to collect for a urinalysis
|
No less than 10 ml
Unless clients not making urine |
|
|
What are the lower UTIs
|
Cystitis
Prostatitis Urethritis |
|
|
What are type of restrictions may a dialysis clients be placed on
|
Fluid Restrictions
|
|
|
What is the most common bacteria that causes a UTI
( Uripathogenic Bacteria) |
E Coli
|
|
|
Why do women have UTIs more often than men
|
Because women have shorter urethra
|
|
|
Do all UTI clients have symptoms
|
No , about half are asymptomatic
|
|
|
Why do post menopausal women have a greater chance for contracting UTI s
|
Because estrogen keeps the peritoneal muscles tighter /toner and post menopausal women losses estrogen as they get older
|
|
|
What is the normal urine specific gravity level
|
1.000-1.030
|
|
|
What is the function of glycosominogly (GAG) and UTIs
|
Protein prevents bacteria from sticking to bladder wall
|
|
|
Signs & Symptoms of UTIs
|
Symptoms include
Pain and burning upon urination Frequency, Nocturia I continence Superapubic , pelvic, or back pain Hematuria or change in urine or urinary pattern Change in mental status |
|
|
What is urolothiasis
|
Kidney stones
|
|
|
What is urinary retention
|
When a person has the urge to void and can't
It creates urinary stasis and increase the possibility of infection |
|
|
What happens when urine over flows
|
Incontinence
Response to stress Benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) Obstruction of the urethra by calculi Calculi concentration of mineral salts ( kidney stones) Tumor, or infection Interference with sphincter muscles |
|
|
What are Side effects during surgery
|
Side effects of medicine
Or perineal trauma |
|
|
Signs/Symptoms
|
Discomfort and anxiety
Frequency of urination Voiding small amounts Distended bladder Which can be palpated above the symphysis |
|
|
Treatments include
|
Urinary analgesics and antispasmodic
To help clients to relax Cholinergic medication Bethanechol Chloride ( urecholine) to promote detrusor muscle contractions and bladder emptying Urinary catheter to empty the bladder or Surgey to remove obstruction |
|
|
What to do when client is unable to void
|
Check for residual urine immediately after the client voided
Use bladder scan Intermittent straight catheter and measure urine output Residual urine should be less than 50 ml |
|
|
What is urinary incontinence
( UI) |
The involuntary loss of urine from the bladder
Maybe a complication of urinary tract problems or neurological disorders and maybe permanent or temporary |
|
|
What are the UI medications
|
Sedatives
Hypnotics Diuretics Anti cholinergics Antipsychotics Alpha antagonist |
|
|
What is UI is classified as
|
Stress
Urge Overflow Total or nocturnal enuresis |
|
|
Urinalysis
|
Color. Bilirubin
Odor. Glucose Albumin ( protein). Specific gravity. Bacteria Acetone ( ketone) RBC. Casts WBC PH Culture and Sensitivity (C& S) Creatinine Clearance Residual Urine (post-voiding residual Urine) |
|
|
Blood Test
|
Blood Urea nitrogen (BUN)
10-39 mg/ dl Serum Creatinine 0.8-1.4 mg/dl |
|
|
Urine Test
|
Voiding Cystourethrography
|
|
|
Endoscopic Exams
|
Cystoscopy
Biopsy Renal Biopsy |
|
|
Anatomy and physiology
|
• Urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, bladder, and urethra
• Functions Manufacturer urine Expels waste products |
|
|
Assessment
|
Pain on urination
Pattern of urination Strength of urine stream Urgency , frequency, incontinence, hematuria And Nocturia Intake and output Urine color, clarity, and odor |
|
|
Edema
|
Right side CHF can be seen everywhere
Left side CHF is in the lungs |
|
|
Urinary Terms
|
• Anuria
Cessation of urine production • Dysuria Difficult Urination • Hematuria Blood in urine • Nocturia Excessive urination at night • Oliguria Decreased urine production • Polyuria Excess urination • Urgency need to urinate immediately |
|
|
Changes with aging
|
• nephrons decreases
• Glomerular filtration rate decreases • Blood urea nitrogen increases • Sodium-conserving ability diminishes • Bladder capacity decreases • Renal function increase when lying down • Bladder and perineal muscles weaken • Incidence of stress incontinence increase in females • Prostate may enlarge in males |
|
|
Urinary retention
|
• Person unable to void when an urge
Stasis may lead to infection May result in distended bladder Urine overflow may cause incontinence • Caused by stress, calculus, obstruction, stones, tumor, infection, medications, or trauma • Symptoms Frequency, voiding small amounts, and distended bladder • Treatment Urinary analgesics, antispasmodics, catheter, and surgey |
|
|
Urinary Incontinence
|
• Involuntary loss of urine from bladder
• Types Stress • Leakages of urine on straining Urge • Sudden need to urinate |
|
|
Nursing Management
Urinary Incontinence |
Affect self image
Bladder re-training every two hours Total = no urine can be re-tained Limited fluid intake for nocturnal enuresis Empty bladder before bed Keep perineum clean, dry and intact Kegel exercise Wake up and toilet training |
|
|
Surgey
|
After all this failed
Pelvic mesh |
|
|
What is Cystitis
( UTI) |
Information of urinary bladder
Caused by Escherichia Coli, Candida albicans, coitus ( sexual intercourse) prostatitis, and diabetes Mellitus Treatment Culture/ sensitivity testing, antimicrobial medication, and urinary tract analgesic Nursing management Increase fluid intake, acidic foods, and intake and output |
|
|
What is Pyelonphritis
|
Bacterial infection of the renal pelvis, tubules, and interstitial tissue of one or both kidneys
Also known as pyelitis or nephropyelitis Treat to prevent from becoming chronic |
|
|
Form of infection/inflammation
|
Upper UTI or lower UTI
Bacteria, E. coli UA testing Clean catch specimen Don't treat client before you sent the culture to the lab Keflex is the only one that pregnant women can take Prevent dehydration Maintain fluid and electrolyte balance Voiding after sex |
|
|
Upper UTI
|
Bacteria generally ascend from the upper urinary bladder through the ureter and enter the kidneys in the renal pelvis
|
|
|
Pyelonephritis treatment
|
Urine culture/ sensitivity testing,
Antimicrobials , antipyretics , Increase fluids, intake and output, and daily weight Follow up appointment within 6 months Preventing from becoming chronic Nephrons units become inflamed if not treated urine will stop |
|
|
Acute Glomerulonephritis
|
Glomerulus within nephrons units becomes inflamed
Maybe bacterial or viral Treat to prevent renal complications, cardiac complications, and complications to cerebral functioning Treatment Drug therapy Fluid restrictions Monitor labs I & O Bed rest Vital signs |
|
|
Chronic Glomerulonephritis
|
Slow progressive, destructive process affecting glomeruli
Cause loss of kidney function Treat to prevent further renal damage and cardiac complications |
|
|
Fluid over load
|
Leads to permanent kidney damage often masks symptoms
Is a slowly progressive destructive disease |
|
|
Urinary Calculi
|
Calculus or stone
Formed in the urinary tract Very small calculi maybe flushed out by peristalsis and fluids All urine must be strained, stones collected and sent to the lab for composition |
|
|
Who is at a greater risk
|
People who don't move around
Must strain their urine for 24 hours Pending on the size and shape |
|
|
What color do Pyridium
change clients urine |
Red-Orange color
|
|
|
What is the most common incontinence
|
•Urge incontinence
Occur when a person is unable to suppress the sudden urge to urinate Leaking without warning Irritated bladder Infection Concentrated urine |
|
|
Treatment if present
|
Clearing up infection
Encouraging Fluid intake 3,000 ml per day |
|
|
What is overflow incontinence
|
The bladder becomes so full and distended causing urine to leak out
Occurs when a blocked uretha or bladder weakness prevent normal emptying Enlarged prostate |
|
|
Maybe indicative of
|
People that are diabetic
Drink large quantities of alcohol And have decreased nerve function Bladder re-training may alleviate the problem |
|
|
Nursing management
|
Identify impaired urinary elimination based on subjective and objective data
Assess vital signs Encourage adequate fluid intake Teach kegel exercises Initiate bladder re-training |
|
|
Chronic renal failure causes
|
Diabetes
Hypertension Glomerulonephritis |
|
|
What is acute Renal failure
|
The rapid deterioration of renal function with rising blood levels of urea and other nitrogenous waste
|
|
|
Kidney transplantation
|
Must be tissue and blood type to determine compatibility
Donor kidneys can be preserved 36 hours in solution Or up to 72 hours if attached to irrigating pump Client is placed on bed rest Nursing management Monitoring urine output Blood test Vital signs Level of consciousness Encourage turning Coughing Deep breathing Assess the incision to ensure that wound closure is intact Assess for rejection |
|
|
Organ rejection
|
Signs of rejection
Generalized edema Tenderness over graft site Fever Decreased urine output Hematuria Edema Weight gain Oliguria or Anuria Increase in tired feeling Bun and Creatinine elevated |
|
|
Drugs used in organ rejection
|
Immunosuppressive drug therapy
Azathioprine ( imuran) Cyclophosphamide ( cytoxan) Cyclosporine ( sandimmune) Corticosteroids such as prednisone ( meticoryen) |
|
|
Complications from organ rejection
|
The greatest complication in renal transplantation is infection
Immunosuppressive therapy to prevent rejection increases the risk and mask the signs and symptoms of infection Slightly increase in temperature Cough Low back pain Cloudy urine Wound drainage Always monitor iron out put |
|
|
Dialysis
|
A mechanical means of removing nitrogenous waste from the blood by imitating the function of the nephrons
|
|
|
Dialysate
|
Is a solution designed to approximate the normal electrolyte structure of plasma and extracellular fluid
|

