![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
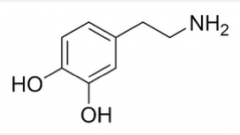
|
Dopamine |
|
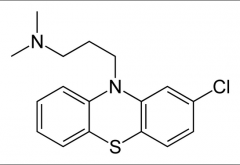
On all: Name, class, efficacy, side effects.
For this one? important considerations for SAR (3) |
Chlorpromazine: Benzodioxane (Antihistamine) Efficacy due to potent D2 receptor antagonism EPS, sedative and hypotensive side effects
3 carbon linker necessary, Tertiary amine is necessary, Cl leads to interaction with side chain that allows appropriate conformation |
|
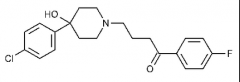
Important SAR points on the skeleton? (3) |
Haloperidol D2 affinity: Potent 5-HT2A affinity: moderate Severe EPS and TD associated Produces a toxic electrophylic by-product (MPTP) F gives enhanced activity, ketone is essential, linear propyl chain connecting two parts is optimal, variations are possible on the alpha end of the butyrophenone linker |
|
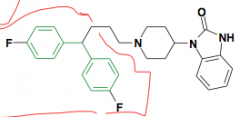
Name? New moiety possible?
|
Pimozide Added diphenylmethane moiety from haloperidol Schizophrenia and Tourette's Syndrome |
|
|
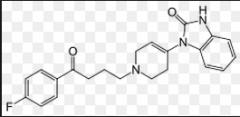
Droperidol same as above |
|
|
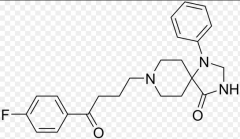
Spiperone Same as above
Rest are atypical antipsychotics |
|
|
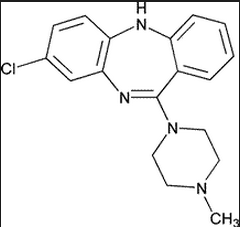
Clozapine Benzazepine Positive and negative effects D2 activity: Moderate 5HT2A activity: Potent antagonism, greatly reduced EPS and TD Major lethal side effect is agranulocytosis - lowered white blood cell counts and increased infections Causes significant weight gain due to 5HT2C activity |
|
|
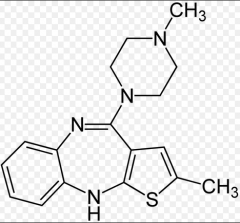
Olanzapine Thienobenzazepine Positive and negative symptoms D2 affinity: moderate 5-HT2A affinity: potent ADE: hyperglycemia, diabetes |
|
|
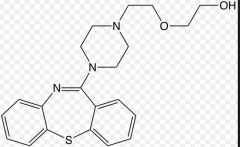
Quetiapine Dibenzothiazepine Positive and negative symptoms D2 affinity: moderate 5-HT2A affinity: potent 100% bioavailable Low tendency to cause seizures relative to other benzazepines Lower weight gain |
|
|
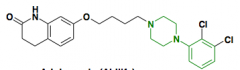
Risperidone Benzisoxale Positive and negative symptoms D2 affinity: moderate 5-HT2A affinity: potent Pro: Only slight weight gain Con: Loss of libido
|
|
|
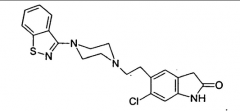
Ziprasidone Benzthiazone Positive and negative symptoms D2 affinity: moderate 5-HT2A affinity: potent Pro: Only slight weight gain Con: Prolongation of QT interval and thus possible onset of ventricular arrhythmias |
|
|
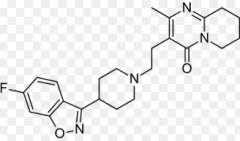
Aripiprazole Arylpiperazine Positive and negative symptoms D2 affinity: moderate 5-HT2A affinity: potent MOA: Partial agonism of D2 autoreceptors Weak antagonist of postsynaptic D2 receptors Partial agonist at the 5HT1A receptor 5-HT2A receptor antagonist Moderate affinity for histamine and alpha-adrenergic receptors
Superior side effect profile: Pros: Only slight weight gain, lower incidence of Type 2 diabetes, No indication of onset of ventricular arrhythmias, no loss of libido, <10% incidence of fatigue
Additional indication for bipolar disorder as well |
|
|
Antiparkinson's drugs |
- |
|
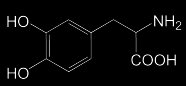
|
Levodopa Dopamine-binding prodrug bioactivated by DDC
|
|
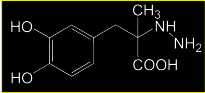
Reversible or irreversible inhibitor?? |
S(-)Carbidopa A hydrazine-based DDC inhibitor that prevents conversion of L-DOPA to DA in the periphery. Carbidopa does not cross the BBB It is a substrate analog that irreversibly inactivates DDC in the periphery Sinemet is form (comes in 1:10 ratio) |
|
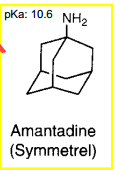
|
Amantadine Multiple effects including enhancing release of DA from neurons and delaying reuptake |
|
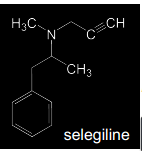
Reversible or irreversible?? |
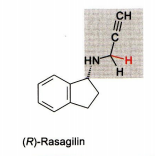
Selegiline Irreversible** MAO-B specific inhibitor Methamphetamine prodrug (CYP N-dealkylated to methamphetamine > indirect inhibition of DA reuptake) - Reverses direction of flow with neurotransmitters released from vesicles into synaptic cleft The propargylamine-derivatives selegiline and Rasagiline are mechanism based inhibitors that inactivate MAO-B through covalent adduction. The adducted target molecule is the FAD-coenzyme moiety of the enzyme |
|
|
Rasegaline Same MOA, but not prodrug |
|
Reversible or irreversible drugs? |
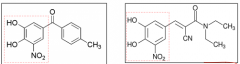
Tolcapone, entacopone Reversible inhibitors of COMT >>>> prolonged activity of levodopa and dopamine PD treatment as adjunct to levodopa/carbidopa medication Side effects: involuntary movements and diarrhea Hepatotoxicity (tolcapone) >> entacapone, for L-DOPA adjunct therapy with better toxicity profile Entacopone: Inhibition of peripheral COMT only. Tolcapone: Poth peripheral and CNS COMT action |
|
|
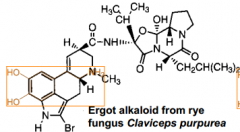
Bromocriptine
Ergot alkaloid that can mimic dopamine |
|
|
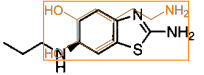
Ropinirole |
|
|
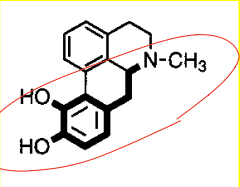
Pergolide
|
|
|
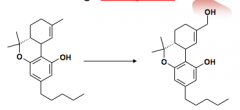
(S)-Pramipexole |
|
|
apomorphine Rigid conformer as potent agonist** (trans rotamer) Apomorphine is lipophilic enough to pass BBB (However), undergoes significant first-pass metabolism and elicits severe side effects |
|
|
Hallucinogens and drugs of abuse |
- |
|
|
Preferred physicochemical property ranges for increasing potential for BBB penetration
PSA HBD cLogP cLogD MW |
PSA: <70 HBD: 0-1 cLogP: 2-4 cLogD: 2-4 MW: <450 |
|
|
Non-classical hallucinogens: Classical hallucinogens
Central stimulants: Designer drugs |
NC: Cannabinoids, PCP related C: Indolealkylamines, Phenylalkylamines
CS: Amphetamine related, cocaine related DD: ecstacy |
|
|
THC (active ingredient) -> 11-hydroxy THC (major metabolic product)
MOA: CB1 agonism Ind: Pain management in several states Metabolism: Opened B segment does not affect THC-like activity. AHH (aromatic, hydrophobe, hydrophobe) pharmacophore |
|
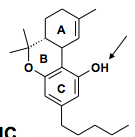
Donor or acceptor? CB1 or CB2 selective? |
Both Both So the phenolic hydroxyl behaves as a donor |
|
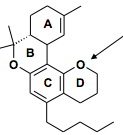
Donor or acceptor CB1 or CB2 selective? |
Acceptor CB2 selective |
|
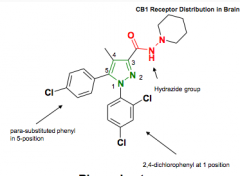
Agonist or antagonist? Protein bound? Side effects? Groups? |
Rimonabant Selective CB1 antagonist 100% protein bound Side effects opposite to benefits ~ depression Pyrazole with attached hydrazide functionality |
|
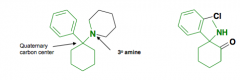
|
Phencyclidine (PCP) and Ketamine (Special K) PCP antagonizes the effects of NMDA at it's ion channel receptor |
|
|
Major sites of metabolism? Role of hydroxyl group for CB1 agonism? How was this determined? What ring can be opened with retention of CB1 activity? Pharmacology behind rimonabant? |
1. Opening of B ring 2. Hydrogen bond donor 3. Removal of the hydrogen bond donor by introducing a 4th ring conferred with the hydroxyl group 4. B ring 5. CB1 antagonist |
|
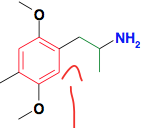
|
Classical Phenylalkylamines This one is "Phenisopropylamine" (DOM) 5-HT2A agonist Slow onset of action |
|
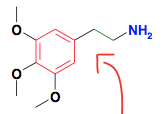
|
Classical Phenylalkylamines This one is "Phenethylamine" (Mescaline) 5-HT2A agonist Slow onset of action |
|
|
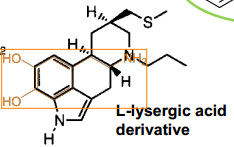
L-Lysergic acid (LSD) |
|
|
Central stimulants |
- |
|

|
Amphetamine and methamphetamine Inhibition of DAT (promotes DA release) Contrast with Cocaine, which inhibits reuptake |
|
|
Ritalin ADD |
|
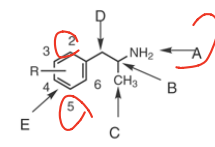
SAR of phenylisopropylamines |
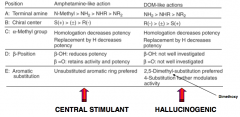
|
|
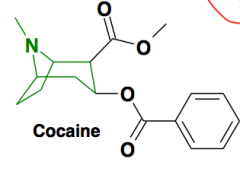
Chemical structure highlighted? |
Tropane: Central stimulant nature related to NET, DAT blockage T1/2 = one hour
|
|
|
Granisetron Weak 5HT3 activity (antagonist) CINV |
|
|
Triple reuptake inhibitor designed from methamphetamine |
|
|
Tranylcypromine (parnate) |
|
|
Key points:
1. What structural evidence suggests LSD acts on the serotonin receptors?
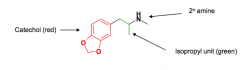
2. MDMA or ADAM contains three key structural motifs?
3. Chemical modification of the simple phenylisopropylamine substructure enables control of two drugs of abuse effects?
4. The central stimulant properties of phenylisopropylamines are enhanced by? |
1. LSD contains a serotonin pharmacophore
2. 1)Secondary amine, 2) isopropyl unit, 3) catechol
3. Central stimulant and hallucinogenic
4. N-methylation and unsubstituted phenyl ring |
|
|
PDE inhibitors |
-- |
|
|
What function does PDE4 have?
What function does PDE5 have? |
PDE4 is cAMP specific and has function for auto-immune disease PDE-5 carries out the principal cGMP-hydrolysing activity in the human corpus cavernosum tissue
This is following the actions of cyclase to create the cyclic structure with phosphate
|
|
|
Binding of endogenous substrates: What amino acid binds guanine for the substrate?
|
Glutamine |
|
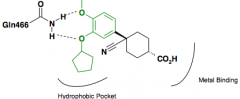
|
Cilomilast Reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-a targets Catechol interacts in a Bidentate fashion with Gln |
|
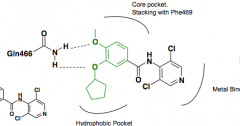
|
Piclamilast Reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-a targets Catechol interacts in a Bidentate fashion with Gln |
|
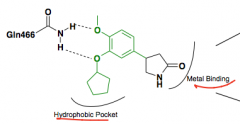
What was the problem with high affinity binding site? |
Rolipram Causes N&V |
|
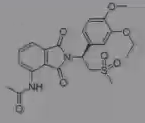
|
Apremilast Psoriatic arthritis Catechol binds invariant glutamine Metal binding region |
|
|
Where does cGMP-specific PDE5 exert it's effects? |
Human corpus cavernosum tissue |
|
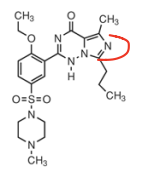
|
Vardenafil |
|
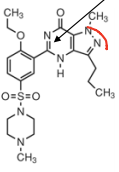
|
Sildenafil |
|
|
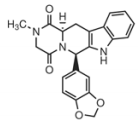
Tadalafil Notice this structure is very different |
|
|
What is the number one cause of ED? |
Vascular damage |
|
|
In terms of selectivity, how does sildenafil compare to it's precursor molecule zaprinast? |
More selective for PDE5 |
|
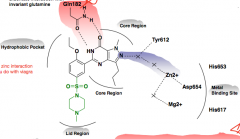
Describe binding sites for sildenafil |
1) Hydrophobic pocket 2) lid 3) Core 4) metal binding site |
|
|
What is the pharmacology behind the side effect of seeing blue in sildenafil? |
inhibition of PDE6 in the eye, affecting rhodopsin |
|
|
What amino acid couples the reation between sildenafi and zinc? |
tyrosine |
|
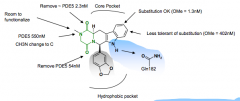
What kind of molecule is tadalafil? How is invariant glutamine engaged? What can replace DKP? Any Lid or metal binding? |
Diketopiperazine Invar. glutamine engaged via monodentate interaction Removed with other heterocycles No Lid or metal binding |
|
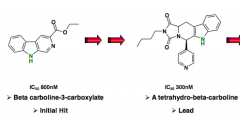
|
Precursor for tadalafil |
|
|
Does tadalafil have the same side effect profile as viagra? Half life better? |
No, it is better. More selective for PDE5 over other PDEs than Viagra Longer half-life than other drugs |
|
|
Anticholinergic drugs as modulators of dopamine in parkinsonism:
|
Central anti-muscarinics are useful as adjunct therapy because they can enhance motor cortex activation in parkinsonism |
|
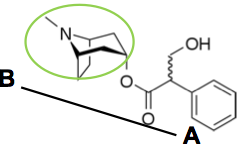
Name? Structure? Use? |
Atropine Benzenacetic acid A tropane: note structure resemplance to cocaine Muscarinic receptor antagonist Alleviate effects of Ach neurotransmission |
|
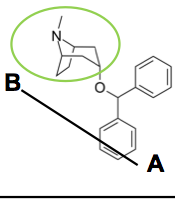
|
Benztropine Second line treatment for PD Improves tremor |
|
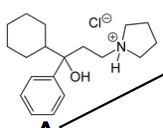
|
Procyclidine Second line for PD Improves tremor |
|
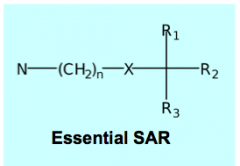
|
X = ester or ether oxygen N = quaternary ammonium salt or tertiary amine. Note exception to rule for BBB penetration R1, R2 = aromatic or heterocyclic rings for maximal antagonist potency R3 = H, OH, CH2OH, or part of R1/R2 ring systems |

