![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
118 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
NSAIDS |
•Inhibitcyclooxygenases (COX1 & COX2) •Anti-inflammatory:inhibit COX2 •Inhibitionof COX1 can lead to adverse effects •MostNSAIDs are NOT selective |
|
|
Prostaglandin D2 |
inflammatory |
|
|
Prostaglandin E2 |
Fever |
|
|
Prostacyclin |
inhibits platelet activation in endothelial cells |
|
|
Thromboxane |
facilitates platelet activation in platelets |
|
|
COX Selectivity |
convert arachidonic acid to prostaglandins, prostacyclin and thromboxane |
|
|
COX 1 |
-constitutive -protect stomach lining -blood coagulation |
|
|
COX2 |
-inflammatory processes -anti thrombotic -constitutively present in heart and kidney |
|
|
NSAIDs |
-acidic, pKa = 3-4 -form in the stomach is unionized -rate of absorption = faster in stomach than intestine -carboxylic acid <--> carboxylate |
|
|
Salicylates |
-competitive inhibitor |
|
|
Salicylic Acid |
occurs naturally in willow bark |
|
|
Diflunisal |
Longer half-life than aspirin |
|
|
Aspirin |
-acylates a serine -covalently attaches -inactivates and irreversible inhibitor |
|
|
Phenyalkanoic Acids |
-competitive inhibitors of COX |
|
|
Arylalkanoic Acid |
Elimination half-life > 24 hr |
|
|
Nabumetone |
-prodrug
-metabolic activation -reduced liver function |
|

|
-OH group and sulfonamide -elimination half life > 24 hr |
|

|
-OH group and sulfonamide |
|
|
Oxicams |
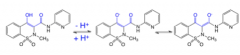
-have an acidic enol -pKa = 4-5 |
|
|
Celecoxib |
-highly selective for COX2 -sulfonamide group |
|
|
Acetaminophen |
-analgesic -not anti-inflammatory |
|
|
Acetaminophen toxicity |
-overdose leads to liver damage -treatment = n-acetyl-cysteine |
|
|
Plasma Protein Binding |
all NSAIDs are highly bound to plasma proteins, especially serum albumin |
|
|
DMARDs |
-immunomodulators which slow progression, don't treat acute -delayed onset -dangerous adverse effects |
|
|
Methotrexate |
-antifolate -folic acid = cell replication -chemotherapeutic agent -action on lymphocytes -contraindicated in pregnancy -transported by OAT3 -source of drug interactions |
|
|
Cyclosporine |
-immunosuppresant -organ transplantation and autoimmune diseases -effect T cells (immune system) -suppress IL2 -hydrophobic, not water soluble |
|
|
Azathioprine |
-immunosuppresant -organ transplantation and autoimmune disease -prodrug = 6-mercaptopurine -serious adverse effects -6 MP metabolism (slow metabolizers) |
|
|
Sulfasalazine |
-Gl bacteria metabolize to sulfapyridine and 5-aminosalicylic acid -COX inhibitor and antifolate - GI symptoms and neutropenia (decrease in neutrophils) |
|
|
TNF-Alpha |
-regulates immune cells -induce fever, apoptosis, inflammation -autoimmune diseases (ex. RA) -infectious diseases -cancer cells |
|
|
Adalimumab |
-monoclonal human -mab = monoclonal antibody -subcutaneous injection |
|
|
Infliximab |
-monoclonal chimeric -intravenous injection |
|
|
TNF receptor |
-death receptor -membrane bound and soluble -forms soluble form as a decoy |
|
|
Etancercept |
-fusion protein -combines soluble TNF receptor 2 with constant end of human Ab -long half life in circulation -subcutaneous injection |
|
|
Penicillin |
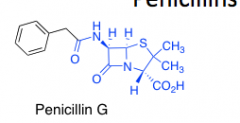
-highly reactive -covalently attaches -5 membered ring |
|
|
Cephalosporins |
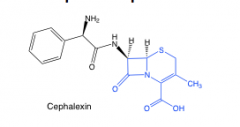
6-membered ring |
|
|
Carbapenems |
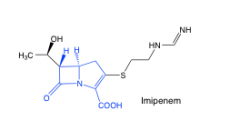
looks like penicillin with no sulfur in 5 membered ring |
|
|
Monobactams |

|
|
|
B-lactamse & Inhibitors |
-hydrolyze the lactic - co-adminster a lactase inhibitor |
|
|
Bacitracin |
-cyclic peptides that inhibit cell wall synthesis -topically |
|
|
Streptogramins |
-pairs that bing to bacterial ribosomes and block protein synthesis -synergistic activity -depsipeptides (lactam/lactone) |
|
|
Oxazolidinones |
-binds to bacterial ribosome -inhibits protein synthesis |
|
|
Macrolides/Ketolides |
-bind to bacterial ribosome, 50S subunit -inhibit protein synthesis -lactones (cyclic esters) |
|
|
Lincosamides |
-bind to bacterial ribosome -inhibit protein synthesis |
|
|
Aminoglycosides |
-aminosugars -cationic -poor oral absorption -rapid renal excretion -block bacterial protein synthesis |
|
|
Tetracyclines |
-inhibit protein synthesis -acidic enols, pKa = 3 & 7 -basic amine, pKa = 9 |
|
|
Glycylcycline
|

|
|
|
Tetracycline effects |
-chelates CA -affects GI absorption and teeth |
|
|
Chloramphenicol |
-nitro compound -one stereoisomer produced -binds bacterial ribosome -inhibits protein synthesis |
|
|
Folic Acid Metabolism Inhibitors |
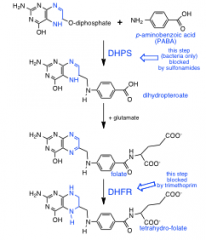
-synergistic combo (sulfonamides/trimethoprim) |
|
|
Sulfonamides |
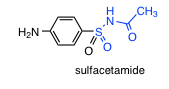
-inhibit dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS) |
|
|
Trimethoprim |
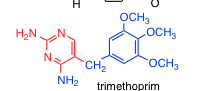
-inhibits dihydrofolate reductase -100,000x better at inhibiting bacterial DHFR than human THFR |
|
|
DNA Replication/Transcription Inhibitors |
-inhibit DNA gyrase/DNA topoisomerase -prevent or alleviate DNA tangles -inhibition leads to DNA damage and cell death -selective for bacterial forms |
|
|
Fluoroquinolones |
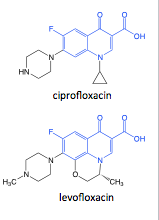
-fluorine boosted potency, broader spectrum -note acidic and basic functional groups on ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin -levofloxacin = single stereoisomer ciprfloxacin levofloxacin |
|
|
Urinary Tract Antiseptics and Topicals |
-pharmacokinetic properties -rapidly absorbed and excreted in urine are urinary antiseptics -those not absorbed = use topical |
|
|
Nitrofurantoin |
-reduce nitro in which radical non-selectively damages -crystal form and particle size effect bioavailability and pharmacokinetics -weak acid |
|
|
Methenamine |
-slow at neutral pH, much faster in acid -oral absorption -in acidic prince, formaldehyde formed (CH2=O) -ammonia --> urea -contraindicated in patients with liver disease |
|
|
Metronidazole |
-reduce nitro group to non-selectively damage |
|
|
Mupirocin |
-not well absorbed -metabolized/inactivated by ester hydrolysis -topical only -bacterial isoleucine tRNA synthetase, prevents protein synthesis |
|
|
Polymyxins |
-detergents that disrupt cell membranes -topical only |
|
|
Isoniazid |
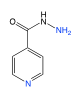
-pyridine N and -NHA are weak bases, pKa = 2-3 -prodrug converted in mycobacteria and not humans to reactive radical -pyridoxal (vitamin B6) function -prevent with vitamin B6 supplementation |
|
|
Rifampin |
-semi-synthetic -inhibits RNA polymerase -highly acidic phenols (pKa = 2) -basic piperazine (pKa = 8) -red orange color |
|
|
Pyrazinamide |
-nicotinamide -hydrolyzed to pyrazinoic acid, which may be active agent -MOA unknown |
|
|
Ethambutol |
-there stereoisomers -cell wall synthesis inhibitor |
|
|
Streptomycin |
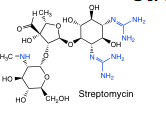
-aminolglycoside -basic -binds to ribosome -inhibit protein synthesis |
|
|
Bedaquiline |
-MDR-TB and XDR-TB -2 chiral centers -4 stereoisomers -sold as single stereoisomer -targets ATP synthesis |
|
|
Dapsone |
-inhibits dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS) in folate pathway -sulfone = electron - withdrawing -amine pKa = 1 |
|
|
Clofazimine |
-poor water solubility -high fat solubility -bioavailability -discolors eye |
|
|
Acyclovir and Valacyclovir |
-analog of guanosine, breaks DNA chain -Valacyclovir is prodrug with L-valine -taken up by transporters for better bioavailability |
|
|
Ganciclovir |
-has 3'-OH but poor substrate -Valganciclovir = prodrug with improved bioavailability |
|
|
Foscarnet |
-poor oral absorption -IV -inhibits viral DNA polymerase -in HIV, inhibits reverse transcriptase |
|
|
Trifluridine |
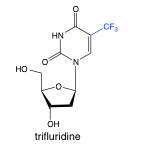
-analog of thymidine -converted to monophosphate, inhibits thymidyalte synthase -converted to triphosphate, inhibits thymidine incorporation -not absorbed orally -topical |
|
|
Amantadine/Rimantidine |
-block an ion channel -resistance |
|
|
Zanamivir |
-analog of sialic acid -inhibits neuraminidase -cleave of sialic acid giving better access to host -charged and polar functional groups -poor oral absorption -give by inhalation |
|
|
Oseltamivir |
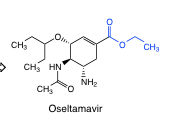
-neuraminidase inhibitor
-orally active -prodrug = hydrolysis of ester |
|
|
interferons |
-a,b,g -cytokines = modulate immune function -proteins not absorbed orally, injected -recombinant, natural, pegylated |
|
|
Ribavbirin |
-nucleoside analog -inhibits viral mRNA -orally, inhalation, injection |
|
|
HIV
|
-RNA virus -viral reverse transcriptase makes DNA copy -inhibition of viral RT |
|
|
NRTIs |
-phophorylated -inhibit viral RT -low affinity for host -inserted by RT -terminate chain |
|

|
cytidine analog (NRTI)
|
|

|
cytidine analog (NRTI) |
|

|
adenosine analog (NRTI) |
|

|
thymidine analog (NRTI) |
|
|
NNRTIs |
-not nucleoside/nucleotide analogs -binding at allosteric site -non-competitive inhibitors |
|
|
Protease Specificity - scissile bond |

|
|
|
-CH(OH)-N- |
-transition state analog |
|
|
HIV Protease Inhibitors - Ritonavir |
-CYP3A4 inhibitors -enhances activity of other HIV-PIs |
|
|
Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibition |
-DNA (reverse transcriptase) -uses integrate -integrase blocked viral DNA is degraded -drugs block the strand transfer step |
|
|
Integrase Inhibitors |
-requires Zn++, Mg++, Mn++ -all are acidic -ionized inhibitors may chelate |
|
|
Why is ergosterol a good target? |
-specific to fungi
-reguired membrane function and integrity |
|
|
Azoles
|
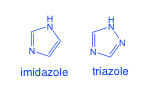
-5 membered aromatic ring with atleast 1 nitrogen
-feature imidazole and triazole rings -inhibit synthesis of ergosterol |
|
|
Fluconazole |
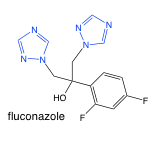
-triazole |
|
|
Voriconazole |
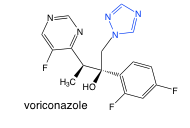
-triazole -sold as single stereoisomer |
|
|
Ketoconazole |
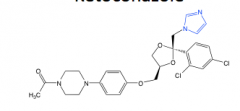
-imidazole -suppresses corticosteroid synthesis -use topically -sold as mixture of two stereoisomers |
|
|
Amphotericin B |
-parenteral administration -formulation affects pharmacokinetics and dosage -inserts in membranes and disrupts them -high affinity for membranes with ergosterol |
|
|
antimetabolite: flucytosine |
-prodrug = 5-flurouracil -further converted to thymidylate synthase inhibitor -used to make thymine, for DNA synthesis -chemotherapeutic agent -humans lack the enzyme to convert |
|
|
echinocandins |
-inhibit cell wall production -lipopeptide |
|
|
Griseofulvin |
-antimitoic (binds to tubulin) -almost no water solubility -enters keratin precursor cells -prevents fungal growth |
|
|
Terbinafine |
-squalene epoxidase for ergosterol -depletes ergosterol -causes accumulation of squalene to toxic levels |
|
|
Quinine |
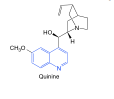
-extracted from cinchona bark -contains quinoline ring |
|
|
Quinidine |
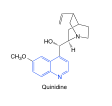
-antiarrhythmic activity -leads to quinacrine and other 4-amino-quinolines |
|
|
Chloroquine |
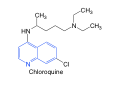
-4 amino quinoline -prevention of heme detoxification |
|
|
Mefloquine |
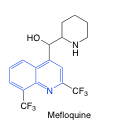
-another quinoline -2 chiral centers -4 stereoisomers -commercial product = mixture of two -bound to plasma proteins, half life of 13-24 days |
|
|
Primaquine |
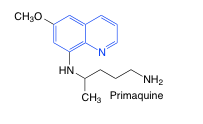
-8-aminoquinoline -oxidation reduction rxns -G6PD deficiency may suffer hemolytic anemia |
|
|
Pyrimethamine |
-antifolate -selective for Su reductase -DHFR inhibitor paired with DHPS inhibitor, sulfadoxine -ionizable groups = sulfonamides |
|
|
Artemisinins |
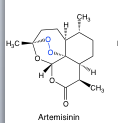
-natural product and semi-synthetic derivatives
-lactone (improve stability) - endoperoxide -MOA: oxidation |
|
|
Suramin |
-parasite takes up drug by endocytosis -acidic sulonic acid groups -MW = 1492, net charge -6, not absorbed orally, injected, won't cross BBB ->99% bound to plasma proteins |
|
|
Eflonithine |
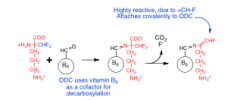
-polyamines help pack DNA -ornithine decarboxylase (target) -eflornitine = suicide inhibitor and enters CNS |
|
|
Nifurtimox |
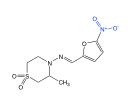
-reactive nitro radial causes nonspecific damage |
|
|
Arsenicals |
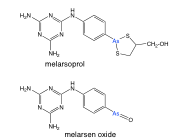
-melarsoprol = prodrug -melarsen oxide = active form -thiol groups -toxic to parasite and human |
|
|
Anti-Leishmanial Drugs |
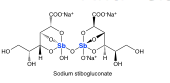
-Sb = antimony (pentavalent) -not absorbed orally |
|
|
Metronidazole |
-reduce nitro group -non-selective damage |
|
|
Iodoquinol |
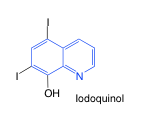
-quinoline derivative -poorly absorbed (~10%) -used as luminal amebicide -weak acid |
|
|
Paramomycin |
-aminoglycoside -inhibits protein synthesis -lots of + charge, not absorbed orally -oral for GI protozoa -give parenteral -topical |
|
|
Nitazoxanide |
-prodrug metabolized by hydrolysis to tizoxanide -tizoxanide = disrupts energy metabolism |
|
|
pyrantel |
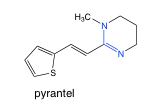
-amidine -pKa = 12 -pamoate salt = poorly soluble -stays in GI tract, mimics acetylcholine, inhibits acetylcholinesterase, paralyzes worms |
|
|
Piperazine |
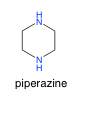
-Dibasic -Activates GABA gated chloride ion channels -leads to flaccid paralysis of worms |
|
|
Albendazole, Mebendazole |
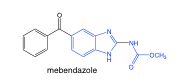
-these bezimidazoles are poorly absorbed, remain largely in GI -albendazole rapidly metabolized to active sulfide -inhibit tubulin polymerization in worms |
|
|
Praziquantel |
-No ionizable groups -paralysis of worms -damages outer covering of worms (tegument) -exposes antigens for immune system |

