![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe the 6 examination methods used by physicians |
1. Inspection (visual exam) 2. Palpation (hands to feel) 3. Percussion (tapping) 4. Auscultation (listening) 5. Mensuration (measuring) 6. Manipulation (assess range of motion) |
|
|
Patient exam positions |
1. Dorsal recumbent (laying flat) 2.lithotomy (laying flat with legs up) 3.fowler and semi (sitting up at an angle) 4.prone (laying on stomach) 5.sims (lay on stomach one knee & arm bent) 6. Knee chest (laying on stomach with hips bent and butt raised) 7. Trendelenburg (head and feet inverted) 8.sitting 9.jackknife (hips at hinge of bed) |
|
|
Biopsy is... |
A removal of a piece of tissue |
|
|
Incision and drainage is... |
Making an incision to create an opening for draining of material |
|
|
Malignant means |
Cancerous |
|
|
Debridement is... |
Removal of dead tissue |
|
|
Angioplasty is... |
Surgical procedure that alters the structure of a vessel by using a balloon inside the vessel. |
|
|
What is diaphoresis |
Excessive sweating |
|
|
Hemoglobin a 1 c test for? |
Tests blood glucose over a 3 month period. |
|
|
Fasting glucose tests for... |
It is a blood test to measure e the amount of glucose in the body after fasting for 12 hours |
|
|
What is the blood chemistry profile? |
Panel of chemistry tests that gives an overview of patients body and is less expensive than individual tests |
|
|
What is the sma 12 or Chem 12? |
It is a panel of 12 chemistry tests |
|
|
What is the sma or Chem 20? |
Panel of 20 tests |
|
|
What is a complete blood count or cbc? |
Includes rbc count, wbc count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, platelets, and differential. |
|
|
Pulmonary function test is? |
Determines respiratory function by measuring lung volume and gas exchange. |
|
|
What is sedimentation rate? |
Measures the rate at which rbc settle out of blood in one hour. |
|
|
Review of systems |
After the physician discusses past medical history, chief complaint, present illness, and then do a complete head to toe exam that evaluates all body systems. |
|
|
What is occult in reference to stool specimens |
Hidden blood in feces that may indicate bleeding in the GI tract |
|
|
Ways to promote open ended communication when charting in the patients record? |
Ask questions like when did start and carefully document exact locations of pain. |
|
|
How are pap specimens graded? |
Dry specimens are made on slides and labeled c, v, and e then sprayed with a fixative. Liquid based are swirled in a liquid by using a brush. |
|
|
Follow up prenatal appointments occur when? |
Every 4 weeks through 28th week Every 2 weeks through 30th week Every week til birth |
|
|
Gravid a means... |
Total number of pregnancies |
|
|
Para means... |
Birth after 20 weeks regardless of dead or alive |
|
|
Abortion means... |
Number of fetus that did not reach viability includes miscarriage |
|
|
Explain Nagel rule |
Lmp + 7days - 3 months + 1 year= edd |
|
|
Alphafetoprotein tests for... |
Neural tube defects between 15th and 18th week |
|
|
Amniocentesis tests for... |
Takes a sample of amniotic fluid between 15th and 20th week and detects syndrome, gender, & development. |
|
|
What is placenta previa? |
Placenta develops in lower portion of uteris. |
|
|
Abruptio placenta |
Placenta tears away from uterine wall. |
|
|
Preclampsia |
Elevated blood pressure occurs And blood flow to placenta is compromised. If seizures occur it is known as eclampsia. |
|
|
List and describe types of sti |
1. Bacterial vaginosis - no known cause, gray or white discharge. 2 . chlamydia- may lead to pelvic inflammatory disease And increased risk of ectopic pregnancy is a parasite. 3 . genital herpes- no cure, painful lesions. 4.hpv- common and is a group of viruses with genital warts. 5. Gonorrhea - caused by bacterium news serial gonorrhea 6.hiv- causes aids 7. Pid - can be cured by antibiotics but not damage done. 8.Syphilis- spread by direct contact, sores 9.trichomoniasis- protozoa caused by trichomniasis vaginalis. |
|
|
What is the function of the urinary system? |
To filter and remove metabolic waste products from the blood, help maintain electrolyte and pH balance, excrete waste, and regulate rbc production and blood pressure |
|
|
Causes of lack of bladder control |
Poor muscle control, trauma, or improper placement of organs. |
|
|
What is myopia |
Nearsightedness, eye can only see near objects well. Light rays do not reach the retina. A concave lens is required to correct |
|
|
What is heropia |
Farsightedness, eyes can see far objects better. Light rays focus behind the retina. Conover lens is needed to correct. |
|
|
What is presbyopia |
Farsightedness with aging |
|
|
What ia strabismus |
Eye disorder caused by weak eye muscles where double vision occurs and person appears cross eyed. |
|
|
What does snellen chart measure |
Distance acuity. |
|
|
What does the Ishihara test measure? |
Color vision |
|
|
What does the Jaeger test measure |
Near vision |
|
|
What does the Pelli Robson test measure? |
Contrast sensitivity |
|
|
Give procedure for irrigating the eye... |
Have patient tilt head, hold a basin below, place tissue below eye, open eye with index finger and thumv, expose conjunctiva, irrigate from inner to outer corners of eye. |
|
|
What are some age related changes to the eye |
Eyelids droop, cornea develops a ring of fat, tears decrease, night vision impaired, & floaters occur |
|
|
Causes of blindness |
Accident, birth defect, blind since birth, and injury |
|
|
2 types of hearing loss |
1. Sensorineural (nerve damage) 2.conduction (obstruction of sounds waves) |
|
|
Explain irrigation of the ear procedure |
Have patient tilt head, place a towel on shoulder , clean external ear , fill basin with warm water, for adults pull ear up and back and children down and back. Pour water into canal from syringe until return is clear. |
|
|
Review development skills from birth to 5 years |

|
|
|
Distinguish between 3 eating disorders |
Anorexia (purging) Bulimia (binging) Not other wise specified (doesn't fit in a category) |
|
|
Physical changes of aging include... |
1. Integumentary ( wrinkles, easy bruising, sensitive to cold, age spots, and nails thicken) 2. Nervous (balance & temperature regulation inconsistent) 3.sensory (cataracts and night vision decrease) 4.muscle strength lessens and movement slower 5 . respiratory (breathing capacity lessens) |
|
|
Explain surgical asepsis versus medical asepsis |

Sterile with no microorganisms versus clean and controls microorganisms |
|
|
Ten conditions that cause body temperature to increase or decrease |
Time of day, age, gender, exercise, emotion, pregnancy, environment, infection, drug, and food |
|
|
List the 9 pulse sites |
Radial (wrist), brachial (antecubital space of elbow), carotid (neck), temporal ( abovd ear), femoral (groin), politeal (behind knee), posterior tibial (ankle), dorsal pedis (top of foot), & apical (left of sternum at apex of heart) |
|
|
List the five phases of korotkoff sounds |

1. Sharp tapping 2. whoosh sound 3. Soft thump 4. Fading sound that fades 5. Silence |
|
|
Physiological factors that affect blood pressure |
Volume of blood, peripheral resistance, condition of heart muscle, & elasticity of vessels |
|
|
Places for measuring body temperature |
Oral, rectal, axillary, tympanic, & temporal |
|
|
Factors that influence pulse rate |
Exerciae, age, gender, size, physical condition, disease condition, medication, depression, and fear/anger/anxiety |
|
|
What is the normal value for respiratory rate |
14 to 20 cycles per minute |
|
|
What is a normal pulse for an adult? |
60 to 80 bpm |
|
|
Types of clinical laboratories |
1.Outside laboratory is hospital bases or independent band less simple to complex specimens 2. reference lab is associated with a teaching hospitals. 3.physican office lab is right in the office. |
|
|
Whats a qualitative test |
Typically gives a result of positive or negative |
|
|
What's a quantitative test |
Gives a numerical value result. |
|
|
What is turnaround time |
How long it takes for the test to be preformed and the results to come back. |
|
|
Requisition is... |
A form that That provides essential information about the test ordered and how results will will be be reported and billed and coded |
|
|
What does clia stand for? |
Clinical laboratories improvement amendment. Developed by cm and are regulatory standards that labs that test human specimens must keep |
|
|
Clia waved tests are what? |
Tests that are simple and used to prevent and diagnose. A facility is required to have a waiver by cms that it's employees can preform these. |
|
|
What does postprandial mean? |
After a meal |
|
|
QNS stands for what? |
Quantity not sufficient. The required amount of a specimen was not met. |
|
|
What is a culture and sensitivity test? |
Also known as c &s. Preformed to determine what organisms are growing and what will effectively kill them. |
|
|
What does micturation mean? |
Urination |
|
|
What is clean catch? |
The preferred method of collecting a urinary specimen. Have patient wipe in one direction only to cleanse himself or herself, begin to urinate into toilet then void in the container not touching the inside of the container. |
|
|
Describe difference between polyurethane and oliguria. |
Poli Uriah is excessive amounts of urine and oliguria is decreased amounts of urine. |
|
|
What is point of cate testing? |
Tests that can be done during a physical exam or at the bwdaide. Example capillary stick. |
|
|
Identify sites for capillary puncture |
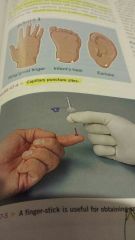
Ring and great finger, infant heal, & earlobe |
|
|
Explain the purpose of filling blood tube in the correct order |

To prevent contamination of the tube with skin bacteria or with an additive from another blood tube. |
|
|
Identify correct electrode placement for chest leads va to v6 |
V1- 4th intercostal space right sternum V2- 4th intercourse space left sternum V3- midway between V2 and v3 V4- 5th intercostal space mid clavicle V5- in line with V4 V6- in line with V4 mid axillary line |
|
|
Ekg /ecg represents what? |
Hearts electrical activity |
|
|
Explain the significance of each ecg/ekg wave... |

The cycle of the electrical impulses travels from atrial and ventricular depolarization to re polarization or contraction and relaxation and represent one heart beat. |
|
|
What are some causes of artifacts ? |
1. Somatic tremor (chills, discomfort, etc) 2. Wandering baseline (due to poor skin contact with sensors) 3. Ac interference (machine picks up electrical equipment in use) 4. Broken recording |

