![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gene - written
|
All caps and italicized
Numeric designations are on same line. Superscript letters are lower case. |
|
|
Antigen - written
|
Single letter: letter with + or -
Superscript: use parantheses Fy(a+) Numeric: Cap letter colon number K:1 if pos; K:-1 if neg HLA: number follows letter denoting series HLA-A1 |
|
|
Gene: A unit of inheritance within a chromsome
|
|
|
Phenotype
|
The outward expression of genes. On blood cells, serologically demonstrable antigens constitute the phenotype (except those sugar sites that are determined by transferases)
|
|
|
Genotype
|
An individual's genetic makeup
|
|
|
Allele
|
One of two or more genes on the same chromosome of an homologous pair. Example: A, B, O
|
|
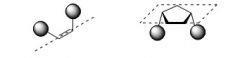
|
Cis - The location of two or more genes on the same chromosome of a homologous pair.
|
|
|
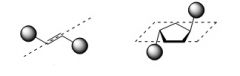
Trans - The location of two or more genes on opposite chromosomes of a homologous pair.
|
|
|
Amorph - define
|
A gene that does not appear to produce a detectable antigen; a silent gene such as Jk, Lu, O
|
|
|
Homozygous
|
possessing a pair of identical alleles
|
|
|
Heterozygous
|
possessing different alleles at a given gene locus
|
|
|
Hemizygous
|
an individual who has only one member of a chromosome pair or chromosome segment rather than the usual two; refers in particular to X-linked genes in males who under normal circumstances have only one X chromosome
|
|
|
Mitosis - define
|
The process where a single somatic cell divides resulting in generally two identical diploid cells, each containing the same number of chromosomes and genetic content as that of the original cell.
|
|
|
Mitosis - list phases
|
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
|
|
|
Polymorphic
|
Having two or more alleles at a given locus. Example: ABO system, HLA system
|
|
|
Co-dominant
|
Equal expression of both traits, most BGS have this inheritance
|
|
|
Dominant
|
Gene product expressed over another gene, only one copy of gene is needed for expression
|
|
|
Recessive
|
Observable product only when not paired with dominant allele, two copies are needed for expression
|
|
|
Trait appears in every generation with no "skipping"
|
Autosomal Dominant
|
|
|
Trait is transmitted by an affected person to approximately half of his children
|
Autosomal Dominant
|
|
|
Unaffected persons do not transmit the trait to their children
|
Autosomal Dominant
|
|
|
The occurrence and transmission of the trait are not influenced by sex
|
Autosomal Dominant or Autosomal Recessive
|
|
|
Trait characteristically appears only in sibs, not in parents, offspring or other relatives; skips generations
|
Autosomal Recessive
|
|
|
On average, 25% of sibs of the propositus are affected.
|
Autosomal Recessive
|
|
|
Parents of the child with trait may be consanguineous
|
Autosomal Recessive
|
|
|
Absence of father to son transmission
|
Sex-Linked Dominant and Sex-Linked Recessive: X-Linked
|
|
|
All daughters of a man expressing trait possess the allele and express the trait
|
Sex-Linked Dominant
|
|
|
Children of heterozygous woman expressing the trait will have 50% chance of inheriting the allele
|
Sex-Linked Dominant
|
|
|
All children of a homozygous woman express trait
|
Sex-Linked Dominant
|
|
|
Offspring of affected males used to determine inheritance
|
Sex-Linked Dominant
|
|
|
Incidence in males is much higher than in females
|
Sex-Linked Recessive: X-Linked
|
|
|
Trait is passed from an affected man to all of his daughters to half of their sons
|
Sex-Linked Recessive: X-Linked
|
|
|
Trait is transmitted only from father to son
|
Sex-Linked Recessive: Y-Linked
|
|
|
Mendel's First Law
|
Independent Segregation: 1. Passing of one gene from each parent to offspring 2. Hereditary characteristics are determined by particulate units or factors.
|
|
|
Mendel's Second Law
|
Independent Assortment: 1. Random behavior of genes on separate chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis that results in a mixture of genetic material in the offspring.
|
|
|
Direct Exclusion of Paternity
|
Genetic marker present in the child but is absent from the mother and the alleged father
|
|
|
Indirect Exclusion of Paternity
|
Child lacks genetic marker that alleged father must transmit to his offspring.
|

