![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The angular momentum of a system is conserved when... |
There is no net torque |
|
|
When is rotational mechanics analogous to Linear mechanics |
Rotation about an axis of symmetry |
|
|
What is the conventional direction of a spinning disc |
Anticlockwise is positive |
|
|
Define centre of mass |
A mass weighted average position of the particles |
|
|
Give a property when finding the centre of mass of an extended object |
Uniform density |
|
|
Three steps for finding the centre of mass for an extended object |
Find DM Find the relationship between l and X (area or volume) Substitute into equation ) Substitute into equation |
|
|
An objects moment of inertia depends on... |
It's axis of rotation |
|
|
What are the units of moment of inertia |
KgM^2 |
|
|
Formula for the total energy of a spinning object |

|
|
|
What is a moment of inertia |
It tells us how hard it is to rotate an object |
|
|
What is the total formula for inertia? |

Top equation |
|
|
What is the parallel axis theorem? |

|
|
|
What is the difference between the centre of mass and inertia integrals? |
com integrates x, whereas inertia integrates x^2 and does not have 1/M before the integral |
|
|
Total kinetic energy is the summation of... |
Translation KE and Rotational KE |
|
|
The ability of a force to cause rotation depends on three factors...? |
The magnitude of the force The distance r from the point of application to the pivot The angle at which the force is applied |
|
|
Formulae for torque, and at what angle it is measured... |
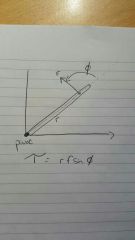
|
|
|
2 conditions for a rigid body to be in total equilibrium |
No net torque No net force |
|
|
The kinetic energy of solely rolling is due to... |
Kinetic energy of both rotation and translation |
|
|
2 Formulae for angular momentum |
L=rxp for a particle L=iw for a rigid body |
|
|
Give an alternative formula for rxp for angular momentum |
mrvsin(beta) |
|
|
The angular momentum vector and angular velocity vector will on point in the same direction when... |
Rotation of a symmetrical object is rotating about the symmetry axis |
|
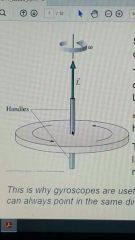
Is it easy or hard to change the vector L in this situation, and why? |
Hard, as a large torque is required to change the direction of L |
|
|
The formula for rotational work is |
dW=T(theta) |
|
|
Total rotational work is |

|
|
|
Rotational power is |
P=dW/dt |
|
|
The final angular velocity is given by |
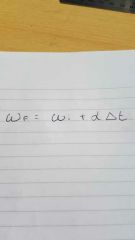
|
|
|
The final angle theta is given by |
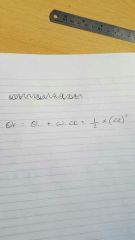
|
|
|
The final angular velocity squared is given by |

|
|
|
Tangential acceleration is given by |

|
|
|
Radial acceleration given by |

|
|
|
The angular momentum of a gyroscope can only change in the direction of |
The torque vector |
|
|
As the angular velocity of a spinning disc decreases does the gyroscope precess faster or slower |
Faster, as d(theta) /dt increases |
|
|
Why does a torque cause a change in direction? |
The torque cannot alter the rotation speed at the disk, so the magnitude of L remains constant. However in a time dT the angular momentum vector Changes by tau*dt and this results in a change in the direction. |
|
|
A use for gyroscopes |
Gyrostabilizer in ships. It uses a large gyroscope to reduce roll on ships by making necessary a large torque to alter L |
|
|
The work done is also the |
Change in Rotational kinetic energy |
|
|
Linear velocity |
V=angular velocity * r |

