![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
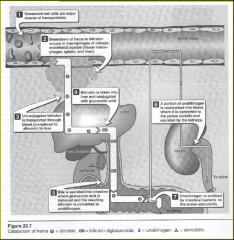
Heme is degraded in two steps =
|
-Bilirubin,
then conjugated to ... -Glucuronic acid ....... excreted. |
|
|
|
Bilirubin is highly lipid _______
|
soluble
|
|
|
What labs are used in the differential diagnosis of hyperbilirubinemia.
|
Indirect bilirubin values
Direct bilirubin values |
|
|
|
Is Heme reutilized?
|
No
it must be degraded excreted. Although heme is not recycled, its iron is conserved. |
|
|
|
hemolysis occurs, hemoglobin (with its iron) is released into the .
|
plasma
Possible causes of hemolysis include: = 3ct |
- erythrocyte fragility
-thermal burns -erythroblastosis fetalis |
|
|
In the plasma, oxyhemoglobin dissociates into alpha-beta dimers, which can escape through the glomerular filtration system of the kidney to appear in the urine.
To prevent this, there is a plasma protein, ______ , which binds the dimer and: |
haptoglobin
delivers it to the reticuloendothelial system for processing activates the heme to prepare it for degradation |
|
|
|
______ , then transports it to the liver for degradation.
|
hemopexin
The first reaction is cleavage of the heme ring by a microsomal heme oxygenase. The substrates for this reaction are: = 3ct |
heme
three molecules of oxygen NADPH |
|
|
biliverdin
produces what dangerous gas = |
CO
(this is the only endogenous source of CO) Fe2+ NADP+ |
|
|
|
In the second reaction
biliverdin reductase reduces the central methene bridge of biliverdin, producing _______ =. |
bilirubin
|
|
|
|
Bilirubin must be conjugated to a water-soluble substance :
The substrates are: bilirubin (or bilirubin monoglucuronide) UDP-glucuronic acid |
The major product is =
|
bilirubin diglucuronide.
|
|
|
The clinical determination of plasma bilirubin distinguishes between =
|
conjugated (direct) and unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin.
The reaction, called the ***___ ____ reaction, is a coupling of bilirubin with a diazonium salt to form a ***___ _____ |
van den Bergh
coloured complex. |
|
|
the INDIRECT bilirubin.
define = |
Total bilirubin =
direct bilirubin + indirect bilirubin i |
Only conjugated bilirubin is water soluble and reacts directly. This is called the DIRECT bilirubin.
To measure the unconjugated bilirubin bound to albumin, alcohol is added to release it into solution, where it can now react with the van den Bergh reagent. |
|
|
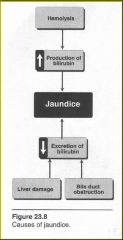
Several diseases are associated with hyperbilirubinemia.
Direct and indirect bilirubin values are used in the differential diagnosis of hyperbilirubinemia. = |
Hyperbilirubinemia could be caused by:
|
- increased bilirubin production
- decreased uptake into the liver cells - impaired conjugation - interference with the secretion of conjugated bilirubin |
|
|
Hemolytic jaundice
results from increased production of bilirubin = |
- increased bilirubin in bile,
- increased urobilinogen, - urine urobilin, - unconjugated bilirubin increases in blood |
|
|
|
preemies especially may have low
___ ____ ____ activity for first two weeks of life |
bilirubin glucuronyl transferase
bilirubin can diffuse into___ ___ and cause encephalopathy |
basal ganglia
blue fluorescent light converts bilirubin into more polar compound that can be excreted in bile without the need for conjugation |
|
|
Synthesis of creatine
Excretion of creatine is in proportional to__ ___ |
muscle mass.
|

|
|
|
Synthesis of histamine
|
histamine is a chemical messenger
A powerful ________ The reaction requires ___ ___ |
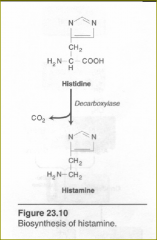
vasodilator
pyridoxal phosphate. |
|
|
Synthesis of serotonin
|
Serotonin: performs :
- pain perception --- regulation of : 3ct -sleep, -temperature -blood pressue Mainly found in the = 3ct Derives from = |
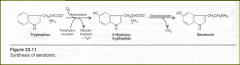
Intestine
platelets CNS. tryptophan |
|
|
Synthesis of catecholamines
Nm the Catecholamines: = 3ct |
-dopamine,
-epinephrine -norepinephrine Derived from =. |
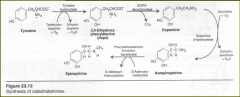
tyrosine
Dopamine and norepinephrine are neurotransmitters in the brain and autonomic nervous system. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are synthesized by adrenal medulla in response to fright, cold low levels of glucose. |
|
|
Degradation of catecholamines
|
Inactivated by
oxidative deamination catalyzed by monoamine oxidase (MAO) or Inactivated by O-methylation catalyzed by catenol-O-methyl-transferase (COMT). The metabolic products of these reactions are excreted in the urine. |
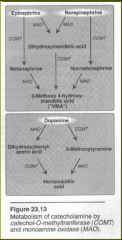
|
|
|
Synthesis of melanin
|
Pigment in the skin, hair and eye. It protect cells from harmful effects of sunlight.
Two common forms: _______ (black-brown) and ________ (red). Derives from ________; synthesized by melanocytes. |
eumelanin
pheomelanin tyrosine |
|
|
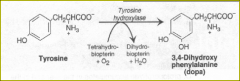
Synthesis of melanin
Two major steps : |
-first step is catalyzed by the copper-containing enzyme =
(Refer to catecholamines). -Second major step: formation of the pigment; involves several smaller steps. |
tyrosine hydroxylase
(or tyrosinase) |

