![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The ___ ___ ___ axis controls the required physiologic changes that occur both in the ovaries and in the uterus of the menstrual cycle.
|
hypothalamus-pituitary-gonad
|
|
|
|
Menstrual Cycle
Duration = Starts with the removal of the ____ & release of ___ by the anterior pituitary |
28 days (ranges 24 – 35 days)
endometrium FSH |
|
|
|
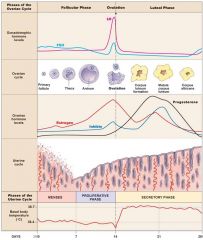
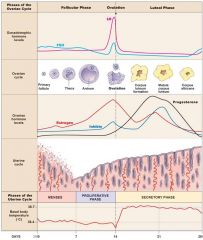
The ovarian cycle
Development of = Production of = Release of ___during ovulation |
ovarian follicle
hormones ovum |
|
|
|
The uterine cycle
Removal of _______ from prior uterine cycle Preparation for implantation of embryo under the influence of = |
endometrium
ovarian hormones |
|
|
|
Negative feedback effects of estrogen and progesterone in decreasing both LH and FSH secretion:
Estrogen in small amounts has strong effect to inhibit the production of ___ & ___ This inhibitory effect of estrogen is increased when ______ is available. |
LH & FSH.
progesterone This inhibitory effects more on the __directly & to lesser extent on the ______- to inhibit the secretion of ____. |
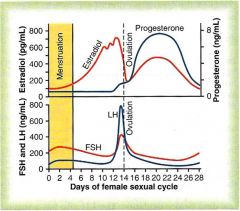
AP hypothalamus
hypothalamus GnRH |
|
|
Hormone inhibin from the corpus luteum inhibits __ & ___ secretion:
The hormone inhibin secreted by the ___ of the ovarian corpus luteum inhibit the secretion of |
FSH & LH
granulosa cells FSH & to lesser extent LH. |
|
|
|
Positive feedback effect of estrogen before ovulation =
AP secretes increased amount of ____ ____ ____ before ovulation. |
the pre-ovulatory LH surge:
LH for 1 to 2 days FSH surge is much smaller in the ____ ____ than LH surge. |
pre-ovulatory
|
|
|
The possible causes of LH secretion could be:
|
estrogen positive feedback stimulating
LH FSH (to a lesser extent) Granulosa cells of the ____ begin to secrete small increasing amount of ______ about 1 day before ovulation which stimulate ____ secretion |
follicle
progesterone LH |
|
|
3 Phases of the Ovarian Cycle
|
Follicular phase
Ovulation phase Luteal phase |
|
|
3 Phases of the Uterine Cycle
|
Menses
Proliferative Phase Secretory Phase |
|
|
|
Fertilization Effects
What happens if fertilization occurs? Uterine endometrium is maintained by = |
the release of progesterone
from the ___ ___ then the release of ___ which maintains the ___ ___ until the 7th week, |
corpus lutem
hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) corpus luteum |
|
|
Fertilization Effects
From 7th week on, the placenta produces ___ |
progesterone
which continues to maintain the _____ & the __ ___ degenerates |
endometrium
corpus luteum |
|
|
Placenta also produces estrogen and progesterone which at high levels blocks ____
________ is also involved in breast development |
GnRH
Estrogen ________ is also involved in uterine maintenance and relaxation (prevents ___ ___ ) |
Progesterone
premature contractions |
|
|
Placenta also produces ___
Implicated in breast development and milk production It has been determined not the only factor involved, as lack of hPL has no ill effects. |
hPL
(human Placental Lactogen) More important is the role hPL plays in ___ ___ by altering maternal glucose and fatty acid metabolism |
fetal nutrition
|
|
|
What changes occur to allow parturition.
Increasing levels of ___ hormone from the placenta a few ___ prior to delivery |
corticotropin-releasing
(CRH) weeks |
|
|
|
Early deliveries have been linked to early elevated levels of ___
|
CRH
|
|

