![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Aneuploidy
Autosomes = 3ct |
Trisomy 21 / Down syndrome
Trisomy 18 Trisomy 13 |
|
|
|
Aneuploidy
Sex Chromosomes = 3ct |
(45,X) Turner syndrome
(47,XXY) Klinefelter syndrome 47,XYY syndrome |
|
|
|
Aneuploidy
The clinical phenotype |
Congenital heart disease
- 15 fold increase risk for leukemia - Premature dementia |
|
|
|
Aneuploidy
Genetic cause (XX≈XY) |
- 47, XX, +21
- 46, XX, rob(14;21)(q10;q10), +21 - 46, XX, rob(21)(q10;q10) Recurrence risk |
- About 1% for 47, XX, +21
- 100% for 21q 21q translocation |
|
|
Aneuploidy
Autosomes |
Down syndrome/Trisomy 21
Trisomy 18 Trisomy 13 Sex Chromosomes Turner syndrome (45,X) Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY) 47,XYY syndrome |
|
|
|
Aneuploidy
Edward syndrome |
- Mental retardation
head: recede jaw hands: fingers - Rocker bottom-feet Genetic cause (XX≈XY) = |
- 47, XX, +18
Recurrence risk |
|
|
Aneuploidy
Patau syndrome |
Mental retardation
head: microcephaly & cleft lip hands: polydactyly - Rocker bottom-feet Genetic cause (XX≈XY) |
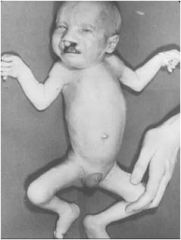
- 47, XX, +13
Recurrence risk - Low (<0.1%) |
|
|
Aneuploidy
Turner syndrome (45,X) Clinical features |
- Lymph edema
Neck: cystic hygroma Congenital heart disease Adult: short stature Lack of 2nd sex characteristics Genetic cause Recurrence risk |
- 45, X
Recurrence risk |
|
|
Aneuploidy
Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY) Clinical features |
- Tall stature
Lack of male secondary characteristics Mental retardation Lack of testosterone Genetic cause Recurrence risk |
- 47, XXY
- About 0.1% |
|
|
Aneuploidy
47,XYY syndrome Clinical features |
- Learning deficits
Genetic cause Recurrence risk |
- 47, XYY
- About 0.1% |
|
|
Disorders caused by deletions
|
-Cri-du-chat syndrome
-Williams syndrome -Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome -DiGeorge syndrome -Wilms tumor -Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes |
|
|
|
-Cri-du-chat syndrome
|
del(5p15.2-p15.3)
Clinical features Recurrence risk |
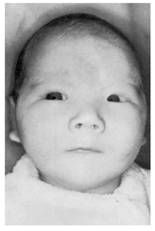
- Mental retardation
- Microcephaly wide set eyes Kitten-like cry - Very low (<1:10,000) |
|
|
del(5p15.2-p15.3)
|
-Cri-du-chat syndrome
|
|
|
|
-Williams syndrome
|
del(7q11.23)
|
|
|
|
del(7q11.23)
|
-Williams syndrome
|
|
|
|
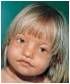
-Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome
|
del(4p16.3)
|
|
|
|
del(4p16.3)
|
-Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome
|
|
|
|
-DiGeorge syndrome
|
del(22q11.2)
Clinical features Genetic cause Recurrence risk |
- Mental retardation
- Heart defects cranial facial anomalies Increased risk of Schizophrenia ((XX≈XY) - 46, XX, del(22q11.2) - Low (<0.1%) |
|
|
del(22q11.2)
|
-DiGeorge syndrome
|
|
|
|
-Wilms tumor
|
del(11p13)
|
|
|
|
del(11p13)
|
-Wilms tumor
|
|
|
|
-Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes
|
del(15q11-q13)
|
|
|
|
del(15q11-q13)
|
-Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes
|
|
|
|
Sex-determination region on the Y
what P@ & arm is errored = |
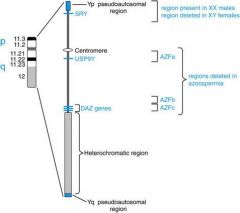
21-hydroxylase
(6p21) |
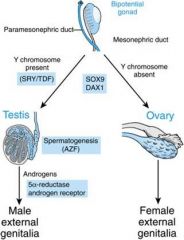
|
|
|
- presence of both testis and ovary
condition name is = |
Hermaphroditism
|
|

