![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Responses to the extracellular environment involve cell membrane or intracellular receptors whose engagement modulates cellular components that:
- generate, -amplify, -coordinate -terminate postreceptor signaling via = |
(cytoplasmic) second messengers.
|
|
|
|
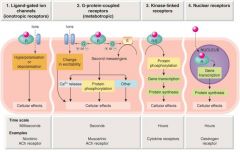
Transmembrane signaling is accomplished by only a few mechanisms:
H+ |
- G-protein-coupled receptors:
- Kinase-linked receptors: - ion channels (Transmembrane-ion): - Nuclear receptors |
G
K I N |
|
|
Transmembrane ion channels:
|
-open or close upon binding of a ligand
or - upon membrane depolarization |
|
|
|
-open or close upon binding of a ligand
or - upon membrane depolarization Type of channel = |
Transmembrane ion channels:
|
|
|
|
G-protein-coupled receptors:
|
-Transmembrane receptor protein
stimulates a GTP-binding signal transducer protein (G-protein) ..... which in turn generates an intracellular second messenger |
GTP-binding signal transducer protein = (G-protein)
|
|
|
stimulates a GTP-binding signal transducer protein (G-protein) .....
which in turn generates an intracellular second messenger Type of channel = |
G-protein-coupled receptors:
|
|
|
|
Nuclear receptors
|
-Lipid soluble ligands
that cross the cell membrane and act on an intracellular receptor |
|
|
|
-Lipid soluble ligands
that cross the cell membrane and act on an intracellular receptor Type of channel = |
Nuclear receptors
|
|
|
|
Kinase-linked receptors:
|
-Transmembrane receptor proteins
with intrinsic or associated kinase activity which is allosterically regulated by a ligand that binds to the receptor’s = |
extracellular domain
allosterically (defined) -binds a compound on an inactive site and thus changes conformation in order to become either active or inactive |
|
|
-Transmembrane receptor proteins
with intrinsic or associated kinase activity which is allosterically regulated by a ligand that binds to the receptor’s Type of channel = |
Kinase-linked receptors:
|
|
|
|
.
|
|
|
|
G-Proteins:
|
-Guanine nucleotide binding proteins: =
- |
participate in reversible, GTP-mediated interactions.
|

