![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Platelets
aka = |
thrombocytes
aka = |
Platelets
|
|
|
Platelets
Megakaryocytes are a = |
Polypoid
MK produces = - Life span = |
4,000 platelets
10 days |
|
|
Platelets contain granules filled with =
2ct |
clotting proteins
cytokines Activated when = |
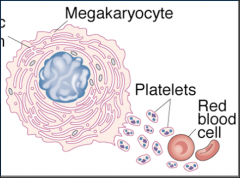
blood vessel wall is damaged
|
|
|
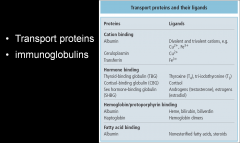
Plasma proteins
2ct |
Transport proteins
immunoglobulins |
|
|
|
Albumin
Main functions 2ct |
Albumin transporter
Albumin buffers pH, maintains osmotic pressure. |
hormones
fatty acids, metal ions others |
|
|
Albumin
Main features |
- Produced in the liver.
- 609 amino acids with a molecular mass of ca. 67 kDa. - Most abundant in the blood: It constitutes 50% of serum proteins. No glycosylation normal range for an adult: 3.5-5.0 g/dL |
|
|
|
immunoglobulin
Main functions |
Used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses.
|
|
|
|
immunoglobulin
Main features |
Produced by plasma cells in the bone marrow.
H chain determines the class of immunoglobulin: IgG (γ), IgA (α), IgM (μ), IgD (δ) and IgE (ε). Light chains are of two types: κ and λ IgG is the most common immunoglobulin that protects tissue space and freely crosses placenta |
|
|
|
immunoglobulin
Monoclonal immunoglobulins ...................(BAD).................... |
- Produced by a single B cell.
- They often arise from benign or malignant transformation of B cells. - Associated with diverse malignant pathologies such as myeloma and Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. - Also associated with more benign transformation (monoclonal gammapathies of uncertain significance (MGUS). |
|
|
|
Monoclonal immunoglobulins
Produced by |
B cells
- They often arise from = - Associated with diverse = |
benign or malignant transformation of B cells.
malignant pathologies -myeloma waldenstroms-macroglobulinemia - benign transformation (monoclonal gammapathies of uncertain significance (MGUS) |
|
|
Monoclonal immunoglobulins
are associated with - benign transformations... (MGUS) = |
(monoclonal gammapathies of uncertain significance
(MGUS) |
|
|
|
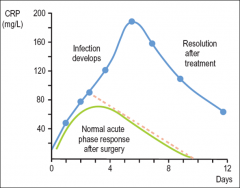
C-reactive protein
Main feature |
- Produced in the liver in response to factors released by macrophages and fat cells (adipocytes).
- It is a member of the pentraxin family of proteins. - a sensitive marker for bacterial infection |
|
|
|
myeloma
and Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. Are a = |
Monoclonal immunoglobulins
|
|
|
|
(MGUS)
Comes from = |
Monoclonal immunoglobulins
|
|
|
|
immunoglobulins
Produced by ___ ___ in the bone marrow. |
plasma cells
On the plasma cell' ___ chain? |
H Chain
|
|
|
immunoglobulins
produced on plasma cells on the Light Chains Light chains there are of two types: κ and λ |
kappa (κ)
lambda (λ). most common immunoglobulin that protects tissue space and freely crosses placenta = |
IgG
|
|
|
T/F
IgG freely crosses placenta = |
True
|
|
|
|
class of immunoglobulins:
Nm them = Light chains are of two types: κ and λ IgG is the most common immunoglobulin that protects tissue space and freely crosses placenta |
IgG (γ)
..IgA (α) ....IgM (μ) ......IgD (δ) ........IgE (ε) |
|
|
|
heavy chain
2 Types of = |
Fab =
Fc = confers biological activity such as phagocytosis of microorganisms, lysis, clumping of organisms together). |
Fab
(Antigen-binding region) Fc (Constant region) |
|
|
Reference Plasma cells & their chains:
Amino Acid sequence determines the type of = |
heavy chains
heavy chains define the ____ of "Ig" |
isotype
|
|
|
Heavy chains define the _____ of
Ig. |
isotype
|
|
|
|
Amino Acid sequence determines the type of heavy chains and heavy chains define the isotype of Ig.
|
Immunoglobulin ____ heavy chains:
G gamma (heavy chains,) IgA has α alpha IgM has μ mu IgD has δ delta IgE has ε epsilon light chains are either 2 types= |
κ kappa light chains
or λ lambda light chains, either of which may be found on any Ig molecule, regardless of isotype. |
|
|
T/F
Light Chains (2 types) may be found on any Ig molecule, regardless of isotype = |
T
|
|

