![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Veins
___? of the total blood volume |
70%
|
|
|
|
Veins:
walls which are thinner more supple less elastic |
still distensible (compliance
Capacitance or Reservoir vessels) |
|
|
|
Vein layers
|
tunica intima
tunica media tunica adventitia |
|
|
|
Classification of Veins
|
Venules (postcapillary & muscular types)
Small to medium sized-veins Large veins |
|
|
|
Tunica intima: is thin. ***
3ct |
1 Endothelial cells
2 subendothelial 3It does not form a distinct internal elastic lamina. |
|
|
|
Special Types of Veins
iliac, femoral, saphenous, cephalic, basilar and umblical veins, there are longitudinal smooth muscle fibers in the subendothelial connective tissue layer of the tunica intima. |
.
|
|
|
|
Special Types of Veins
In certain veins the longitudinal orientation of cellular elements is also noticed in the innermost layer of tunica media. |
.
|
|
|
|
Special Types of Veins
In a considerable portion of the inferior vena cava, the tunica media is absent, and the well-developed longitudinal muscle bundles of the tunica adventitia are directly adjacent to the intima. |
.
|
|
|
|
Large veins
The adventitial muscle serves to strengthen the wall and prevent distension of the vessel. The circular and longitudinal muscle arrangement of smooth muscle in the vessels of lower extremities may oppose the action of gravity by providing a peristaltic pumping of the blood up to the heart. Many vasa vasorums are present in adventitia. |
.
|
|
|
|
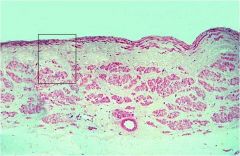
Tunica adventitia: layer description:
3ct |
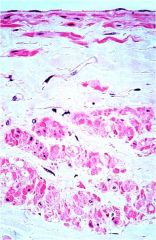
-a zone of dense fibroelastic connective tissue
-middle zone contains many longitudinal muscle fibers -outermost zone consists only of a coarse network of collagenous and elastic fibers. |
|
|
|
Special Types of Veins
pulmonary veins, the media is well |
developed
|
|
|
|
Special Types of Veins
Smooth muscle is particularly prominent in all the layers of the veins in |
pregnant uterus
|
|
|
|
Special Types of Veins
Other veins are entirely devoid of |
-smooth muscle
-tissue and consequently lack a tunica media. |
|
|
|
Special Types of Veins
Other veins are entirely devoid of smooth muscle tissue and consequently lack a tunica media. In this group belong the |
-veins of the maternal part of the -placenta
-spinal pia mater -retina -sinuses of the dura mater -cerebral veins -nailbed -trabeculae of the spleen. |
|
|
|
extends for a distance into the adventitia of the venae cavae and pulmonary veins near their entrance into the heart. =
|
Cardiac muscle
|
|
|
|
the blood is shunted from the arterioles directly into the venules without having to circulate through a capillary network is called =
|
Arteriovenous Anastomoses
|
|
|
|
Arteriovenous Anastomoses
located where = |
nail beds
auricle of the ear, the arteriovenous anastomoses |
|
|
|
Clinical Note
A vein is said to be ______ when its diameter is greater than normal and it is elongated and tortuous. |
vericosed
|
|
|
|
Vericose Veins
definition = |
: A vein is said to be vericosed when its diameter is greater than normal and it is elongated and tortuous.
|
|
|
|
Vericose veins occur at three sites:
|
superficial veins of lower limb
veins at the lower end of the esophagus (called esophageal varices) ***veins of the anal canal (called hemorrhoids). |
|

