![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Describe the structural organization of lymphoid tissues
Describe the structural organization and major cell types of the Lymph Node Describe the structural organization and major cell types of the Spleen Describe the structural organization and major cell types of the Thymus Describe the structural organization and major cell types of the Tonsil |
Clinical Correlations:
AIDS -DiGeorge syndrome -Autoimmune PolyEndocrinopathy-Candidiasis-Ectodermal Dystrophy (APECED) acute lymphadenitis |
|
|
|
1. primary lymphoid organs
|
the bone marrow
the thymus |
|
|
|
secondary lymphoid organs
are the sites where immune responses occur |
tonsils
lymph nodes spleen ALAP Cells MALT aggregates of lymphocytes and antigen-presenting cells associated with mucosa (Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue [MALT]). |
|
|
|
two key cell components of the immune system are
|
lymphocytes
accessory cells. |
|
|
|
Lymphocytes include two major cell groups:
|
B cells
T cells |
|
|
|
T cells, subdivided into two categories:
|
helper T cells
cytotoxic T cells. (cytolytic ) T cells respond to cell-bound antigens presented by specific molecules. NKs (Natural killer cells are the third subtype of lymphocytes) |
|
|
|
the third subtype of lymphocytes)
|
NKs
Natural killer cells |
|
|
|
Natural killer cells are the third subtype of
|
lymphocytes
|
|
|
|
T cells respond to
|
cell-bound antigens presented by specific molecules.
|
|
|
|
Cell components of immune system
accessory cells include |
monocyte-derived cell types =
follicular dendritic cell |
|
|
|
monocyte-derived cell types:
|
macrophages
dendritic cells (e.g. Langerhans cell found in the epidermis of the skin) |
|
|
|
_________ _________ cells differ from ordinary dendritic cells in that they do not derive from a bone marrow precursor.
|
Follicular dendritic
|
|
|
|
Immunity
reaction to foreign (nonself) There are two types of responses = |
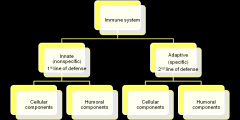
. Innate immune responses
. Acquired immune responses |
|
|
|
Innate or natural immunity is the simplest mechanism of protection
3ct |
does not require previous exposure to a pathogen
has rapid responsiveness. consequence of an initial exposure to a pathogen is adaptive or acquired immunity. |
|
|
|
The contributors to innate immunity are =
6ct |
-Skin
-Macrophages -Neutrophils -NKs -Phagocytes PROTIENS -Cytokines -complement System (heme Portiens) |
an epithelial surface or barrier,
neutrophils and macrophages with phagocytic properties, natural killer cells, and a number of proteins, including cytokines blood proteins: components of the complement system |
|
|
Adaptive immune response
aka |
humoral immunity
|
|
|
|
Humoral Immunity
is located where? |
-outside a cell
-bound to surface. |
|
|
|
________ _______ results in persistent antibody production and production of memory cells.
|
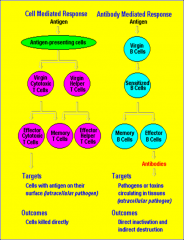
Humoral immunity
|
|
|
|
Adaptive immunity involves two types of responses to an antigen (pathogen):
The 1st response is mediated by = 2nd type of response |
-Plasma Cell produced Anitibodies.
-phagocyte uptake |
The 1st response mediated by antibodies produced by Plasma Cells
The 2nd type requires uptake of a pathogen by a -phagocyte |
|
|
Humoral immunity results in =
|
-persistent antibody production
-production of memory cells. |
|
|
|
3ct __ __ __ the key players in cell-mediated immunity.
|
-T cells
-B cells -antigen-presenting cells cell-mediated immunity |
|
|
|
**A consequence of adaptive or acquired immunity =
|
the protection when a
second pathogen encounter occurs. |
|
|
|
______ ______ is the form of immunity resulting from exposure to a pathogen (post disease =
|
Active immunity
|
|
|
|
______ _______ is a temporary form of immunity conferred by serum or lymphocytes transferred from an immunized individual to another individual who has not been exposed or cannot respond to a pathogen.
|
Passive immunity
|
|
|
|
The transfer of maternal antibodies to the fetus is a form of _________ immunity that protects newborns from infections until they can develop ___________ immunity.
|
Passive immunity
active immunity |
|
|
|
Antibodies of immunized animals (rabies, tetanus)
Antitoxins (diphtheria) stack what type of response = |
Passive immunity
|
|

