![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Parotid Gland Dz =
|
Mumps
|
|
|
|
Mumps is in what gland =
|
Parotid
|
|
|
|
Salivary Glands
|
Parotid
Sublingual Submandiular |
|
|
|
Hepato : VISCERAL SURFACE
|
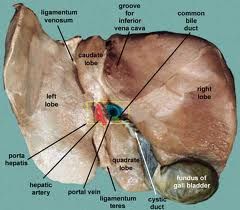
(LP) Fissure for
Ligamentum Venosum (LA) Fissure for Round Ligament of Liver (RP )Inferior Vena Cava (RA ) Gall Bladder (Middle) Porta Hepatis |
|
|
|
obliteration of the umbilical vein
|
Round Ligament
|
|
|
|
Round Ligament
|
obliteration of the umbilical vein
|
|
|
|
Vein that Drains Hepato =
|
RHV
MHV LHV to the IV-C (inferioir venaava) |
|
|
|
quadrate lobe – location
|
anterior to the porta hepatis
|
|
|
|
caudate lobe – location
|
posterior to the porta hepatis
|
|
|
|
porta hepatis – location
|
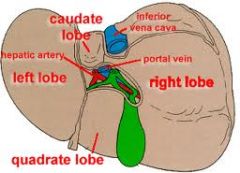
contains the hepatic ducts,
hepatic artery, portal vein, autonomic nerves, lymph nodes |
|
|
|
Divisions of the Liver
|
Anatomical Division
Functional Division |
|
|
|
Anatomical Division
|
– right and left lobes by the falciform ligament
right lobe – further subdivided into quadrate lobe a caudate lobe by the presence of the gall bladder, IVC, Fissure Ligamentum venosum |
|
|
|
Functional Division
|
the quadrate and caudate lobes are functionally a part of the anatomical left lobe because they are supplied by the left branches of the hepatic artery and portal vein and drained the left hepatic ducts
|
|
|
|
Small to medium-sized veins
These veins include the distal veins of limbs and the veins of viscera. They have a diameter ranging from 1 to 9 mm |
Tunica intima: is thin.
Endothelial cells = subendothelial = It does not form a distinct = |
Tunica intima: is thin.
Endothelial cells are short and polygonal in shape. subendothelial connective tissue is inconspicuous with occasional smooth muscle cells. It does not form a distinct internal elastic lamina. |
|
|
Large veins
These veins include the superior and inferior venae cavae, the portal vein, the iliac veins, the renal and mesentric veins. Veins with a diameter greater than 10 mm are classified as large veins. |
Tunica intima:
Tunica media |
Tunica intima:
This consists of a lining of endothelial cells resting on a thick layer of subendothelial connective tissue. Tunica media: This layer is poorly developed and is sometimes absent. |
|
|
Large veins
Tunica adventitia: The adventitia is the thickest of the three coats and shows three zones. Immediately external to the tunica media is = 4 ct |
a zone of dense fibroelastic connective tissue with coarse collagenous fibers, frequently arranged in open spirals.
the middle zone contains many longitudinal muscle fibers the outermost zone consists only of a coarse network of collagenous and elastic fibers. The adventitial muscle serves to strengthen the wall and prevent distension of the vessel |
|
|
|
Special Types of Veins
pulmonary veins, the media is = __________ ______- is particularly prominent in all the layers of the veins in pregnant uterus = veins of the maternal part of the placenta, the spinal pia mater, the retina, as well as the sinuses of the dura mater, the majority of the cerebral veins, and the veins of the nailbed and the trabeculae of the spleen. are devoid _______ _______? = |
pulmonary veins, the media is well developed,
Smooth muscle Smooth muscle extends for a distance into the adventitia of the venae cavae and pulmonary veins near their entrance into the heart. = |
Cardiac muscle
|
|
|
Valves of the Veins
Each valve is formed by a = 4ct |
intima,
strengthened by connective tissue elastic fibers, is covered on both surfaces by endothelium, |
|
|
|
In certain areas of the body, notably the skin, the blood is shunted from the arterioles directly into the venules without
a capillary network. Such a bypass is |
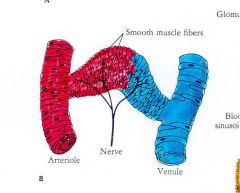
arteriovenous anastomoses or AV shunt.
The walls of the shunt are __________ = & innervated with = |
thick and muscular
thick and muscular and are well supplied with |
|
|
Arteriovenous anastomoses control blood flow and assist in
|
temperature regulation of the body.
|
|
|
|
***Vericose Veins: A vein is said to be vericosed when its diameter is
|
greater than normal and it is elongated and tortuous.
|
|
|
|
***Vericose veins occur at three sites:
|
superficial veins of lower limb
veins at the lower end of the esophagus (called esophageal varices) *** veins of the anal canal (called hemorrhoids). *** |
|

