![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
99 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What do administrative templates allow you to do?
|
They allow you to control the environment of the operating system and user experience.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-3) |
|
|
How many sets of Administrative Templates are there?
|
2
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-3) |
|
|
What are the types of Administrative Templates?
|
- Users
- Computers (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-3) |
|
|
What is a result of using the administrative template section of the GPO?
|
You can deploy hundreds of modifications to the registry
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-3) |
|
|
What is an administrative template?
|
It is a text file that specifies the registry change to be made and that generates the user interface to configure the Administrative Template Policy settings in the GPME.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-4) |
|
|
The registry edit tool provides a _____________ with which to disable Regedit.exe
|
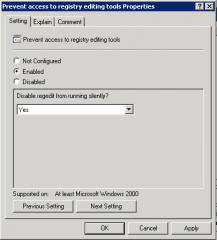
drop down list
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-4) |
|
|
How are Administrative Templates organized?
|
They are organized into sub-folders that deal with specific areas of the environment, such as network, system, and Windows components.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-5) |
|
|
With Administrative Templates the settings in the computer section edit the ______________________
|
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHONE hive in the registry
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-5) |
|
|
With Administrative Templates settings in the user section edit the _______________________
|
HKEY_CURRENT_User hive in the registry
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-5) |
|
|
If settings exist in both user and computer settings which setting prevails if the two settings conflict?
|
The computer setting wins
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-5) |
|
|
What is a .ADM File?
|
In versions of Windows prior to Windows Vista, an administrative template had an .ADM extension.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-5) |
|
|
What are the drawbacks with .ADM files?
|
1. .ADM files must be created for each language used
2. The way they are stored. |
|
|
How is a .ADM file stored?
|
An .ADM File is stored as part of the GPT in the SYSVOL. If an .ADM file is used in multiple GPOs, it is stored multiple times, contributing to SYSVOL bloat. There were also challenges in maintaining version control over .ADM
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-5) |
|
|
How would you add classic administrative templates to the GPME
|
right click the Administrative Templates node and
then click Add/Remove Templates (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-5) |
|
|
What is an .ADMX/.ADML Files?
|
In Windows Cista, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008, an administrative template is a pair of XML files, one with an .ADMX extention that specifies changes to be made to the registry and the other with an .ADML extension that provides a language-specific user interface in the GPME.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-5) |
|
|
What happens when changes need to be made to a .ADMX/.ADML?
|
When changes need to be made to settings managed bu the administrative template, they can be made to the single .ADMX file. Any administrators who modifies a GPO that uses the template accesses the same .ADMX file and calls the appropriate .ADML file to populate the users interface.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-5) |
|
|
How do you add .ADMX/,ADML administrative templates to the GPME.
|
Copy the .ADMX file into the 5SystemRoot%/PolicyDefinitions folder on your client or in the central store. Copy the .ADML file into the language-and-region-specific subfolder, such as en-us, of %SystemRoot%\PolicyDefinitions on your client or in the central store.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-5) |
|
|
How would you migrate .ADM files to .ADMX?
|
With the ADMX migrator
http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?Linkid=99466 (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-6) |
|
|
Policies in the Administrative Templates node make changes to the ______________
|
Registry
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-7) |
|
|
Settings provided in the Computer Configuration node will modify registry values in the
|
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM) key the machine where Group Policy is applied.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-7) |
|
|
Name 2 ways to disableRegeditMode
|
1. Regedit UI tool only
2. Also disable regedit /s (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-7) |
|
|
What are some Managed Policy Settings Characteristics?
|
- User Interface (UI) is locked; user cannot make a change to the setting.
- Changes are made in one of four registry keys. - Change and UI lock are "released" when the user/computer falls out of scope (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-8) |
|
|
What are some characteristics of unmanaged UI settings?
|
- UI not locked
- Makes a change that is persistent; "tattoos" the registry (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-8) |
|
|
Characteristics options for Administrative Templates
|
- managed policy settings
- unmanaged policy setting - only managed setting shown by default - change and UI lock are "released" when the user/computer falls out of scope (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-8) |
|
|
In administrative templates, what settings are shown by default?
|
managed
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-8) |
|
|
How would you view unmanaged policy options in administrative templates?
|
set filter options to view unmanaged settings
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-8) |
|
|
What are the four registry keys for managed templates?
|
1. HKLM\Software\Policies (computer settings)
2. HKCU\Software\Policies (user settings) 3. HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Current Version\Policies (computer settings) 4. HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Current Version\Policies (user settings) (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-8) |
|
|
Can non administrators make changes to the registry keys.
|
These keys are secured so that only administrators can make a change. Together with UI lockout, this means that nonadministrative users will receive the change specified by the policy setting and cannot modify the setting on their computer.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-8) |
|
|
When are changes made by Group Policy Settings and the UI Lockout released?
|
If the user or computer falls out of scope of the GPO. For example, if you delete a GPO, managed policy settings that had applied to a user will be released. This means that, generally, the setting resets to its previous state. Additionally, the UI interface for the setting is enabled.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-8) |
|
|
An unmanaged policy setting makes a change that is _____________ in the registry.
|
Peristant, If the GPO no longer applies, the setting remains. This is often called "tatooing" the registry, in other words, making a permanent change. To reverse the effect of teh policy setting, you must deploy a change that reverts the configuration to the desired state. Additionally, an unmanaged policy setting does not lock the UI for that setting.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-9) |
|
|
How would you control which policy settings are visible in AD?
|
right click Administrative Templates
Click Filter Options then select from the managed drop-down list (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-9) |
|
|
In the Central store .ADM files are
|
- Stored in the GPT
- Leads to version Control and GPO bloat problems (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-10) |
|
|
In the Central Store .ADMC/ADML filed are
|
- retrieved from the client
- Problematic if the client doesn't have the appropriate files (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-10) |
|
|
In the Central Store how do you remotely create a folder called Policy Definitions on a DC
|
\\contoso.com\SYSVOL\contoso.com\Policies\Policy Definitions
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-10) |
|
|
In the Central Store how do you Locally create a folder called Policy Definitions on a DC
|
%SystemRoot%\SYSVOL\contos.com\Policies\PolicyDefinitions
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-10) |
|
|
Can you use the central store in mixed mode environments?
|
Yes with systems earlier than windows vista?
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-11) |
|
|
Can you use the central store in mixed mode environments to manage groups?
|
You must use Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or later to manage Group Policy. That is your administrative workstation must be running a version of Windows.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-11) |
|
|
Can you filter Group Policies based on a specific version of Windows?
|
Yes
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-13) |
|
|
What server can you search based on policy-setting comments
|
Windows Server 2008 and higher enables you to add comments to policy settings in the Administrative Templates node. To do so double-click a policy setting and click the comment tab.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-13) |
|
|
What is the starter GPO?
|
new to windows server 2008 is Starter GPO/ A Starter GPO contains administrative Template settings. You can create a new GPO from a starter GPO. A starter GPO is, in effect, a template.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-13) |
|
|
Group Policy preferences expand the range of configurable settings within a GPO and ___________
|
- are not enforced
- enable IT pros to configure, deploy, and manage operating system and application settings that were not managed by using group policy (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-20) |
|
|
Four features of group policy preferences?
|
1. Create
2. Delete 3. Replace 4. Update (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-20) |
|
|
What is the create feature of group policy preferences?
|
Create a new item on the targeted computer.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-20) |
|
|
What is the delete feature of group policy preferences?
|
Remove an existing item from the targeted computer
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-20) |
|
|
What is the replace feature of Group Policy Preferences?
|
Delete and re-create an item on the targeted computer
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-20) |
|
|
What is the update feature of Group Policy Preferences?
|
Modify an existing item on the targeted computer.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-20) |
|
|
Windows server 2008 includes more than ____ extensions that expand the range of configurable settings within a GPO.
|
20
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-20) |
|
|
What are some benefits of Group Policy Preferences?
|
- Reduces the need for logon scripts
- Limits Configuration Errors - Minimizes image maintenance (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-20) |
|
|
In the common tab: what is the stop processing items in this extension if an error occurs?
|
By default, errors do not prevent Group Policy Preferences from processing the remaining preference items in the same extension. If you want preferences to stop processing additional items if an error occurs, enable this option.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-21) |
|
|
In the common tab: What is the Run in logged-on user's security context?
|
By default, Group Policy preferences process preference items by using the local System account. As a result, these items can only access system environment resources, including network drives, you must enable this option to process the item by using the logged-on account.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-21) |
|
|
In the common tab: What is the Remove this item when it is no longer applied
|
Unlike policy settings, Group Policy does not remove preferences, when the GPO is removed from the user or the computer. Choosing this option changes the default behavior: when the GPO is removed from the user or computer.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-21) |
|
|
In the common tab: What is Apply once and do not reapply?
|
Group policy preferences items during the regular refresh interval, by default. As a result, Group Policy restores preference items, even though users can change the settings once they create.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-21) |
|
|
In the common tab: What is Item Level Targeting?
|
Targeting Determines to which users and computers a preference item applies. Enable this option, and then clic the Targeting button to configure targeting items for the preference item.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-21) |
|
|
What is targeting Control?
|
Item-level targeting determines the user and computers to which Group Policy applies individual preference items within a GPO. You can target different preference items within a single GPO at computer based on different criteria, You can use logical operators to join criteria, For example you can apple a preference if the computer matches a specific IP address range and operating system version.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-22) |
|
|
Where are group Policy Preferences Written?
|
Are written to the normal locations in the registry tha the application or operating system feature uses to store the setting.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-23) |
|
|
Where are the Group Policy Settings Written?
|
Strictly enforce policy settings by writing the settings to areas of the registry that standard users cannot modify
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-23) |
|
|
Is the user interface disabled in Group Policy Preferences?
|
No, they Do not cause the application or operating system feature to disable the user interface for the settings they configure.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-23) |
|
|
Is the user Interface disabled In Group Policy Settings?
|
Yes, they Typically disable the user interface for settings that Group Policy is managing.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-23) |
|
|
How often are refresh preferences in Group Policy Preferences refreshed ?
|
Refresh preferences by using the same interval as Group Policy settings by default.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-) |
|
|
How often are refresh policies in Group Policy Settings, refreshed?
|
Refresh policy settings at regular interval
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-23) |
|
|
Where are group policy preferences not available?
|
Local computers
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-23) |
|
|
Where are Group Policy Settings available?
|
through local group policy
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-23) |
|
|
SMS
|
System Management Server
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-29) |
|
|
GPSI
|
Group Policy Software Installation
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-29) |
|
|
CSE
|
Client Side Extension
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-30) |
|
|
.msi
|
Windows installer package
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-30) |
|
|
Windows installer package (.msi)
|
- Operationally modified by transform (.mst) or patches (.msp)
- GPSI automatically installs with elevate privileges (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-30) |
|
|
.zap
|
Downlevel application package
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-30) |
|
|
Downlevel application package is supported by
|
"Publish" option only
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-30) |
|
|
What kind of privileges do you need to have to access downlevel application?
|
Admin privileges
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-30) |
|
|
.mst
|
Transform files
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-30) |
|
|
What are transform files?
|
.mst - These files provide a means for customizing the installation of an application. Some applications provide wizards or templates that permit a user to create transforms. For example, Adobe provides an enterprise deployment tool for Adobe Acrobat Reader that generates a transform. Many enterprises use the transform to configure agreement with the end-user license agreement and to disable certain features of the application, such as automatic updates that involve access to the internet.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-30) |
|
|
.msp
|
update files
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-31) |
|
|
What are update files?
|
.msp - These files are used to update an existing .msi file for security updates, bug fixes, and service packs. An .msp file provides instructions about applying the updated files and registry keys in the software patch, service pack, or software update, For example updates to Microsoft Office 2003 and later are provided as .msp files.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-31) |
|
|
How must you deploy .mso and .mst files be deployed?
|
They must be applied to an existing Windows Installer Package.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-31) |
|
|
What are downlevel application packages?
|
GPSI can make limited use of non-MSI applicationfiles (.zap files), also known as down-level application packages that specify the location of the software distribution point (SDP) and the setup command. See knowledge base article 231747 at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=214197 for details.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-31) |
|
|
When can GSPI fully manage an application?
|
only if the applications are deployed by using Windows Installer Packages. Other tools, including configuration Manager and SMS, can manage applications that use other deployment mechanisms.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-31) |
|
|
SDP
|
Software Distribution Point
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-31) |
|
|
What are software deployment options?
|
- Assign Application to users
- Publish Application to users - Assign to computers (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-32) |
|
|
What happens when you assign applications?
|
When you assign an application to a user, the application's local registry settings, including file name extensions, are updated and it's shortcuts are created on the Start Menu, or desktop, advertising the availability of the application.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-32) |
|
|
What happens when you publish an application?
|
When you publish an application to users, the application does not appear as if it is installed on the users' computer. No shortcuts are visible on the desktop or start menu. Instead, the application appears as an available application for the user to uninstall using Add or Remove Programs in control panel on windows XP system or in programs and features on a Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, or Windows 7 system. Additionally, the application can be installed when a user opens a file type associated with the application .
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-32) |
|
|
Many organizations have found that it is easiest to manage software by
|
linking an application's GPO to the domain and filtering the GPO so that it contains the users and computers to which the application should be deployed.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-38) |
|
|
Steps to maintain software deployed with GPSI?
|
- Redeploy applications
- Upgrade applications - Remove Applications (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-39) |
|
|
Redeploy applications with GPSI
|
- After a successful instal, client will not attempt to reinstall app
- You might make a change to the package - Package -> All Taks -> Redeploy Applications (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-39) |
|
|
Upgrade applications with GPSI?
|
- Create new package in same or different GPO
- Advanced -> Upgrade -> Select Package to upgrade - Uninstall old version first; or install over old version (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-39) |
|
|
Remove Applications with GPSI
|
- Package -> All Tasks -> Remove
- Uninstall immediately (forced removal) or Prevent new installations (optional removal) - Don't delete or unlink GPO until all clients have applied settings (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-39) |
|
|
What is the option to - Immediately uninstall the software from users and computers
|
This option is known as forced removal, causes computers to remove the application. The software installation extension will remove an application when the computer restarts if the application was deployed with a package in the Computer Configuration portion of the GPO. If the package is in the User Configuration portion, the application is uninstalled the next time the user logs on.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-40) |
|
|
What is the option to - Allows users to continue to use the Software, but prevents New Installations.
|
This setting, known as optional removal, causes the software installation extension to avoid adding the package to systems that do not yet have the package installed. Computers that had previously installed the application is uninstalled the next time the user logs on.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-40) |
|
|
What is the option - Uninstall this application when it falls out of the scope of management
|
you can simple delete, disable, or uplink the GPO, and the application will be forcibly removed by all clients that have installed the package with that setting.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-40) |
|
|
A slow link by default fot GPSI is
|
less than 500 kbps
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-41) |
|
|
When does a CSE not process
|
By default when GPSI is running over a slow link, less than 500kbps
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-41) |
|
|
How do you change slow link processing behavior og each CSE
|
Computer Configuration\Policies\Administrative Templates\System\Group Policy
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-41) |
|
|
How do you change the slow link threshold?
|
Computer [or user] Configuration\Policies]Administrative Templates\System]Group Policies
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-41) |
|
|
What are the best practices related to Group Policy Management?
|
- MAke comments on GPO settings
- Use Central store for Administrative Templates when having clients with Windows Vista and Windows 7 - Use Group Policy preferences to configure settings not available in Group Policy set of settings - Use Group Policy Software installation to deploy packages in .msi format to a large number of users or computers. (Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-47) |
|
|
What is the Group Policy Reporting RSoP Tool?
|
Reporting information about the current polices being delivered to the clients
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-48) |
|
|
What is the GPResult tool?
|
A command-line utility that displays RSoP information.
|
|
|
What is GPUdate tool
|
Refreshing local and AD DS - Based Group Policy settings via cmd
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-48) |
|
|
What is DCGpofix tool
|
Restoring the default group policy objects to their original state after initial installation via cmd
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-48) |
|
|
What is the GPOLogView tool
|
Exporting Group Policy-related events from the system and operational logs into text. HTML, or XML file. For use with Windows Vista and later versions via cmd
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 7-48) |

