![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
218 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Configuration Management
|
- A centralized Approach to on or more changes to one or more users or computers
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-5) |
|
|
Define the key elements of Configuration Management?
|
- A centralized definition of change, which is known as a setting. The setting brings a user or a computer to a desired state of configuration
- A definition of the user(s) or computer(s) to whom the change applies, which is known as the scope of the change. - A mechanism or process that ensures that the setting is applied to users and computers within the scope, which is known as the application (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-5) |
|
|
What are the key elements of Configuration Management
|
- Setting
- Scope -Application - Tools (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-5) |
|
|
In configuration management what is the setting
|
Definition of a change configuration
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-5) |
|
|
In configuration management what is the scope?
|
A definition of the users or computers to which the change applies
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-5) |
|
|
What is the granular definition of change or configuration?
|
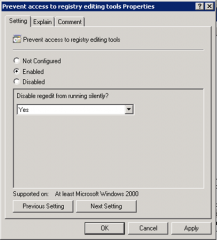
- Prevent access to Registry-Editing Tools
-Rename the administrator account (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-6) |
|
|
Policy settings are divided by ___________ and ____________
|
- User configuration [users only]
- computer configuration (computer policies) [Computers only] (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-6) |
|
|
What are the 3 definitions of a setting?
|
1. Not configured (default)
2. Enabled 3. Disabled (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-6) |
|
|
What does the not configured policy setting mean?
|
In a new GPO, every policy setting is set to not configured. This means that the GPO will not modify the existing configuration of that particular setting for a user or computer. If you enable or disable a policy setting, a change will be made to the configuration of users and computers to which the GPO is applied.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-6) |
|
|
What happens if you enable Prevent Access to Registry Editing Tools policy setting?
|
Users will be unable to launch the Regedit.exe Registry editor.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-6) |
|
|
What happens if you disable the Prevent Registry Access to registry Editing Tools policy setting?
|
You ensure that the users can launch the registry Editor. Notice the double negative in this policy setting. You disable a policy that prevents an action, so you allow the action.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-7) |
|
|
With RegEdit can you define whether registry files can be merged silently into a system?
|
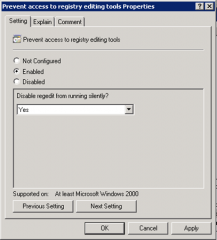
Yes
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-7) |
|
|
What are some Benefits of Using Group Policy?
|
1. Apply Security Settings
2. Manage Desktop and application settings 3 Deploy Software 4. Manage Folder redirection 5. Configure Network settings (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-8) |
|
|
Security settings using Group Policy
|
In Windows server 2008 R2, GPO include a large number of security-related settings that you can get and apply to both users and computer, For example, you can enforce settings for windows firewall and configure Auditing, Encrypting File System policies and other security settings. You can also configure a full set of user rights assignments.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-8) |
|
|
Manage Desktop and Application Settings using Group Policy
|
You can use a group policy to provide a constant desktop application environment to all users in you organization using GPOs, it is possible to configure each setting that affects the look and feel of a user environment and also to configure settings for some applications that support GPOs
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-8) |
|
|
Deploy software using Group Policy
|
Group Policies can also be used to deploy software for users or computers. All software that is provided in the .msi format can be developed by using Group Policy. You can enforce automatic software installation or you can let users decide if they want the software to be deployed to their machines or not.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-8) |
|
|
Manage Folder Redirection with Group Policies
|
With folder Redirection, you can easily manage and back up data. By redirecting folders you can ensure that users have access to their data regardless of the computer that they can use to log on. Also, you can centralize all users data to one place on the network server, while still providing the user an experience similar to storing these folders on their computer.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-9) |
|
|
Configure Network Settings with Group Policies
|
Using Group Policies, You can configure various settings on a client computer, For example, you can enforce settings for wireless networks to allow users to connect only to specific SSIDs and with predefined authentication and encryption settings. You can also deploy policies that apply to a wired network setting as well as configure client side of services such as Network Access Protection.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-9) |
|
|
Components of Group Policy Objects
|
- Container for one or more policy setting
- Managed with the GPMC - Stored in Group Policy Objects container - Edited with the GPME - Applied to a specific level in AD DS hieracrchy (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-10) |
|
|
WHAT is a GPO
|
Group Policy Object
A GPO is an object that contains one or more policy settings and thereby applies one or more configuration settings for a user or computer (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-10) |
|
|
GPO can be managed in the Active Directory by using _____________________________________________________
|
GPMC
Group Policy Management Console (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-10) |
|
|
For a GPO to work ___________________
|
it must be applied to the domain, site or OU in the AD DS hierarchy for the settings to take effect
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-11) |
|
|
What is a GPO Scope?
|
Definition of objects (users or computers) to which GPO applies
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-12) |
|
|
GPO Links
|
- GPO can be linked to multiple sites, domain, or organizational unit (OU) (SDOU)
- GPO link(s) define the maximum scope of GPO (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-12) |
|
|
What can you do with Security Group Filtering?
|
- Apply or deny application of GPO to members of global security Group
- Filter application of scope of GPO within its link scope (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-12) |
|
|
What does WMI Filtering do?
|
Refine scope of GPO within the link based on WMI Query
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-12) |
|
|
WMI
|
Windows Instrument Management
Filters that specify a scope by using characteristics of a system, such as an operating system version of free disk space |
|
|
Two types of GP filters
|
- specify global security groups in which the GPO should not apply
-WMI (Windows Management Systems) specifies what to apply (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-12) |
|
|
What are targeted preferences
|
New to Windows server 2008, targeting preference allows you to further refine the scope of preferences within a single GPO.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-12) |
|
|
CSE
|
Client Side Extension
Series of processes that interpret the settings in a GPO ans make appropriate changes to the local computer and the currently logged in user (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-13) |
|
|
An important concept about GPOs is the it is ______________ driven
|
Client (pull)
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-13) |
|
|
Can you reapply GPO settings if the policy has not changed?
|
Yes you can configure CSEs to reapply policy settings, even if the GPO has not changed at background refresh. To do so, configure a GPO scoped to computers and define the settings n the Computer Configuration\Policies\Administrative Templates\System\ Group Policy node. For Each CSE you want to configure, open its policy processing policy setting such as Registry Policy Processing for the Registry CSE. Click enabled and select the Process even if the group Policy Objects have not been changed check box.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-14) |
|
|
Why do you always enable the Always wait for network at startup and logon policy setting for all windows client?
|
Without this setting, by default windows perform only background refreshes - a client might start up, and a user might log on without receiving the latest policies from the domain
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-14) |
|
|
When should you Group Policy Refresh
|
1. When GPOs and their settings are applied
2. Computer Configuration 3. User Configuration (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-14) |
|
|
When are policy Settings in computer configuration applied?
|
1. System Startup
2. Every 90-120 minutes 3. Triggered: GPUpdate command (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-15) |
|
|
Can you force a policy refresh?
|
Yes, by using GPUpdate command
|
|
|
User configuration policies are applied at ___________
|
1. Logon
2. Every 90-120 minutes 3. Triggered: GPUdate command (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-15) |
|
|
In Windows Server 2008R2, there are almost _____________ different settings.
|
3,000 different settings
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-16) |
|
|
Group Policy settings provide the ______________
|
meaning and purpose of group policy.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-16) |
|
|
Where do you apply the GPO
|
This is known as the scope
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-16) |
|
|
When planning Group Policy Applications you should be aware of _____
|
refresh intervals
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-16) |
|
|
GPOs are managed through
|
GPO Policy Management Console
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-16) |
|
|
Policy settings within a GPO are configured by using __________
|
the GPME
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-16) |
|
|
What allows you to manually trigger Group Policy Refresh?
|
GPUdate
|
|
|
What allows you to evaluate and model the settings that were applied by group policy?
|
RSop Tool
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-16) |
|
|
Group policy settings also known as ____________
|
policies
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-17) |
|
|
what are the two major divisions of policy settings?
|
- Computer Settings
- User Setting (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-17) |
|
|
What setting applies policy settings to computers regardless of who logs on
|
Computer Configuration Node
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-17) |
|
|
What setting applies settings when a user logs on to the computer?
|
The user configuration node.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-17) |
|
|
What is the first node?
|
Software Setting node
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-17) |
|
|
What is the softwre setting node
|
The software setting node is the first node. It contains only the software installation extension.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-17) |
|
|
What does the software extension do?
|
This extension helps you specify how applications are installed and maintained within your organization. It provides a place for independent software vendors to add settings. Software deployment with Group Policy is discussed in Module 7.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-17 and 6-18) |
|
|
What is windows setting node?
|
- contained in both computer Configuration and User configuration
- includes the Scripts, Settings, and Policy Based QoS nodes (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-18) |
|
|
What does the scripts extension do?
|
enables you to specify the two types of scripts,
-startup/shutdown (in the computer configuration node), and - logon/logoff (in the User configuration node) (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-18) |
|
|
When a computer first is shut down _____________ process the logoff scrips?
|
CSE first process the logoff scripts
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-18) |
|
|
When do you have to adjust the timeout value for a logoff script?
|
By default the timeout value for processing scripts is 10 minutes, so anything that takes longer than that should be adjusted.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-18) |
|
|
What does the security settings node do?
|
Allows a security administrator to configure security by using GPOs
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-18) |
|
|
What is the Policy Setting QoS node
|
Defines Policies that manage network traffic
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-18) |
|
|
What is the Administrative Template Node
|
contains registry based group policy settings
|
|
|
Any setting specified by a domain based GPO will ________________ the setting specified by the local GPOs
|
Override
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-21) |
|
|
How many lcal GPOs are in windows 2000 server, Windows XP, Windows server 2003
|
1
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-21) |
|
|
What are the multiple GPOs in Windows Vista and beyond
|
- Local GPO
- Administrators GPO - Non-Administrators GPO - Per-user GPO: (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-21) |
|
|
Local GPO
|
The local GPO exist whether or not the computer is part of the domain, a workgroup, or a non-networked environment
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-21) |
|
|
Administators GPO
|
This applies settings for users in administrators group.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-21) |
|
|
Non-adminstrative GPO
|
This applies settings for users not in admin.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-21) |
|
|
Per-User GPO
|
This applies settings for a specific users.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-21) |
|
|
Where are domain based GPO created?
|
Active Directory
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-23) |
|
|
Where are Domain-based GPOs stored?
|
Domain Controllers
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-23) |
|
|
What are the two default GPOs
|
- Default Domain Policy
-Default Domain Controllers Policy (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-23) |
|
|
What is the Default Domain Policy
|
Defines account policies for the domain:Passwod, account, lockout, and kerberos policies
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-23) |
|
|
Default Domain Controllers Policy
|
Define auditing policy for domain controllers and Active Directory
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-23) |
|
|
What is the breakdownj of Default Domain Policy
|
This GPO is linked to the domain and has no security group or WMI filters. Therefore, it affects all users and computers in the domain, including computers that are domain controllers. This GPO contains policy settings that specify password, accout lockout, and kerberos policies. In module 10, you will learn how to modify the deffault settings in this GPO to align withyour enterprise password and account lockout policies. You should not add unrelated policy settings to this GPO. If you need to configure other settings to applu broadly in your domain, create additional GPOs linkied to the domain.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-23 |
|
|
The breakdown of Default domain Cotrollers policy
|
This GPO is linked to the OU of the domain controllers. Because computer accounts for domain controllers are kept exclusively in the Domain Controllers OUm, and other computer accounts should be kept in other OUs, this GPO affects only Domain Controllers. The default Domain Controller GPO should be modified to implement you auditing policies, as you will see in Module 8 through 10.. it should also be modified to assign user rights required on domain controllers.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-23) |
|
|
What are the two componets of Group policy settings
|
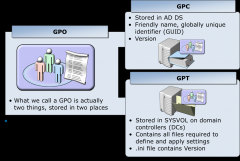
- Goup Plicy Cntainer (GPC)
- Group Policy Template (GPT) (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-26 |
|
|
GPC
|
Group Policy Container
The GPC is an Active Directory Object stored in the Group Policy Objects container within the domain-naming context fof the directory. Like all Active Directoy objects, each GPC includes a globally unique identifier (GUID) attribute that uniquely identifies the objects with Active Directory. The GPC Defines basic Attributes of the GPO, but does not contain any of the settingss. The settings are contained in the GPT. (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-26 |
|
|
GPT
|
Group Policy Template
A collection of files stored in the SYSVOL of each domain controller in the %SystemRoot%\SYSVOL\Domain\Policies\GPOGUID path, where GPOGUID is the GUID of the GPC. (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-26 |
|
|
When you make changesw to GPOGUID, where are the changes saved?
|
Ther are saved to the GPT of ther server from which the GPO was opened.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-26 |
|
|
What happens by default when the Group Policy refresh occurs?
|
The CSEs apply settings in a GPO only if the GPO has been updated.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-26) |
|
|
How can a group policy client identify an update GPO?
|
By its policy number.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-26) |
|
|
How is the GPO verson number incremented?
|
Each time a change is made.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-26) |
|
|
How is GPO replicated?
|
Group Policy Container and Group Policy Template are both replicated between all domain contollers in Active Directory. However different replication mechanisms are used for these two items.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-26) |
|
|
How is the GPC (Group Policy Container) replicated in Active Directory?
|
by the DRA (directory Repplication Agent).
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-26) |
|
|
The DRA (Directory Replication Agent) uses a topology checker known as ____
|
KCC
Knowledge Consistency Checker (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-26) |
|
|
How can the KCC (Knowledge Consistency Checker) be defined or refined?
|
Manually
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-26) |
|
|
How lonmg does it take for the GPC (Grou Policy Container) to be replicated?
|
Seconds to all domain controllers in a site and is replicated between sites based on your intersite replication configuration.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-27) |
|
|
How is the GPT (Group Policy Template) replicated in SYSVOL?
|
1. The FRS (File Replication Service
2. DFSR (Distribured File System Replication) (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-27) |
|
|
When would you use DFSR (Distributed File System, Replication to replicate the GPT (Group Policy Template?
|
If all domain controllers are running Windows Server 2008 or earlier, you can configure SYSVOL replication using DFSR (Distributed File System Replication)
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-27) |
|
|
Can the GPC (Group Policy Container) and the GPT(Group Policy Template) become out of sync?
|
Yes, typically, whyen this happens, the GPC will repllicate to a domain controller first. Systems obtained their ordered list of GPOs from the domain controller will identify the new GPC, will attempt to download the GPT, and will notice the version numbers are not the same. A policy processing errror will be recorded in the event logs. if the reverse happens, and the GPO replicates to a domain controller before the GPC, client obtianing their ordered list of GPOs from that domain controller will not be notified of the new GPO until the GPC has replicated.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-27) |
|
|
Copy
By Right Clicking GPO in the GPMC |
You can copy a GPO and the right-click the Group Policy Objects container and select Past to create a Copy of the GPO. This is useful when you want to create a new GPO in the same domain and start with the same settings as an existing GPO. it is also useful to copy a GPO into another domain, for example, between a test domain and a production domain. To copy a GPO between domains, add the target trusted domain to the GPMC. you must have permission to create GPO between domain, add the target trusted domain to the GPMC. you must have permission to create GPOs in the target domain. When you paste a GPO, you are given the option to copy the access control list (ACL) from the original GPO, which preserves the security filtering, or to use the default ACL for new GPOs in the target domain.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-28) |
|
|
Back up
By right Clicking a GPO in The GPMC |
As with any critical data, it is important to back up GPOs Because a GPO consists of sever files, objects, permissions and links, managing the backup and restore of GPOs is quite difficult. Luckily, the back up command pulls all those pieces into single place and makes restore a simple task.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-28) |
|
|
Restore from Backup
By right Clicking a GPO in the GPMC |
Restore an entire GPO, including its files, objects, permissions, and links int the same domain in which the GPO originally existed
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-28) |
|
|
Import Settings
by right clicking the GPO in the GPMC |
Import only the settings from a backed-up GPO. Although this option does not import permissions or links, it can be useful for transferring GPOs between nontrusted domains that cannot use copy and past. If a GPO includes potentially domain-specific settings, including the UNC paths or domain names of security groups, you will be prompted as to whether you want to import those settings as they were backed yo or to use a migration table that maps source to destination names.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-28) |
|
|
Save report
By right clicking the GPO in the GPMC |
Use this to save an HTML report of the GPO settings
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-28) |
|
|
Delete
By right clicking the GPO in GPMC |
Use the delete a GPO
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-28) |
|
|
Rename
By Right Clicking the GPO in the GPMC |
Use this to rename a GPO
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-28) |
|
|
What is the GPO by itself?
|
A collection of configuration instructions that will be processed by the CSEs of which computers will receive and process the GPO and only the computers or users within the scope of a GPO.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-33) |
|
|
What does a GPO link do?
|
Causes policy settings in GPO to apply to users or computers within that container
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-35) |
|
|
What can you link.
|
- GPO to site
- domain -OU (SDOU) (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-35) |
|
|
G=Can you link a GPO to multiple sites?
|
yes
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-35) |
|
|
Can a link exist in an unused state?
|
Yes in the disable state
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-35) |
|
|
If you delete a link is the GPO deleted?
|
The links can be deleted and the GPO remains.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-35) |
|
|
What happens when you link a GPO to a site?
|
the GPO can be applied to multiple domains within a forest.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-35) |
|
|
Site Linked GPOs are stored on _________________
|
domain controllers in the domain in which the GPO was created
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-35) |
|
|
What should you consider when implementing a site-linked policy?
|
You must consider policy application when planning your network infrastructure
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-35) |
|
|
Where must you place a GPO domain?
|
- the site to which the policy is linked
- a site to which the GPO is linked or - ensure WAN has accessibility to domain controller in the GPOs domain (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-35) |
|
|
When you first link a GPO what should you do?
|
Define the initial scope of the GPO.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-36) |
|
|
If you apply settings to a GPO, what happens?
|
Changes will apply to all OUs to which the GPO is linked.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-35) |
|
|
What us the Group Policy Processing Order?
|
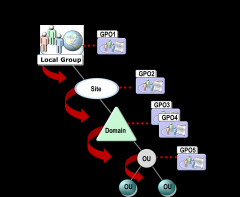
1. Local Group Policies
2. Site Group Policies 3. Domain Group Policies 4. OU group policies 5. Child OU group Policies (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-38) |
|
|
When are the local policies applied in the Group Policy processing?
|
first
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-38) |
|
|
What happens when processing multiple site policies?
|
They are processed syncronously
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-38) |
|
|
What happens when processing multiple domain policies?
|
They are processed syncronously
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-38) |
|
|
What happens when there are multiple OU group policies being processed?
|
They are process synchronously
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-38) |
|
|
When applying policies what is the general rule?
|
last policy applied wins
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-38) |
|
|
If you link several GPOs to an OU, what order are they specified?
|
In the order the administrator specifies.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-38) |
|
|
The application of GPOs linked to each container results in a cumulative effect called ___________________
|
inheritance
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-40) |
|
|
The default inheritance of GPO inheritance is
|
->Local
-->Site --->Domain ---->OU ----->OU (LSDOU) (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-40) |
|
|
What is Link Order ?
(attribute of GPO Link) |
->Lower number
--> Higher on List ---> Precedent (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-40) |
|
|
What is Block inheritance?
(attributes of OU) |
blocks the processing of GPOs from above
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-40) |
|
|
What happens when inheritance is enforced?
(attribute of GPO link) |
- Enforced GPOs "Blast through" Block inheritance
-Enforced GPO settings win over conflicting settings in lower GPOs (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-40) |
|
|
What does the precedence of a GPO determine?
|
It determines which policy settings the client applies.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-40) |
|
|
What is a policy setting set to by default?
|
Not configured
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-40) |
|
|
What is the default behavior of Group Policy?
|
is that the GPOs linked to a higher-level container are inherited by lower-level containers
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-40) |
|
|
What is the effect of sequential applications of GPOs?
|
Policy Inheritance
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-40) |
|
|
By default __________ GPOs have lower precedence than GPOs ____________________________
|
lower precedence than GPOs linked directly to the container
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-41) |
|
|
If there are multiple GPOs, ______________ determines their precedence
|
link order
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-40) |
|
|
How do you change the precedence of a GPO Link?
|
1. Select the OU,site, or domain in the GPMC console tree.
2. Click the Linked Group Policy Objects tab in the details pane. 3. Select the GPO 4. Us the Up, Down, Move To Top, and Move to Bottom arrows to change the link order of the selected GPO (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-41) |
|
|
What is block inheritance
|
Configuring or preventing inheritance of policy settings
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-41) |
|
|
What happens when you Enforce a GPO?
|
The GPO takes the highest level of precedence; policy settings in that a GPO will prevail over any conflicting policy settings in other GPOs
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-42) |
|
|
The enforced policy option causes the policy to ______________________
|
apply to all objects within its scope
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-42) |
|
|
What do you find in the Group Policy Inheritance Tab?
|
shows the GPO takes precedence even over the GPOs linked to the People OU itself.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-42) |
|
|
Where is the Group Policy ACL?
|
Delegation tab --> Advanced
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-43) |
|
|
Authenticated users have allow apply group policy is ______________?
|
Default policy permissions
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-43) |
|
|
What does the ACL do in a GPO?
|
defines the permissions to the GPO
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-43) |
|
|
What are the permissions required for a GPO to apply to a user or computer?
|
- Allow Read Group Policy
-Allow Apply Group Policy (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-43) |
|
|
By default, Authenticated users are given the __________________ permission on each new GPO
|
Allow Apply Group Policy
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-43) |
|
|
When you deny permissions can you see the exclusion in the security filtering tab?
|
No
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-45) |
|
|
What is WMI?
|
is a management infrastructure technology that enables administrators to monitor and control managed objects in the network.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-46) |
|
|
A WMI query is capable of filtering systems based on ________________
|
- Ram
- Processor Speed - Disk Capacity - IP Address _ Operating System Version - Service Pack level - List of attributes - many more (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-46) |
|
|
How do you write a WMI Query?
|
WQL
WMI Query Language (WQL) (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-46) |
|
|
Three significant caveats regarding WMI Filters
|
1. WMI Queries can be challenging to master
2 WMI filters are expensive in terms of Group Policy Processing performance 3. WMI Filters are not processed by computers running Windows 2000 Server (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-48) |
|
|
WHat happens when GPOs are enabled?
|
Both Computer configuration settings and user configuration settings will be processed by CSEs during policy refresh.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-48) |
|
|
What happens when GPO: all settings are disabled
|
CSEs will not process the GPO during policy refresh
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-48) |
|
|
What happens when computer configuration settings are disabled in GPOs
|
During Computer Policy refresh, computer configuration settings in the GPO will not be applied.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-49) |
|
|
What happens in GPOs when User configuration settings are disabled?
|
During User policy refresh, user configuration settings in the GPO will not be applied.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-49) |
|
|
What happens with GPOs in an Emergency?
|
You can define a configuration that should take effect in case of an emergency security incident, or other disasters in a GPO and link the GPO so that it is scoped to appropriate users and computers. Then disable the GPO if you require the configuration to be deployed, enable the GPO
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-6-49) |
|
|
What formula provides the ability to target within a GPO?
|
scope of targeting + Scope of GPO = Scope
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-50) |
|
|
What are the elements of Target Preferences
|
- Targeting within a GPO
- Multiple Options - Test Effect - Test Performance Impact (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-50) |
|
|
Which operating system introduced preferences?
|
Windows server 2008
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-50) |
|
|
What are item-level targeting?
|
Built in scoping mechanism
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-50) |
|
|
What do WMI filters and Item level targeting of preference have in common?
|
Requirement of CSE to perform a query and determine whether to apply the settings in a preference item.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-50) |
|
|
item level target may have a impact __________
|
the performance of your system
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-51) |
|
|
Where does user settings come from?
|
GPOs scoped to the users object in active directory
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-52) |
|
|
VDI
|
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-52) |
|
|
RDS
|
Remote Desktop Services
aka Terminal Services in previous versions (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-52) |
|
|
What does loopback policy processing do?
|
alters the default algorithm used by the group Policy Client to obtain the ordered list of GPOs that should be applied to a user's configuration.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-52) |
|
|
What are the settings for loopback processing?
|
- Not Configured
- Enabled - Disabled (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-52) |
|
|
What is the replace mode in Loopback Policy Processing?
|
In this case, the GPO list for the user (obtained in step 5 in the " Group Policy Processing" the next section) is replaced entirely by the GPO list already obtained for the computer start-up (in step 2). The setting in User Configuration Policies of the computer's GPO are applied to the user. The replace mode us useful in a situation such as a classroom where users should receive a standard configuration rather than the configuration applied to those users in a less managed environment,
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-53) |
|
|
What is the Merge Mode in Loopback Policy Processing?
|
In this case, the GPO list obtained for the computer at computer startup (step 2 in the Group policy processing" section) is appended to the GPO list obtained for the user when logging on (step 5). Because the GPO list obtained for the computer is applied later, settings in the GPos on the computer's list have precedence if they conflict with settings in the user's list. This mode would be useful to apply additional settings to users ' typical configuration when logging on to a computer in a conference room or reception area, but replace the wallpaper with a standard bitmap and disable the user of certain application or device.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-53) |
|
|
What happens when you combine the loopback processing with security group filtering?
|
the application of user settings during policy refresh sees the credentials of the computer to determine which GPOs to apply as part of the loopback processing. However, the logged- on user must also have the Apply Group Policy permission for the GPO to be successfully applied.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-53) |
|
|
7 steps of the details review of Group Policy Processing
|
1. Computer Starts; RPCSS and MUP are started
2. Group Policy Client Starts and obtains an ordered list of GPOs that are scoped to the computer 3. GPC processes each GPO in order 4. User Logs on 5. Process Repeats for user settings 6. Every 90-120 minutes after startup, computer refresh 7. Every 90-120 minutes after logon, user refresh (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-60) |
|
|
What is the ordered list of GPOs?
|
- Local GPOS
- Site GPOs - Domain GPOs - OU GPOs - Enforced GPOs (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-53 and 6-54) |
|
|
How are GPOs processed?
|
synchronously in the order specified in the order list
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-53) |
|
|
WMI filters are applied to what computers?
|
Any computers running Windows XP or later
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-53) |
|
|
If GPOs are applied to the system. ___________trigger to process the GPO settings.
|
CSE
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-53) |
|
|
If the child container is configured with the block inheritance option the parent setting is _______________
|
Not inherited unless the GPO link is configured with the Enforced Option
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-53) |
|
|
If the parent link is configured with the enforced option, the parent setting _____________
|
has precedence
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-61) |
|
|
If a policy setting of GPOs linked to parent containers is Not Configured, and the child OU is also not configured for a child, the child OU setting is _______________
|
also not configured, the resultant policy setting that results from the processing of local GPOs
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-61) |
|
|
How often does a computer policy refresh?
|
Every 90 -120 minutes
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-62) |
|
|
What is determined a slow link?
|
Less than 500kilobites per second (kbps)
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-63) |
|
|
What happens when A Group Policy is disconnected?
|
- settings previously applied will continue to take effect
- Exception includes startup, logon, logoff, and shutdown scripts (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-63) |
|
|
Group Policies in windows vista and higher to what?
|
detect new connections and perform group policy refresh if the refresh window was missed while the system was disconnected.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-6-63) |
|
|
Who provides GPSI?
|
Group Policy Software Installation
software installation CPE provides GPSI (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-63) |
|
|
If a slow ink is detected software is
|
usually not installed
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-63) |
|
|
Can you configure the default slow speed?
|
Yes
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-63) |
|
|
If a computer wakes up and realizes the group policy has been missed
|
it will perform a group policy to obtain the GPOs from the domain
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-64) |
|
|
Before a GPO can take effect, the Group Policy Container (GPC) in Active Directory must be replicated to____
|
The domain Controller from which the Grou Policy Client Obtains its ordered list of GPOs. Additionally the Group Policy Template (GPT in SYSVOL must replicate to the same domain controller)
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-65) |
|
|
If you have added a new group or changed the membership of a group that is used to filter the GPO, that change must be ________
|
replicated, and the change must be in the security token of the computer and the user, which requires a restart (for the computer to update its group membership) or a logoff and logon (for the user to update its group membership.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-65) |
|
|
By default, Windows CP, Windows Vista and Windows 7 client perform background refreshes at
|
start-up and logon
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-65) |
|
|
How do you manually refresh a Group Policy?
|
GPUdate [/force][/logoff][/boot]
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-65) |
|
|
Most CSEs ________________ settings if GPO has not changed.
|
do not reapply settings if the GPO has not changed.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-65) |
|
|
____________ is the net effect of GPOs applied to a user or computer taking into account GPO links, exceptions, such as Enforced and Block inheritance, and application of security and WMI filters.
|
RSoP
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-68) |
|
|
RSoP is also a collection of tools that help you ______________
|
evaluate, model, and troubleshoot the application of Group Policy settings.
|
|
|
RSoP Query
|
can search for local or remote computer and report back the exact settings that were applied to the computer and to any user who has logged on to the computer,
|
|
|
RSoP Model
|
RSoP can model the policy settings that are anticipated to be applied to a user or computer under a variety of scenarios, including moving the object between OUs or sites or changing the object's group membership.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-68) |
|
|
Requirements to generate RSoP Reports
|
- Administrative credentials on the target computer
- Access ti WMI (firewall) - User must have logged on at least once (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-69) |
|
|
Can you save an RSoP report?
|
Yes
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-69) |
|
|
When you view RSoP in advanced mode what happens?
|
Show some settings that do not show in the HTML report
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-69) |
|
|
How can you view group policy processing events?
|
GPResults.exe /s ComputerName /h filename
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-69) |
|
|
What are the requirements for running Group Policy Wizard?
|
- You must have administrative credentials
- The target computer must be running Windows XP or newer. The group Policy Results wizard cannot access Windows 200 systems. - You must be able to access WMI on the target computer. This means it must be powered on, connected to the network, and accessible through ports 135 and 445 - The WMI service must be started on the target computer - If you want to analyze RDoP for a user, that user must have logged on at least once to the computer, it is not necessary for the user to be currently logged on (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-69) |
|
|
In AD how do you run RSoP reports?
|
right click Group Policy Resilts
In th GPMC console tree and than click Group POlicy Reports Wizard (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-70) |
|
|
RSoP Report Summary
|
The summary tab displays the status of Group Policy processing at the last refresh. You can identify information that was collected about the system, the GPOs that were applied and denied, security group membership that might have affected GPOs filtered with the security groups. WMI filters that were analyzed, and the status of CSEs.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-70) |
|
|
RSoP Report Settings
|
The settings tab displays the resultant set of policy settings applied to the computer or user. This tab shows you exactly what has happened to the user through the effects of your Group Policy implementation. A tremendous amount of information can be gleaned from the Settings tab, but some data isn't reported, such as IPSec, wireless, and disk quota policy settings,
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-70) |
|
|
RSoP Report Policy Events
|
The policy events tab displays group policies events from the event logs of the target computer
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-70) |
|
|
How would you generate RSoP reports in command prompt?
|
GPResult.exe
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-70) |
|
|
GPResult /scomputername
|
This option specifies the name or IP address of a remote system. If you use a dot (.) as the computer name, or do not include the /s option, the RSoP analysis is performed in the local computer.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-70) |
|
|
GPResult /scope [user |computer]
|
This displays RSoP analysis for user or computer settings. If you omit the /scop option, RSOP analysis includes both user and computer settings.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-71) |
|
|
GPResult /userusername
|
This specifies the name of the user for which RSoP data is to be displayed
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-71) |
|
|
GPResult /r
|
This option displays the summary of RSoP data.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-71) |
|
|
GPResult /v
|
This option displays a verbose data, including the details of all policy settings applied to the system. Often, this is more information than you will require for typical Group Policy troubleshooting.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-71) |
|
|
GPResult /z
|
This displays super verbose data, including the details of all policy settings applied to the system. Often, this is more information than you will require for typical Group Policy Troubleshooting.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-71) |
|
|
GPResult /udomain\user/ppassword
|
This provides credentials that are in the Administrators group of a remote system. Without these credentials. GPResult runs by using the credentials with which you are logged on.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-71) |
|
|
GPResult [/x | /h] filename
|
This option saves the reports in the CML or HTML format. These options are availiable in Windows Vist SP1 and later, Windows Server 2008 and later, and Windows 7.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-71) |
|
|
How do you perform Group Policy Modeling in AD?
|
Right click Group Policy Modeling node in the GPMC console treem
Click group policy modeling wizard than perform steps in the wizard (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-71) |
|
|
What does the Group Policy Modeling Wizard do?
|
- Emulates Group Policy application to report anticipated RSoP
- Can be used prior to GPO application - Recommended in Group Policy design phase (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-71) |
|
|
How is modeling performed?
|
by conducting a simulation on a domain controller.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-71) |
|
|
Once connected to a domain controller, what are you asked to specify in Group Policy Modeling?
|
- select user or computer objects to evaluate or specify the OU, site or domain to evaluate
- Choose whether slow lonk processing should be simulated - Specify to simulate loopback precessing and if so, choose Replace or Merge Mode - Select Site to simulate - Select security Groups for the user and for the computer - Chose which WMI Filters to apply in the simulation of user and computer policy processing (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-71) |
|
|
After the settings are specified on a group policy modelling what happens?
|
A report is produced
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-71) |
|
|
What do you find in the system log?
|
You will find high-level information about Group Policy, including errors created by the group policy client when it cannot connect to a domain controller or locate GPOs
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-74) |
|
|
What are some Policy Event Logs?
|
- System Log
- Application Log - Group Policy Operational log (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-74) |
|
|
What is an application log?
|
Captures the events recorded by CSEs
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-74) |
|
|
What is a new log called the Group Policy Operational Log?
|
it provides detailed information about Group Policy Processing
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-74) |
|
|
What are 4 best practices for Group Policy Management?
|
1. Name Group Policy Objects, so you can easily identify them by name.
2. Apply Group Policy Objects as high as possible in AD DS hierarchy 3. Use Block Inheritance and Enforced options only when really necessary 4. Make Comments of GPO settings (Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-81) |
|
|
What is the Group Policy Reporting RSoP Tool?
|
Reporting information about the current policies being delivered to clients.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-81) |
|
|
What is the GPResult tool?
|
A command-line utility that displays RSoP information.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-81) |
|
|
What is th GPU Update tool
|
Refreshing local and AD DS-based Group Policy Settings
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-82) |
|
|
What is the Dcgpofix tool?
|
Restoring the Group Policy Objects to their original stat after initial installation.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-82) |
|
|
What is the GPOLogView Tool?
|
Exporting Group Policy-related events from the systen and operational logs into text HTML or XML files. For use with Windows Vista, Windows 7 and later versions
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-81) |
|
|
What is the Group Policy Management Scripts?
|
Sample scripts that perform a number of troubleshooting and maintenance tasks.
(Microsoft, 2011 p. 6-81) |

