![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Amphipathic lipid
|
Have hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts
polar head groups are hydrophilic hydrocarbon chain "tails" are hydrophobic |
|
|
polar head group
|
alcohol+phosphate
|
|
|
transverse vs lateral diffusion
|
transverse- flip flop, occurs with help of flippases, very rare
lateral diffusion- pairwise exchange of neighboring phospholipid molecules in the same bilayer leaflet |
|
|
melting (transition) temperature
|
temperature where transition between rigid and liquid states occur
|
|
|
membrane permeability of lipid bilayer
|
-highly impermeable to polar substances
-impermeable to ions |
|
|
integral vs. peripheral membrane proteins
|
integral is actual inside of the membrane
-transmembrane, mono-layer associated, lipid-linked peripheral is when the protein is on the outside of the membrane -protein-attached |
|
|
fluid mosaic model
|
1) lipid bilayer acts as a solvent for membrane proteins
2)membrane proteins are free to diffuse laterally, but cannot flip-flop |
|
|
sources of membrane protein immobility
|
- anchoring the protein to an intracellular structure such as cytoskeleton
- protein-protein interaction between two cells such as neurological of immunological synapses - integral membrane proteins can be "corraled" to a single area on the cell, such as the apical or basolateral face, by cell-cell interactions such as tight junctions -anchoring protein to extracellular structure, such as the extracellular matrix |
|
|
oriented monolayer
|
formed by an ampithatic lipid at an air water interface
|
|
|
FRAP- florescent recovery after photobleaching
|
attach flourescence to the membrane proteins, zap a small area of membrane to bleach it and then see how long it takes for the proteins to migrate into the bleached area so it flouresces again
|
|
|
factors governing membrane fluidity
|
temperature-high temp increases fluidity
length and degree of unsaturation of fatty acid chains-saturated decreases fluidity cholesterol-decrease |
|
|
detergent solubilization
|
membrane proteins can be removed from bio membranes by the addition of detergents
|
|
|
lipid rafts
|
regions of the membrane that are less fluid, and more resistant to solubilization by detergents. In addition to lipids such as sphingolipids and cholesterol, transmembrane domains also show a preference to rafts.
they are implicated in: -signal transduction -protein sorting -recognition -viral entry or exit from the cell |
|
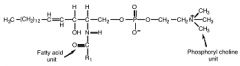
|
sphingomyelin
HYDROPHOBIC PART fatty acid chain plus phosphoryl choline HYDROPHILIC PART hydrocarbon chain of |
|

|
Phospholipid
Hydrophobic part- fatty acid chains Hydrophilic part- phosphorylated alcohol |
|

|
Glycolipid
hydrophobic part-fatty acid chain plus hydrocarbon chain of sphingosine hydrophilic part- one or more sugars |
|

|
Cholesterol
Hydrophobic- everything except OH Hydrophilic- OH |

