![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
422 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nationalism, Alliances, Imperialism, and Militarism
|
Causes of World War I
|
|
|
A desire to expand and be more powerful than other nations.
|
Nationalism
|
|
|
A desire by a national group to have its own state or country.
|
Nationalism
|
|
|
Establishing authority over areas of the world outside a country's natural boundaries.
|
Imperialism
|
|
|
Establishing colonies throughout the world.
|
Imperialism
|
|
|
Resulted in conflicts over colonial possessions.
|
Imperialism
|
|
|
The glorification of armed strength.
|
Militarism
|
|
|
Militarism resulted in an _______.
|
arms race
|
|
|
Militarism and imperialism were components of ____________.
|
Nationalism
|
|
|
The European balance of power was disrupted by the unifications of _________________
|
Germany and Italy
|
|
|
European nations sought a new balance of power through __________.
|
alliances
|
|
|
Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy. (Name of Alliance)
|
Triple Alliance
|
|
|
Kaiser William II let Germany's friendship treaty lapse with ___________.
|
Russia
|
|
|
Great Britain, France and Russia (name of alliance)
|
Triple Entente
|
|
|
Pulled all of Europe into the war.
|
Alliance system
|
|
|
German ruler during WWI
|

Kaiser William II (Kaiser Wilhelm II)
|
|
|
Kaiser William II sought to compete with Britain by building a _____________.
|
large navy
|
|
|
Wanted Alsace and Lorraine back from Germany.
|
France
|
|
|
Austria-Hungary and Ottoman Turkey feared they would lose territory in the ____
|
Balkans
|
|
|
Held that all Slavic people shared a common nationality.
|
Pan-Slavism
|
|
|
Unrest in this region made it a "powder keg" prior to World War I.
|
Balkans
|
|
|
Austria-Hungary and Russia struggled over the _____________. (area)
|
Balkans
|
|
|
Province of Austria-Hungary with a large Serbian population
|
Bosnia
|
|
|
Nationalists from this country believed Bosnia should belong to their country.
|
Serbia
|
|
|
Heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne.
|

Archduke Francis Ferdinand
|
|
|
Was assassinated by a Serbian nationalist.
|

Archduke Francis Ferdinand
|
|
|
Germany promised Austria-Hungary total support.
|

"Blank Check"
|
|
|
Russians and Serbians were both _________.
|
Slavic
|
|
|
Russians hoped to gain access to IT through the Balkans.
|
Mediterranean Sea
|
|
|
Austria-Hungary issued Serbia an __________.
|
Ultimatum
|
|
|
Austria-Hungary's ultimatum would have limited ____________.
|
Serbia's independence
|
|
|
In the first move of the war Austria Hungary declared war on ___________.
|
Serbia
|
|
|
Nation that supported Serbia
|
Russia
|
|
|
To get an army in position for war. (term)
|
Mobilize
|
|
|
Russia decided to mobilize early because it lacked ____________.
|
railroads
|
|
|
In German eyes Russia's mobilization amounted to a ____________.
|
declaration of war
|
|
|
Declared war on Russia.
|
Germany
|
|
|
When France promised to support Russia __________.
|
Germany declared war on France
|
|
|
Germany hoped to avoid fighting a _________.
|
two front war
|
|
|
German plan to defeat France before Russia could mobilize.
|

Schlieffen Plan
|
|
|
The Schlieffen Plan was intended to keep Germany from fighting a __________.
|
two front war
|
|
|
Germany requested passage to France through ______________.
|
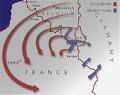
neutral Belgium
|
|
|
When they refused Germany passage, Germany invaded __________.
|
Belgium
|
|
|
Germany invaded France through ___________.
|
neutral Belgium
|
|
|
It declared war on Germany because Germany had violated Belgium neutrality.
|
Great Britain
|
|
|
World War I began in ______. (year)
|
1914
|
|
|
Germany, Austria-Hungary, Ottoman Turks and their allies. (what they were called)
|
Central Powers
|
|
|
France, Britain, Russia and their allies. (what they were called)
|
Allies
|
|
|
Allied victory that saved Paris. (early in the war)
|
Battle of the Marne
|
|
|
Allied victory that destroyed the Schlieffen Plan
|
Battle of the Marne
|
|
|
Made the defense stronger than the offense. (in warfare)
|
Trench Warfare
|
|
|
Made the fighting even more brutal. (in warfare)
|
Trench Warfare
|
|
|
As a result of trench warfare the war became a ____________.
|
stalemate
|
|
|
In a struggle where neither side can improve its position
|
stalemate
|
|
|
Played a major part in the deadlock and slaughter of trench warfare. (weapon)
|
Machine Gun
|
|
|
Choked and blinded victims. (weapon)
|
Poison Gas
|
|
|
The space between two sets of trenches.
|
No-man's-land
|
|
|
Most World War I soldiers were __________.
|
draftees
|
|
|
Both sides attempted to prevent the enemy from getting supplies. (method)
|
blockades
|
|
|
The Allies had a more effective blockade because of the ____________.
|
British Navy
|
|
|
To make their blockade more effective the Germans began to use ____________.
|
Submarine Warfare
|
|
|
Broke international law by not giving warning or taking passengers.
|
Submarine Warfare
|
|
|
British Luxury liner sunk by German Sub. (120 Americans die)
|
Lusitania
|
|
|
When countries mobilize all their resources into the war effort.
|
Total War
|
|
|
Used by governments to conserve supplies
|
Rationing
|
|
|
Using information to encourage a particular point of view.
|
Propaganda
|
|
|
Propaganda was used by _____________.
|
both sides
|
|
|
Were more effective in the use of propaganda.
|
Allies
|
|
|
Was the first of the major countries to become exhausted from total war.
|
Russia
|
|
|
Resulted in the setting up of a liberal government. (during World War I)
|
First Russian Revolution (of 1917)
|
|
|
After this event, this country still tried to continue fighting the war.
|
First Russian Revolution
|
|
|
Secret weapon shipped into Russia by the Germans.
|
Vladimir Lenin
|
|
|
Results in the setting up of a Communist Gov.
|
Second Russian Revolution (of 1917)
|
|
|
Communist Russia makes a separate peace with Germany.
|
Treaty of Brest Litovsk
|
|
|
Allows Germany to fight a one front war.
|
Treaty of Brest Litovsk
|
|
|
The area of contact between opposing sides in warfare.
|
front
|
|
|
To starve the allies in hopes of defeating them before America entered the war Germany resumed ______________.
|
unrestricted submarine warfare
|
|
|
Germany offered Mexico a part of the U.S. if it would join the war.
|
Zimmerman Note
|
|
|
Unrestricted Submarine Warfare and the Zimmerman note ________________.
|
bring U.S. into the war
|
|
|
Year of America's entrance into WWI.
|
1917
|
|
|
Year of both Russian Revolutions.
|
1917
|
|
|
Arabs seeking independence helped the allies fight against the _____________.
|
Ottoman Turks
|
|
|
Machine gun, tanks, submarines, airplanes, gas.
|
new weapons of WWI
|
|
|
New weapons and trench warfare turned WWI into a _____________.
|
war of attrition
|
|
|
When the winner in war is determined by who can continue to fight the longest.
|
war of attrition
|
|
|
Helps break the stalemate and bring an allied victory.
|
U.S. entrance
|
|
|
Ends the fighting after the Kaiser abdicated his throne.
|
Armistice
|
|
|
Date of the Armistice
|
1918
|
|
|
Russia and the defeated Central powers were not invited to the _____________.
|
Paris Peace Conference
|
|
|
Most influential man at the peace conference.
|
Woodrow Wilson
|
|
|
Leader of the American delegation to the peace conference
|
Woodrow Wilson
|
|
|
Wilson's goals for the war and peace plan after the war.
|
Fourteen Points
|
|
|
Included reduction of armaments, national self determination, end to secret alliances, and a League of Nations.
|
Fourteen Points
|
|
|
Attempting to draw boundaries around recognizable national groups.
|
National Self Determination
|
|
|
Was to support peace by solving conflict through negotiations.
|
League of Nations
|
|
|
It was based on the idea of collective security.
|
League of Nations
|
|
|
System in which a group of nations acts as one to preserve the peace of all.
|
Collective Security
|
|
|
Wilson compromised on other points to secure the inclusion of the ______________.
|
League of Nations
|
|
|
The U.S. Senate did not ratify the Treaty of Versailles because they thought the _________ would limit the war making powers of congress.
|
League of Nations
|
|
|
Placed total blame for the war on Germany
|
Treaty of Versailles
|
|
|
The Treaty of Versailles forced Germany to pay ____________.
|
reparations
|
|
|
Payment for damages in a war.
|
reparations
|
|
|
The treaty of Versailles failed to create a lasting peace because it was ___________.
|
too harsh on Germany
|
|
|
The two Russian revolutions in 1917 were largely the result of the hardship caused by ___________.
|
World War I
|
|
|
The biggest mistake made by Czar Nicholas II.
|
going to war
|
|
|
Russian Czar overthrown by the revolution.
|
Nicholas II
|
|
|
After a revolution in 1905, Nicholas Ii approved the creation of a parliament called the _______.
|
Duma
|
|
|
Believed revolution against the Czar would be led by peasants.
|
Social Revolutionaries
|
|
|
Wanted to replace the czar with a democratic government.
|
Social Revolutionaries
|
|
|
Russian Marxists
|
Social Democrats
|
|
|
Believed revolution in Russia would come from urban workers.
|
Social Democrats
|
|
|
Social Democrats who believed the Industrial Revolution had to precede the workers revolt.
|
Mensheviks
|
|
|
Social Democrats who wanted a broadly based party.
|
Mensheviks
|
|
|
The Social Democrats were NOT _________.
|
Democratic
|
|
|
Social Democrats who believed the workers revolt could precede the Industrial Revolution.
|
Bolsheviks
|
|
|
Social Democrats who believed the Communist party should be an elite group of professional revolutionaries.
|
Bolsheviks
|
|
|
Leader of the Bolsheviks
|
Vladimir Lenin
|
|
|
Workers' councils organized in Russia in 1917.
|
Soviets
|
|
|
While Nicholas II was at the front he left control of Russia to ____________.
|
Czarina Alexandra
|
|
|
Czarina Alexandra was influenced by the mystic __________.
|
Rasputin
|
|
|
Nicholas II was forced to abdicate in February of 1917 by __________________.
|
Bread Riots and Strikes in St. Petersburg
|
|
|
After Nicholas II abdicated the Duma set up a _______________.
|
Provisional Government
|
|
|
Leader of the Provisional Government. (Russia)
|
Alexander Kerensky
|
|
|
In St. Petersburg the ________ was more powerful than the provisional government.
|
Soviet
|
|
|
The mistake of the provisional government was to ___________________. (Russia)
|
continue the war
|
|
|
Lenin's slogan.
|
"Peace, Land, and Bread"
|
|
|
Took over Government offices in October 1917. (Russia)
|
Bolshevik Red Guards
|
|
|
The second Russian Revolution of 1917 was a _____________.
|
Coup d' etat
|
|
|
Won a majority in the popular elections held in 1917.
|
Social Revolutionaries
|
|
|
When the Bolsheviks did not win a majority in the elections they ___________.
|
closed the Assembly
|
|
|
From 1918 to 1920 Russia was in __________.
|
Civil War
|
|
|
Those who fought against the Bolsheviks.
|
White Army
|
|
|
A mixture of: Czarists, Social Revolutionaries and Mensheviks.
|
White Army
|
|
|
Leader of the Red Army.
|
Leon Trotsky
|
|
|
Won the Russian Civil War.
|
Red Army
|
|
|
Was supported by the Allies (including the U.S.) in the Russian Civil War.
|
White Army
|
|
|
The government established by Lenin and the Bolsheviks was ___________.
|
Communist
|
|
|
Brutal secret police force of the Bolheviks.
|
Cheka
|
|
|
Red Army officers were kept under close watch of _____.
|
commissars
|
|
|
Communist party officials.
|
commissars
|
|
|
In 1922, Lenin's communist government united much of the old Russian empire into the ____>
|
Soviet Union
|
|
|
Union of Soviet Socialist Republics/USSR
|
Soviet Union
|
|
|
According to the new Constitution of the Soviet Union all political power, resources, and means of production would belong to the _______.
|
workers and peasants
|
|
|
In reality in the Soviet Union the ______ held all of the power.
|
Communist Party
|
|
|
To help save the Soviet economy Lenin was forced to use some features of _______.
|
capitalism
|
|
|
Struggled for power after the death of Lenin.
|
Trotsky and Stalin
|
|
|
Took ruthless steps to win total power over the Soviet Union.
|
Joseph Stalin
|
|
|
In the 1900s much of Latin America's natural resources were controled by ______.
|
investors from other countries
|
|
|
In Latin America in the early 1900s most of the power was held by ______.
|
Military leaders and wealthy land owners
|
|
|
Large farms in Mexico worked by the peasants owned by the rich.
|
haciendas.
|
|
|
When dictator Porfirio Diaz left office in Mexico in 1911 the ______________ began.
|
Mexican Revoltion
|
|
|
He apporoved a new constitution that included land and labor reform when he was elected Mexico's president in 1917.
|
Venustiano Carranza
|
|
|
Made church land "the property of the nation," set a minimum wage and protected the right of workers' to strike in Mexico.
|
Constitution of 1917
|
|
|
Carranza's new government strengthened the government's control over the economy through ________.
|
nationalization
|
|
|
Government takeover of natural resources.
|
nationalization
|
|
|
Organized by the government it brings some stablity to Mexico by accomadating some desires of bussiness, military leaders, peasants and workers.
|
PRI
|
|
|
Institutional Revolutionary Party
|
PRI
|
|
|
Dominated Mexican politics from the 1930s until free elections in 2000.
|
PRI
|
|
|
Hurt Latin American economies as it did the rest of the world in the 1930s.
|
Great Depression
|
|
|
Became popular in Latin America as a result of the Great Depression.
|
Economic Nationalism
|
|
|
Home control of an economy.
|
Economic Nationalism
|
|
|
In Latin America in the 1930s it resulted in the rejection of Euoropean influences.
|
Cultural Nationalism
|
|
|
President Franklin Roosevelt's policy to stay out of Latin American politics.
|
Good Neighbor policy
|
|
|
In the 1900s controlled most of Africa and kept the best lands or themselves.
|
Europeans
|
|
|
From 1910 to 1940 blacks here lost the right to vote and were kept from certain jobs.
|
South Africa
|
|
|
The system of strict segregation that became law in South Africa in 1948.
|
Apartheid
|
|
|
A movement that called for the unity of Africans and those of African descent around the world.
|
Pan-Africanism
|
|
|
Marcus Garvey and W.E.B. Dubois were leaders in the _______.
|
Pan-African movement
|
|
|
A movement in West Africa and the Carribbean, in which writers expressed pride in their African roots and protested colonial rule.
|
negritude movement
|
|
|
Overthrew the Ottoman ruler and created the Republic of Turkey.
|
Mustafa Kemel
|
|
|
Mustafa Kemal worked to __________.
|
modernize Turkey
|
|
|
Inspired by Mustafa Kemal he overthrew the Persian shah and worked to modernize Persia/Iran.
|
Reza Khan
|
|
|
Both Mustafa Kemal & Reza Khan replaced Islamic traditions with _____________.
|
Western ways
|
|
|
Arab nationalism.
|
Pan-Arabism
|
|
|
Arabs had hoped to gain independence after World War I but felt betrayed when ______.
|
French and British took control of their lands.
|
|
|
Jewish Nationalist dreamed of a homeland in ________.
|
Palestine
|
|
|
To show support for European Jews, Britain issued the _______.
|
Balfour Declaration
|
|
|
A statement advocating a homeland for Jews in Palestine in 1917.
|
Balfour Declaration
|
|
|
In April of 1919, British soldiers killed and wounded hundreds of peaceful Indian protesteters.
|
Amristar massacre
|
|
|
Convinced Indians that their country should be independent of Britain.
|
Amristar massacre
|
|
|
For 20 years, he fought laws in South Africa that discriminated against Indians.
|
Mohandas Gandhi
|
|
|
Emerged as the leader of the Indian indpendence movement.
|
Mohandas Gandhi
|
|
|
Gandhi followed Henry David Thoreau's ideas of _______.
|
civil disobedience
|
|
|
The practice of not obeying unjust laws.
|
civil disobedience
|
|
|
Indians following Gandhi's nonviolent civil disobedience and British reactions slowly led to the British _______.
|
giving some power to Indians
|
|
|
When the Qing dynasty collapsed and Sun Yixian became president, China fell into chaos and __________.
|
warlords battled for control
|
|
|
Was issued by Japan during World War I in an attempt to give Japan control over China.
|
Twenty-One Demands
|
|
|
During the early 20th century China was weak and gave into many of _____.
|
Japan's demands
|
|
|
After World War I the allies gave Japan control over some former __________.
|
German lands in China
|
|
|
Was inspired by the Allies giving German lands in China to Japan.
|
May Fourth Movement
|
|
|
An intellectual movement to make China strong and to resist European imperialsm through the use of Western ideas.
|
May Fourth Movement
|
|
|
Encouraged by the Soviet Union some Chinese turned to ______.
|
Marxism
|
|
|
Nationalist party in China
|
Guomindang
|
|
|
Leader of the Guomindang from the late 1920s until 1949.
|
Jiang Jieshi
|
|
|
Chiang Kai-Shek
|
Jiang Jieshi
|
|
|
Used the help of the Chinese communists to crush the warlords.
|
Jiang Jieshi
|
|
|
In the middle of his campaign against the warlords he turned on the communists and slaughtered many of them.
|
Jiang Jieshi
|
|
|
Becomes the leader of the Chinese Communists by seeking the support of the peasant masses.
|
Mao Zedong
|
|
|
A trek of 6000 miles by Chinese Communists led by Mao Zedong to relocate their power base.
|
The Long March
|
|
|
The Guomindang under the leadership of Jiang Jieshi attacked the communists throughout the _____.
|
Long March
|
|
|
The Guomindang fought the Communists in a 22 year ______.
|
Civil War
|
|
|
Invaded China in 1937.
|
Japan
|
|
|
Because of the invasion Jiang Jieshi and Mao Zedong formed an alliance until the ________.
|
Japanese threat ended
|
|
|
Because of exports to the Allies Japan's economy grew during ______.
|
World War I
|
|
|
Became emperor of Japan in 1926.
|
Hirohito
|
|
|
During the 1920s Japan had a more ______.
|
Liberal/democratic government
|
|
|
A group of business leaders who manipulated politicians.
|
Zaibatsu
|
|
|
Were angry with the government of Japan for giving into Western demands and for accepting payoffs from the Zaibatsu
|
Military leaders and ultranationalists
|
|
|
Blew up railroad tracks in Manchuria and blamed it on the Chinese as an excuse to invade Manchuria.
|
Japanese Militarists
|
|
|
Increased their power in Japan throughout the 1930s.
|
Military leaders and Ultranationalists
|
|
|
In 1940 it signed an agreement with Italy and Germany to form the Axis Powers.
|
Japan
|
|
|
Nationalism, Alliances, Imperialism, and Militarism
|
Causes of World War I
|
|
|
A desire to expand and be more powerful than other nations.
|
Nationalism
|
|
|
A desire by a national group to have its own state or country.
|
Nationalism
|
|
|
Establishing authority over areas of the world outside a country's natural boundaries.
|
Imperialism
|
|
|
Establishing colonies throughout the world.
|
Imperialism
|
|
|
Resulted in conflicts over colonial possessions.
|
Imperialism
|
|
|
The glorification of armed strength.
|
Militarism
|
|
|
Militarism resulted in an _______.
|
arms race
|
|
|
Militarism and imperialism were components of ____________.
|
Nationalism
|
|
|
The European balance of power was disrupted by the unifications of _________________
|
Germany and Italy
|
|
|
European nations sought a new balance of power through __________.
|
alliances
|
|
|
Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy. (Name of Alliance)
|
Triple Alliance
|
|
|
Kaiser William II let Germany's friendship treaty lapse with ___________.
|
Russia
|
|
|
Great Britain, France and Russia (name of alliance)
|
Triple Entente
|
|
|
Pulled all of Europe into the war.
|
Alliance system
|
|
|
German ruler during WWI
|
Kaiser William II (Kaiser Wilhelm II)
|
|
|
Kaiser William II sought to compete with Britain by building a _____________.
|
large navy
|
|
|
Wanted Alsace and Lorraine back from Germany.
|
France
|
|
|
Austria-Hungary and Ottoman Turkey feared they would lose territory in the ____
|
Balkans
|
|
|
Held that all Slavic people shared a common nationality.
|
Pan-Slavism
|
|
|
Unrest in this region made it a "powder keg" prior to World War I.
|
Balkans
|
|
|
Austria-Hungary and Russia struggled over the _____________. (area)
|
Balkans
|
|
|
Province of Austria-Hungary with a large Serbian population
|
Bosnia
|
|
|
Nationalists from this country believed Bosnia should belong to their country.
|
Serbia
|
|
|
Heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne.
|
Archduke Francis Ferdinand
|
|
|
Was assassinated by a Serbian nationalist.
|
Archduke Francis Ferdinand
|
|
|
Germany promised Austria-Hungary total support.
|
"Blank Check"
|
|
|
Russians and Serbians were both _________.
|
Slavic
|
|
|
Russians hoped to gain access to IT through the Balkans.
|
Mediterranean Sea
|
|
|
Austria-Hungary issued Serbia an __________.
|
Ultimatum
|
|
|
Austria-Hungary's ultimatum would have limited ____________.
|
Serbia's independence
|
|
|
In the first move of the war Austria Hungary declared war on ___________.
|
Serbia
|
|
|
Nation that supported Serbia
|
Russia
|
|
|
To get an army in position for war. (term)
|
Mobilize
|
|
|
Russia decided to mobilize early because it lacked ____________.
|
railroads
|
|
|
In German eyes Russia's mobilization amounted to a ____________.
|
declaration of war
|
|
|
Declared war on Russia.
|
Germany
|
|
|
When France promised to support Russia __________.
|
Germany declared war on France
|
|
|
Germany hoped to avoid fighting a _________.
|
two front war
|
|
|
German plan to defeat France before Russia could mobilize.
|
Schlieffen Plan
|
|
|
The Schlieffen Plan was intended to keep Germany from fighting a __________.
|
two front war
|
|
|
Germany requested passage to France through ______________.
|
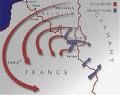
neutral Belgium
|
|
|
When they refused Germany passage, Germany invaded __________.
|
Belgium
|
|
|
Germany invaded France through ___________.
|
neutral Belgium
|
|
|
It declared war on Germany because Germany had violated Belgium neutrality.
|
Great Britain
|
|
|
World War I began in ______. (year)
|
1914
|
|
|
Germany, Austria-Hungary, Ottoman Turks and their allies. (what they were called)
|
Central Powers
|
|
|
France, Britain, Russia and their allies. (what they were called)
|
Allies
|
|
|
Allied victory that saved Paris. (early in the war)
|
Battle of the Marne
|
|
|
Allied victory that destroyed the Schlieffen Plan
|
Battle of the Marne
|
|
|
Made the defense stronger than the offense. (in warfare)
|
Trench Warfare
|
|
|
Made the fighting even more brutal. (in warfare)
|
Trench Warfare
|
|
|
As a result of trench warfare the war became a ____________.
|
stalemate
|
|
|
In a struggle where neither side can improve its position
|
stalemate
|
|
|
Played a major part in the deadlock and slaughter of trench warfare. (weapon)
|
Machine Gun
|
|
|
Choked and blinded victims. (weapon)
|
Poison Gas
|
|
|
The space between two sets of trenches.
|
No-man's-land
|
|
|
Most World War I soldiers were __________.
|
draftees
|
|
|
Both sides attempted to prevent the enemy from getting supplies. (method)
|
blockades
|
|
|
The Allies had a more effective blockade because of the ____________.
|
British Navy
|
|
|
To make their blockade more effective the Germans began to use ____________.
|
Submarine Warfare
|
|
|
Broke international law by not giving warning or taking passengers.
|
Submarine Warfare
|
|
|
British Luxury liner sunk by German Sub. (120 Americans die)
|
Lusitania
|
|
|
When countries mobilize all their resources into the war effort.
|
Total War
|
|
|
Used by governments to conserve supplies
|
Rationing
|
|
|
Using information to encourage a particular point of view.
|
Propaganda
|
|
|
Propaganda was used by _____________.
|
both sides
|
|
|
Were more effective in the use of propaganda.
|
Allies
|
|
|
Was the first of the major countries to become exhausted from total war.
|
Russia
|
|
|
Resulted in the setting up of a liberal government. (during World War I)
|
First Russian Revolution (of 1917)
|
|
|
After this event, this country still tried to continue fighting the war.
|
First Russian Revolution
|
|
|
Secret weapon shipped into Russia by the Germans.
|
Vladimir Lenin
|
|
|
Results in the setting up of a Communist Gov.
|
Second Russian Revolution (of 1917)
|
|
|
Communist Russia makes a separate peace with Germany.
|
Treaty of Brest Litovsk
|
|
|
Allows Germany to fight a one front war.
|
Treaty of Brest Litovsk
|
|
|
The area of contact between opposing sides in warfare.
|
front
|
|
|
To starve the allies in hopes of defeating them before America entered the war Germany resumed ______________.
|
unrestricted submarine warfare
|
|
|
Germany offered Mexico a part of the U.S. if it would join the war.
|
Zimmerman Note
|
|
|
Unrestricted Submarine Warfare and the Zimmerman note ________________.
|
bring U.S. into the war
|
|
|
Year of America's entrance into WWI.
|
1917
|
|
|
Year of both Russian Revolutions.
|
1917
|
|
|
Arabs seeking independence helped the allies fight against the _____________.
|
Ottoman Turks
|
|
|
Machine gun, tanks, submarines, airplanes, gas.
|
new weapons of WWI
|
|
|
New weapons and trench warfare turned WWI into a _____________.
|
war of attrition
|
|
|
When the winner in war is determined by who can continue to fight the longest.
|
war of attrition
|
|
|
Helps break the stalemate and bring an allied victory.
|
U.S. entrance
|
|
|
Ends the fighting after the Kaiser abdicated his throne.
|
Armistice
|
|
|
Date of the Armistice
|
1918
|
|
|
Russia and the defeated Central powers were not invited to the _____________.
|
Paris Peace Conference
|
|
|
Most influential man at the peace conference.
|
Woodrow Wilson
|
|
|
Leader of the American delegation to the peace conference
|
Woodrow Wilson
|
|
|
Wilson's goals for the war and peace plan after the war.
|
Fourteen Points
|
|
|
Included reduction of armaments, national self determination, end to secret alliances, and a League of Nations.
|
Fourteen Points
|
|
|
Attempting to draw boundaries around recognizable national groups.
|
National Self Determination
|
|
|
Was to support peace by solving conflict through negotiations.
|
League of Nations
|
|
|
It was based on the idea of collective security.
|
League of Nations
|
|
|
System in which a group of nations acts as one to preserve the peace of all.
|
Collective Security
|
|
|
Wilson compromised on other points to secure the inclusion of the ______________.
|
League of Nations
|
|
|
The U.S. Senate did not ratify the Treaty of Versailles because they thought the _________ would limit the war making powers of congress.
|
League of Nations
|
|
|
Placed total blame for the war on Germany
|
Treaty of Versailles
|
|
|
The Treaty of Versailles forced Germany to pay ____________.
|
reparations
|
|
|
Payment for damages in a war.
|
reparations
|
|
|
The treaty of Versailles failed to create a lasting peace because it was ___________.
|
too harsh on Germany
|
|
|
The two Russian revolutions in 1917 were largely the result of the hardship caused by ___________.
|
World War I
|
|
|
The biggest mistake made by Czar Nicholas II.
|
going to war
|
|
|
Russian Czar overthrown by the revolution.
|
Nicholas II
|
|
|
After a revolution in 1905, Nicholas Ii approved the creation of a parliament called the _______.
|
Duma
|
|
|
Believed revolution against the Czar would be led by peasants.
|
Social Revolutionaries
|
|
|
Wanted to replace the czar with a democratic government.
|
Social Revolutionaries
|
|
|
Russian Marxists
|
Social Democrats
|
|
|
Believed revolution in Russia would come from urban workers.
|
Social Democrats
|
|
|
Social Democrats who believed the Industrial Revolution had to precede the workers revolt.
|
Mensheviks
|
|
|
Social Democrats who wanted a broadly based party.
|
Mensheviks
|
|
|
The Social Democrats were NOT _________.
|
Democratic
|
|
|
Social Democrats who believed the workers revolt could precede the Industrial Revolution.
|
Bolsheviks
|
|
|
Social Democrats who believed the Communist party should be an elite group of professional revolutionaries.
|
Bolsheviks
|
|
|
Leader of the Bolsheviks
|
Vladimir Lenin
|
|
|
Workers' councils organized in Russia in 1917.
|
Soviets
|
|
|
While Nicholas II was at the front he left control of Russia to ____________.
|
Czarina Alexandra
|
|
|
Czarina Alexandra was influenced by the mystic __________.
|
Rasputin
|
|
|
Nicholas II was forced to abdicate in February of 1917 by __________________.
|
Bread Riots and Strikes in St. Petersburg
|
|
|
After Nicholas II abdicated the Duma set up a _______________.
|
Provisional Government
|
|
|
Leader of the Provisional Government. (Russia)
|
Alexander Kerensky
|
|
|
In St. Petersburg the ________ was more powerful than the provisional government.
|
Soviet
|
|
|
The mistake of the provisional government was to ___________________. (Russia)
|
continue the war
|
|
|
Lenin's slogan.
|
"Peace, Land, and Bread"
|
|
|
Took over Government offices in October 1917. (Russia)
|
Bolshevik Red Guards
|
|
|
The second Russian Revolution of 1917 was a _____________.
|
Coup d' etat
|
|
|
Won a majority in the popular elections held in 1917.
|
Social Revolutionaries
|
|
|
When the Bolsheviks did not win a majority in the elections they ___________.
|
closed the Assembly
|
|
|
From 1918 to 1920 Russia was in __________.
|
Civil War
|
|
|
Those who fought against the Bolsheviks.
|
White Army
|
|
|
A mixture of: Czarists, Social Revolutionaries and Mensheviks.
|
White Army
|
|
|
Leader of the Red Army.
|
Leon Trotsky
|
|
|
Won the Russian Civil War.
|
Red Army
|
|
|
Was supported by the Allies (including the U.S.) in the Russian Civil War.
|
White Army
|
|
|
The government established by Lenin and the Bolsheviks was ___________.
|
Communist
|
|
|
Brutal secret police force of the Bolheviks.
|
Cheka
|
|
|
Red Army officers were kept under close watch of _____.
|
commissars
|
|
|
Communist party officials.
|
commissars
|
|
|
In 1922, Lenin's communist government united much of the old Russian empire into the ____>
|
Soviet Union
|
|
|
Union of Soviet Socialist Republics/USSR
|
Soviet Union
|
|
|
According to the new Constitution of the Soviet Union all political power, resources, and means of production would belong to the _______.
|
workers and peasants
|
|
|
In reality in the Soviet Union the ______ held all of the power.
|
Communist Party
|
|
|
To help save the Soviet economy Lenin was forced to use some features of _______.
|
capitalism
|
|
|
Struggled for power after the death of Lenin.
|
Trotsky and Stalin
|
|
|
Took ruthless steps to win total power over the Soviet Union.
|
Joseph Stalin
|
|
|
In the 1900s much of Latin America's natural resources were controled by ______.
|
investors from other countries
|
|
|
In Latin America in the early 1900s most of the power was held by ______.
|
Military leaders and wealthy land owners
|
|
|
Large farms in Mexico worked by the peasants owned by the rich.
|
haciendas.
|
|
|
When dictator Porfirio Diaz left office in Mexico in 1911 the ______________ began.
|
Mexican Revoltion
|
|
|
He apporoved a new constitution that included land and labor reform when he was elected Mexico's president in 1917.
|
Venustiano Carranza
|
|
|
Made church land "the property of the nation," set a minimum wage and protected the right of workers' to strike in Mexico.
|
Constitution of 1917
|
|
|
Carranza's new government strengthened the government's control over the economy through ________.
|
nationalization
|
|
|
Government takeover of natural resources.
|
nationalization
|
|
|
Organized by the government it brings some stablity to Mexico by accomadating some desires of bussiness, military leaders, peasants and workers.
|
PRI
|
|
|
Institutional Revolutionary Party
|
PRI
|
|
|
Dominated Mexican politics from the 1930s until free elections in 2000.
|
PRI
|
|
|
Hurt Latin American economies as it did the rest of the world in the 1930s.
|
Great Depression
|
|
|
Became popular in Latin America as a result of the Great Depression.
|
Economic Nationalism
|
|
|
Home control of an economy.
|
Economic Nationalism
|
|
|
In Latin America in the 1930s it resulted in the rejection of Euoropean influences.
|
Cultural Nationalism
|
|
|
President Franklin Roosevelt's policy to stay out of Latin American politics.
|
Good Neighbor policy
|
|
|
In the 1900s controlled most of Africa and kept the best lands or themselves.
|
Europeans
|
|
|
From 1910 to 1940 blacks here lost the right to vote and were kept from certain jobs.
|
South Africa
|
|
|
The system of strict segregation that became law in South Africa in 1948.
|
Apartheid
|
|
|
A movement that called for the unity of Africans and those of African descent around the world.
|
Pan-Africanism
|
|
|
Marcus Garvey and W.E.B. Dubois were leaders in the _______.
|
Pan-African movement
|
|
|
A movement in West Africa and the Carribbean, in which writers expressed pride in their African roots and protested colonial rule.
|
negritude movement
|
|
|
Overthrew the Ottoman ruler and created the Republic of Turkey.
|
Mustafa Kemel
|
|
|
Mustafa Kemal worked to __________.
|
modernize Turkey
|
|
|
Inspired by Mustafa Kemal he overthrew the Persian shah and worked to modernize Persia/Iran.
|
Reza Khan
|
|
|
Both Mustafa Kemal & Reza Khan replaced Islamic traditions with _____________.
|
Western ways
|
|
|
Arab nationalism.
|
Pan-Arabism
|
|
|
Arabs had hoped to gain independence after World War I but felt betrayed when ______.
|
French and British took control of their lands.
|
|
|
Jewish Nationalist dreamed of a homeland in ________.
|
Palestine
|
|
|
To show support for European Jews, Britain issued the _______.
|
Balfour Declaration
|
|
|
A statement advocating a homeland for Jews in Palestine in 1917.
|
Balfour Declaration
|
|
|
In April of 1919, British soldiers killed and wounded hundreds of peaceful Indian protesteters.
|
Amristar massacre
|
|
|
Convinced Indians that their country should be independent of Britain.
|
Amristar massacre
|
|
|
For 20 years, he fought laws in South Africa that discriminated against Indians.
|
Mohandas Gandhi
|
|
|
Emerged as the leader of the Indian indpendence movement.
|
Mohandas Gandhi
|
|
|
Gandhi followed Henry David Thoreau's ideas of _______.
|
civil disobedience
|
|
|
The practice of not obeying unjust laws.
|
civil disobedience
|
|
|
Indians following Gandhi's nonviolent civil disobedience and British reactions slowly led to the British _______.
|
giving some power to Indians
|
|
|
When the Qing dynasty collapsed and Sun Yixian became president, China fell into chaos and __________.
|
warlords battled for control
|
|
|
Was issued by Japan during World War I in an attempt to give Japan control over China.
|
Twenty-One Demands
|
|
|
During the early 20th century China was weak and gave into many of _____.
|
Japan's demands
|
|
|
After World War I the allies gave Japan control over some former __________.
|
German lands in China
|
|
|
Was inspired by the Allies giving German lands in China to Japan.
|
May Fourth Movement
|
|
|
An intellectual movement to make China strong and to resist European imperialsm through the use of Western ideas.
|
May Fourth Movement
|
|
|
Encouraged by the Soviet Union some Chinese turned to ______.
|
Marxism
|
|
|
Nationalist party in China
|
Guomindang
|
|
|
Leader of the Guomindang from the late 1920s until 1949.
|
Jiang Jieshi
|
|
|
Chiang Kai-Shek
|
Jiang Jieshi
|
|
|
Used the help of the Chinese communists to crush the warlords.
|
Jiang Jieshi
|
|
|
In the middle of his campaign against the warlords he turned on the communists and slaughtered many of them.
|
Jiang Jieshi
|
|
|
Becomes the leader of the Chinese Communists by seeking the support of the peasant masses.
|
Mao Zedong
|
|
|
A trek of 6000 miles by Chinese Communists led by Mao Zedong to relocate their power base.
|
The Long March
|
|
|
The Guomindang under the leadership of Jiang Jieshi attacked the communists throughout the _____.
|
Long March
|
|
|
The Guomindang fought the Communists in a 22 year ______.
|
Civil War
|
|
|
Invaded China in 1937.
|
Japan
|
|
|
Because of the invasion Jiang Jieshi and Mao Zedong formed an alliance until the ________.
|
Japanese threat ended
|
|
|
Because of exports to the Allies Japan's economy grew during ______.
|
World War I
|
|
|
Became emperor of Japan in 1926.
|
Hirohito
|
|
|
During the 1920s Japan had a more ______.
|
Liberal/democratic government
|
|
|
A group of business leaders who manipulated politicians.
|
Zaibatsu
|
|
|
Were angry with the government of Japan for giving into Western demands and for accepting payoffs from the Zaibatsu
|
Military leaders and ultranationalists
|
|
|
Blew up railroad tracks in Manchuria and blamed it on the Chinese as an excuse to invade Manchuria.
|
Japanese Militarists
|
|
|
Increased their power in Japan throughout the 1930s.
|
Military leaders and Ultranationalists
|
|
|
In 1940 it signed an agreement with Italy and Germany to form the Axis Powers.
|
Japan
|

