![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Define: Anemia |
Reduced oxygen-carrying ability of blood resulting from too few erythrocytes (RBC) or abnormal hemoglobin |
|
|
|
Define: Anatomoses or (sis) |
A union or joining of nerves, blood vessels, or lymphatics |
|
|
|
Define: Antigen |
A substance or part of a substance (living or non-living) that is recognized as foreign by the immune system, activates the immune system, and reacts with immune cells or their products |
|
|
|
Define: antibody |
A protein molecule that is released by a plasma cell [a daughter cell of an activated B lymphocyte] and that binds specifically to an antigen; an immunoglobulin |
|
|
|
Define: arrhythmia |
Irregular heart rhythm, often caused by defects in the intrinsic conduction system |
|
|
|
Define: arterioles |
A minute artery |
|
|
|
Define: Arteries |
Blood vessels that conduct blood away from the heart and into circulation |
|
|
|
Define: autoregulation |
The automatic local adjustment of blood flow to a particular body area in response to its current requirements |
|
|
|
Define: bradycardia |
A heart rate below 60 beats per minute |
|
|
|
Define: cardiac output (CO) |
Amount of blood pumped out of a ventricle in one minute |
|
|
|
Define: capillaries |
The smallest of the blood vessels and the sites of exchange between the blood and tissue cells (mail men - drop off & pick up), single, flat layer of epithelial cells + thin basement membrane, 3 types |
|
|
|
Define: coronary circulation |
The functional blood supply of the heart; shortest circulation in the body |
|
|
|
Define: Atrioventricular (AV) Node |
Specialized mass of conducting cells located at the atrioventricular Junction in the heart |
|
|
|
Define: diapedesis |
Passage of white blood cells through intact vessel walls into tissue; emigration or movement out of blood into the surrounding tissues |
|
|
|
Define: depolarization of cardiac muscle cells |
Reduction of negative membrane potential caused by an influx of calcium ions into the cell |
|
|
|
Define: embolus |
A blood clot, the result of the clotting Cascade |
|
|
|
Define: erythropoiesis |
Process of erythrocyte formation |
|
|
|
Define: erythropoietin (EPO) |
Hormone that stimulates production of red blood cells in bone marrow |
|
|
|
Define: electrocardiogram [ECG] or [EKG] |
Graphic record of the electrical activity of the heart |
|
|
|
Define: fibrin |
Fibrous insoluble protein formed during blood clotting, final step |
|
|
|
Define: fibrillation |
Conduction of rapid and irregular or out of phase heart contractions |
|
|
|
Define: hematopoiesis |
Blood cell formation; homopoiesis |
|
|
|
Define: hemoglobin |
Oxygen-transporting protein of erythrocytes |
|
|
|
Define: hemostasis |
Stoppage of bleeding |
|
|
|
Define: hematocrit |
The percentage of total blood volume occupied by erythrocytes |
|
|
|
Define: hypotension |
Low blood pressure |
|
|
|
Define: hypertension |
High blood pressure |
|
|
|
Define: leukocytes |
White blood cells, formed elements involved in body protection that take part in inflammatory and immune responses, five types |
|
|
|
Define: lymphocyte |
Agranular white blood cell that arises from bone marrow and becomes functionally mature in the lymphoid organs of the body |
|
|
|
Define: lymph node |
Small lymphoid organ that filters lymph, contains macrophages and lymphocytes |
|
|
|
Define: myoglobin |
Oxygen-binding pigment in muscle |
|
|
|
Define: myocardial infarction (MI) |
Condition characterized by dead tissue areas in the myocardium, caused by interruption of blood supply to the area. Commonly called heart attack |
|
|
|
Define: myocardium |
Layer of the heart wall composed of cardiac muscle |
|
|
|
Define: neutrophil |
Most abundant type of white blood cell |
|
|
|
Define: osmotic pressure |
A measure of the tendency of a solvent to move into a more concentrated solution |
|
|
|
Define: oxyhemoglobin |
Oxygen-bound form of hemoglobin |
|
|
|
Define: parathyroid hormone(PTH) |
Hormone released by the parathyroid glands that regulates blood calcium level |
|
|
|
Define: pericardium |
Double-layered Sac enclosing the heart and forming its superficial layer, has fibrous and serous layers; parietal pericardium lines the cavity |
|
|
|
Define: peripheral congestion |
Condition caused by failure of the right side of the heart. Results in edema in the extremities |
|
|
|
Define: peripheral resistance |
A measure of the amount of friction encountered by Blood as it flows through the blood vessels |
|
|
|
Define: plasma |
The nonliving fluid component of blood within which formed elements and various solute are suspended and circulated. |
|
|
|
Define: platelet |
Cell fragment found in blood, involved in clotting |
|
|
|
Define: polycythemia |
An abnormally High number of erythrocytes |
|
|
|
Define: pulmonary arteries |
Vessels that deliver blood to the lungs to be oxygenated |
|
|
|
Define: pulmonary veins |
Vessels that deliver freshly oxygenated blood from the respiratory zones of the lungs back to the heart |
|
|
|
Define: repolarization of cardiac cells |
Movement of the membrane potential to the initial resting (polarized) state due to an influx of potassium (K+) ions |
|
|
|
Define: semi-lunar valves |
Valves that prevent blood return to the ventricles after contraction, aortic and Pulmonary valves |
|
|
|
Define: precapillary sphincter |
A circular muscle surrounding an opening, acts as a valve |
|
|
|
By what function do oxygen and nutrients leave the blood and enter the body tissues? |
Diffusion. Carbon dioxide and wastes move from the tissues to the bloodstream by the same method |
|
|
|
Where would you find oxygen deficient blood? |
Veins and venules |
|
|
|
Describe the location of the heart in relation to other thoracic organs |
The heart rests on the superior surface of the diaphragm and lies medially between the lungs. The base is directed toward the right shoulder. The Apex points inferiorly toward the left hip. |
|
|
|
Describe the structure of the pericardial cavity |
the pericardium is a double-walled sac that encloses the heart. The parietal membrane lines the cavity. The visceral membrane lines the heart. The pericardial cavity is the slit like cavity between the parietal and visceral membranes and contains a film of serous fluid. [The visceral membrane is also known as the epicardium (outermost layer) which is an integral part of the heart outer wall.] |
|
|
|
Name the three layers of the heart |
Outermost layer is the epicardium, middle layer is The myocardium, the innermost layer is the endocardium |
|
|
|
Describe the location, structure and function of the epicardium |
[A.K.A. visceral membrane of the pericardium] the superficial layer of the serous pericardium, serous fluid lubricates the sac allowing the mobile heart to work in a relatively friction-free environment |
|
|
|
Describe the structure and function of The myocardium |
The middle layer of the heart, mainly cardiac muscle, forms the bulk of the heart. This is the layer that contracts. Formed of branching cardiac muscle cells tethered by connective tissue fibers, arranged in spiral bundles. The connective tissue fibers form a dense network: the cardiac skeleton |
|
|
|
Is connective tissue electrically excitable? |
No. The cardiac skeleton [ myocardium's reinforcing network of connective tissue containing collagen and elastic fibers] limits the spread of action potentials to specific Pathways in the heart |
|
|
|
Describe the function and structure of the endocardium |
The endocardium is the inner most layer of the heart, lining the heart chambers, and is made of squamous epithelium and rests on a thin connective tissue layer. The endothelium is continuous with the endothelial lining of the blood vessels leaving and entering the heart. |
|
|
|
Describe the gross anatomy of the heart |
The heart has four chambers: two Superior Atria and two inferior ventricles. Chambers are separated by the interatrial septum and the interventricular septum |
|
|
|
What are the receiving chambers of the heart? |
Deoxygenated blood enters the right Atria. Oxygenated blood returning from the lungs enters the left atrium |
|
|
|
What are the small, wrinkled, protruding appendages which increase the atrial volume somewhat? |
Auricles |
The ears |
|
|
What are the bundles of muscle tissue that form ridges on the anterior portion of the right Atria called? |
Pectinate muscles. These muscles are only located in the auricle of the left atrium |
|
|
|
What is the shallow depression in the right auricle? |
Fossa ovalis |
|
|
|
What is the name of the structure that the fossa ovalis replaces once a baby is born? |
Foramen ovale |
|
|
|
What three veins Supply the returning deoxygenated blood into the right atrium? |
Superior vena cava, inferior venacava, coronary sinus |
|
|
|
Blood entering the right atrium via the superior venacava is returning the oxygenated blood from what body regions? |
Body regions superior to the diaphragm |
|
|
|
Deoxygenated blood entering the right atrium via the inferior vena cava returns blood from which body areas? |
Body regions Inferior of the diaphragm |
|
|
|
Deoxygenated blood entering the right atrium via the coronary sinus collected from what layer of the heart? |
Myocardium |
|
|
|
What are the irregular Ridges of muscle in the ventricles called? |
Trabeculae carneae |
|
|
|
What is the name of the muscle bundle which secures the AV valve and mitral valve to the wall of The ventricle? |
Papillary muscles |
|
|
|
Which Chambers are the discharging or actual pumps of the heart? |
The ventricles |
|
|
|
How do you discern between the left and the right ventricle in a dissected heart? |
The walls of the left ventricle are much thicker |
|
|
|
To which artery does the right ventricle pump blood into? |
Pulmonary trunk |
|
|
|
What arteries bring deoxygenated blood to the lungs to be oxygenated? |
Left and right Pulmonary arteries |
|
|
|
What artery does the left ventricle pump blood into? |
Aorta |
|
|
|
What is the largest artery in the body? |
Aorta |
|
|
|
Name the dip on the outer surface of the epicardium that separates the two ventricles? |
Interventricular sulcus |
|
|
|
Name the dip that separates the right atrium from the right ventricle on the epicardium of the heart? |
Coronary sulcus |
|
|
|
What artery rests in the (right) coronary sulcus? |
Right coronary artery |
|
|
|
What vessels rest in the anterior interventricular sulcus? |
Anterior interventricular artery and the great cardiac vein |
|
|
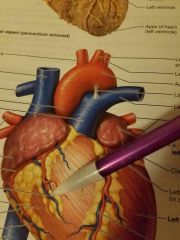
Name the blue vessel |
Anterior cardiac vein |
|
|
|
Name the inferior point of the heart |
Apex |
|
|
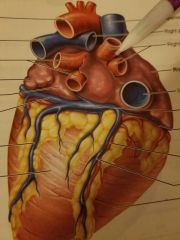
Name the posterior vessels that are on the far right of the heart. |
Right pulmonary veins |
|
|
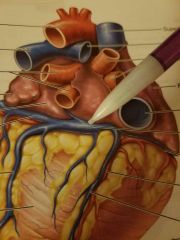
Name the bulging, pooling site of the posterior veins of the heart |
Coronary sinus |
|
|
|
List the pathway of deoxygenated blood as it enters the right atrium: |
Right atrium to the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle through the pulmonary valve to the pulmonary trunk to the pulmonary arteries to the lungs to the pulmonary veins to the left Atria through the bicuspid valve to the left ventricle to the aortic valve to the aorta and into systemic circulation |
|
|
|
What makes blood flow in One Direction? |
Heart valves including atrioventricular valves and semi-lunar valves |
|
|
|
What are other names for the right atrioventricular valve? |
Right AV valve or the tricuspid valve |
|
|
|
What are other names for the left atrioventricular valve? |
Left AV valve or bicuspid or mitral valve |
|
|
|
White collagen cords which anchor AV valve flaps to the papillary muscles on ventricular walls are called? |
Chordae tendineae (also known as heart strings) |
|
|
|
How do the bicuspid and tricuspid prevent blood from returning to the heart? |
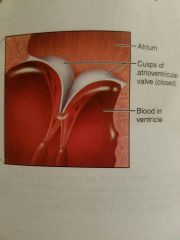
As The ventricle muscles contract the blood is forced against the umbrella like valve cusps which force the AV valves to close. |
|
|
|
Define margination |
The phenomenon of leukocytes clinging to the inner walls or margins of capillaries at the site of injured cells |
|

