![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
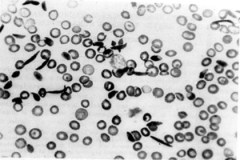
What is this and what is the cuase? Explain. |
Sickle Cell Disease: Mutation of Glutamic Acid to Valine can lead to hemoglobin (HbS) polymerization in T state and formation of sickled cells which can cause infartions and ischemic attacks. |
|
|
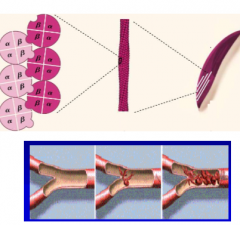
What causes HbS to polymerize? |
1. ß-Chain Glu6 to Valine substitution creates a hydrophobic patch that causes hemoglobin to polymerize when it is in the T deoxy state |
|
|
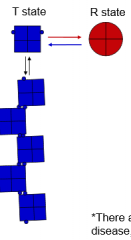
Give a brief explanation of the differences in affinity and stabilizing influences in T and R state of hemoglobin. |
1. T State= Low affinity for O2, stabilized by acidic conditions and 2,3-BPG. An ion pair forms on each of 4 subunits between an Aspartate and Histidine residue. 2. R State= Ion pairs break due to O2 binding. O2 binding stabilizes and favors the R state |
|
|
What type of curve is O2 binding in hemoglobin and why? |
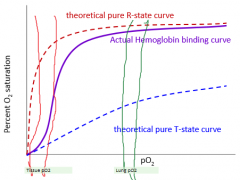
Sigmoid curve indicative of cooperative binding. As one oxygen binds, the affinity for oxygen increases. The opposite is true for dumping oxygen in the tissues. |
|
|
What does an increase in H+ ions or a decrease in pH actually do to stabilize the T state? (Bohr Effect) |
1. Histidine in the ion pair must be protonated in order to form the ion pair. With a pKa close to 7, protonation of histidine is favored in lower pH. |
|
|
What two molecules favor/stabilize the R state? |
1. O2 2. CO |
|
|
What two mechanisms are involved in CO2 transport? |
1. Carbonic Anhydrase: 80% of CO2 travels to the lungs as Bicarbonate in the plasma 2. Carbamate: 20% of CO2 is directly bound by hemoglobin as carbamate on the N terminus of hemoglobin. ***Carbamino-Hb favors the T state due to formation of ion pairs. |
|
|
What is the effect of 2,3-BPG and how does it function? |
1. Allosteric regulator of hemoglobin. 2. Binds the T state and stabilizes it upregulating the release of O2 to the tissues. *This is made only by RBCs. |
|
|
Why are infants protected from sickle cell crisis? |
1. Infants still have fetal hemoglobin and will not be effected until the fetal hemoglobin concentration has been sufficiently reduced. |
|
|
Why is fetal hemoglobin necessary for proper development? |
1. HbF has very low affinity for 2,3 BPG aiding in maternal delivery of oxygen to the fetus. 2. pO2 in mothers tissues higher than in Fetus. Without 2,3 BPG in fetus, the R state is more heavily favored. |
|
|
What are the causes of amyloid formation and what does this do? |
1. Intermediate state of a protein can aggregate to form oligomers and later amyloid fibrils. 2. Alzheimers, Parkinsons, Prion Diseases, Amyloidoses, and Diabetes |
|
|
What are the similarities (2) and Differences (2) between amyloid and sickle cell diseases? |
1. Similar: Both deal with polymerization of proteins. Both form aggregates of protein. Both are protein folding diseases. 2. Differences: HbS tetramers maintain alpha helical fold and native structure within polymer. Amyloids involve polymerization of beta sheets. HbS genetic, Amyloid has many causes. HbS well understood, Amyloids still a mystery. |

