![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
group of specialized cardiac muscle cells which allows the heart to contract automatically (located in RA)
|
sinoatrial node (SA node)
|
|
|
SA node spreads its contractions to the surrounding cardiac muscles via _______________ made from gap junctions
|
electrical synapses
|
|
|
slows the rate of heart contractions and increases digestive activity in the intestines
|
vagus nerve (parasympathetic)-innervates the heart and digestive system
|
|
|
slower contracting node, causes a delay which allows the atria to finish their contraction, and to squeeze their contents into the ventricles before the ventricles begin to contract
|
atrioventricular (AV) node
|
|
|
From the AV node, the AP moves down conductive fibers called the ______________ which is located in the wall separating the ventricles. The AP branches out through the ventricular walls via conductive fibers called ____________, which allow for a more unified, and stronger, contraction of the ventricles.
|
bundle of His
Purkinje fibers |
|
|
blood flows through these away from the heart; they are elastic, and they stretch as they fill with blood. They are wrapped in smooth muscle that is usually innervated by the sympathetic nervous system
|
arteries
|
|
|
smaller than arteries, wrapped with smooth muscle
|
arterioles
|
|
|
microscopic blood vessels with walls only one cell thick; function in nutrient and gas exchange
|
capillaries
|
|
|
contain a far greater volume of blood than arterioles and arteries, also have larger cross sectional area. carries blood toward the heart
|
vein (and venules)
|
|
|
carry the most deoxygenated blood in the body
|
pulmonary arteries
|
|
|
What is the relationship between cross sectional area vs velocity as blood flows through the body?
|
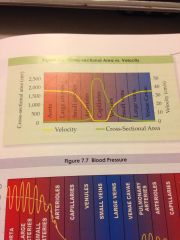
|
|
|
BP is lowest at the ___________
|
capillaries
|
|
|
Hypovolemic shock represents a set of symptoms that occur when a patient's blood volume falls abruptly. Hypovolemic shock is most likely to occur during ______
|
arterial bleeding (high blood pressure)
|
|
|
skeletal muscle innervated by the phrenic nerve
dome shaped while relaxed, flattens upon contraction, expanding the chest cavity and creating negative gauge pressure |
diaphragm
|
|
|
job is to deliver oxygen to the blood and expel carbon dioxide
|
respiratory system
|
|
|
functions of this system are to prepare the air by warming, moistening, and cleaning
|
respiratory tract
|
|
|
Microtubules are found in cilia. Ciliated cells are found in the respiratory tract and where else?
|
Fallopian tubes and ependymal cells of the spinal cord. Thus, a problem in microtubule production might result in a problem breathing; or fertility or circulation of cerebrospinal fluid
|
|
|
space inside the nose which filters, moistens, and warms incoming air
|
nasal cavity
|
|
|
this is at the front of the nasal cavity and it traps large dust particles
|
course hair
|
|
|
secreted by goblet cells, traps smaller dust particles and moistens air
|
mucus
|
|
|
moves the mucus and dust in the nasal cavity back toward the pharynx, so that it may be removed by spitting or swallowing
|
cilia
|
|
|
functions as a passageway for food and air
|
pharynx
|
|
|
voice box
|
larynx
|
|
|
larynx sits behind the _____________, which is the cartilaginous member that prevents food from entering the trachea during swallowing
|
epiglottis
|
|
|
lies in front of the epophagus. composed of ringed cartilage covered by ciliated mucous cells
|
trachea
|
|
|
trachea splits into this before entering the lungs
|
right and left bronchi, whch branch many more times to become tiny bronchioles
|
|
|
terminate grape-like clusters composed of tiny alveoli
|
branchioles
|
|
|
oxygen diffuses from these into a capillary where it is picked up by red blood cells
|
alveoli
|
|
|
98% of the oxygen in the blood binds rapidly and reversibly with the protein ___________ inside the erythrocytes forming ______________.
|
hemoglobin-4 subunits, each with a single heme cofactor (organic molecule with an atom of iron at its center)
oxyhemoglobin |
|
|
oxygen dissociation curve shifts right with an _____________ in Co2 pressure, hydrogen ion concentration, or temperature.
|
increase
a shift to the right indicates a lowering of hemoglobin's affinity for Oxygen |
|
|
in the case of acidosis (too much acid in the blood), the body compensates by _________ the breathing rate thereby expelling carbon dioxide and raising the pH of the blood.
|
increasing
|
|
|
the greater to pressure of CO2, the ________ the blood content of C02, however when hemoglobin becomes saturated with O2, it's capacity to hold CO2 is __________
|
greater
reduced |
|
|
Nitrogen is stable bc of it's ___________, but doesn't react with the chemicals in the blood. As pressure increases with depth, what happens to the nitrogen concentration in the blood? When the diver comes back up?
|
strong triple bonds
more N2 diffuses into the blood, when the divers come back up the pressure decreases and the gas volume increases (if they come up too fast the N2 won't have time to diffuse out of the blood and into the lungs, and bubbles can form=the bends) |
|
|
What type of system is the lymph system?
|
open: fluid enters at one end and leaves at another end
|
|
|
In the lymphatic system, fluid returns to the blood at the _____________ and the ______________.
|
right lymphatic duct
thoracic |
|
|
small portions of membrane-bound cytoplasm torn from megakaryocytes, which contain actin and myosin. They are capable of making protoglandins and some important enzymes
|
platelets
|
|
|
what type of tissue is blood?
|
connective
|
|
|
what are the important proteins located in the blood plasma?
|
albumin, immunoglobins, and clotting factors
|
|
|
transport fatty acids and steroids, also regulate the osmotic pressure in the blood
|
albumin
|
|
|
plasm in which the clotting protein __________ has been removed is called ________
|
fibrinogen
serum |
|
|
connective tissue contains what 2 things?
|
cells and a matrix
|
|
|
what is the job of the erythrocytes?
|
deliver oxygen and remove carbon dioxide
they do not contain organelles |
|
|
blood cells which contain organelles, but not hemoglobin. What is the function of these cells?
|
leukocytes; protect the body from foreign invaders
|
|
|
blood cells differentiate from a common precursor called?
|
stem cell (resides in bone marrow0
|
|
|
leukocytes which live a very short time bc they function non-specifically against all infective agents
|
granulocytes
|
|
|
leukocytes which live for a long time because they work against specific agents of infection
|
agranulocytes
|
|
|
process which involves many factors starting with platelets and also including the plasma proteins prothrombin and fibrin
|
coagulation
|
|
|
occurs when an injury to tissue takes place. Causes dilation of blood vessels, increased permeability of capillaries, swelling of tissue cells, and migration of granulocytes and macrophages to the inflamed area
|
inflammation
|
|
|
what are the 2 types of acquired immunity?
|
humoral (Beta cell immunity) and cell-mediated (T-cell immunity)
|
|
|
each B lymphocyte is capable of making a single type of __________ which it displays on its membrane
|
antibody (or immunoglobulin)
|
|
|
foreign body which an antibody recognizes
|
antigen
|
|
|
If the B lymphocyte antibody contacts a matching antigen, the B lymphocyte, assisted by a ___________, differentiates into plamsa cells and _____________.
|
helper T cells
memory B cells |
|
|
first time the immune system is exposed to an antigen is known as _______________
|
primary response (requires 20 days to reach its full potential)
next time, effect is faster acting and more potent (secondary response) |
|
|
cell-mediated immunity involves ______, which mature in the thymus
|
T-lymphocytes (never make free antibodies)
|
|
|
T lymphocytes that are not destroyed differentiate into ___________ (4).
|
helper T cells, memory T cells, suppressor T cells, killer T cells
|
|
|
T-lymphocyte cell which plays a negative feedback role in the immune system
|
Suppressor T cells
|
|
|
helper T cells assist in activating ____________ (3)
|
B lymphocytes, killer and suppressor T cells
|
|
|
T-lymphocyte cell which binds to the antigen-carrying cell and release perforin. The cells reponsible for fighting some forms of cancer, and for attacking transplanted tissue
|
killer T cells
|
|
|
organ which destroys old, worn out red blood cells
|
spleen
|
|
|
lymphatic vessels absorb fluid from the interstitial spaces and carry it to the ___________
|
lymphatic ducts, which return it to circulation
|
|
|
Type B negative blood will make antibodies that attack ________ antigens but not ___________ antigens
|
type A
type B |
|
|
An individual exposed to a pathogen for the first time will exhibit an innate immune response involving:
|
granulocytes (innate immune system does not involve humoral or cell mediated immunity, it responds to any and every foreign invader)
|

