![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How to calculate Minute Volume? |
Minute Volume = Tidal Volume x Respiratory Rate |
|
|
What is the formula for FiO2? FiO2 = fractional concentration of inspired air |
FiO2 = ((Number of litres/min of Oxygen) x 1.0 + (Minute volume – Number of litres/min) x 0.21) / Minute volume |
|
|
What is the relation of Minute Volume to FiO2? |
High MV = Low FiO2 Low MV = High FiO2 |
|
|
What is; 1. Normal O2 sats 2. O2 sats showing respiratory failure |
1. Normal = 95 - 100% 2. Respiratory failure = 90% or 60mmHg |
|
|
List two methods we can use the monitor oxygen. |
1. Pulse oximetry 2. Arterial blood gas analysis |
|
|
List early clinical signs of hypoxemia: |
1. Tachycardia 2. Dyspnoea 3. Restlessness 4. Agitation 5. Disorientation |
|
|
List oxygen delivery devices according to 1. Low flow/Variable performance 2. High flow/Fixed performance |
1. Low flow - Nasal Cannula (most commonly use, no rebreathing) - Simple face mask - Non - rebreather mask 2. High flow - High flow nasal prong - Venturi mask (useful for patient with CO2 retention, non - rebreathing) - Bag-valve-mask (BVM) |
|
|
What are some disadvantages of all face masks? |
- Irritation to skin - Hot and confining - Claustrophobic - Talking and hearing as added challenge - Difficulty with eating and drinking |
|
|
Why must we avoid high concentration of oxygen in patients with COPD? |
It may cause: Reduction in hypoxic drive --> worsening respiratory acidosis --> hypoventilation |
|
|
An airway must be? |
Patent and not obstructed |
|
|
What are some steps to ensure the patency of an airway? |
1. No SOB 2. Via Auscultation 3. No obvious neck injury/signs of aspiration or airway blockage 4. Use of airway adjuncts: OPA and NPA |
|
|
What are some signs of altered airway? |
1. Patient apprehension and irritability 2. Abnormal air entry / breath sound 3. Accessory muscle use 4. Altered GCS 5. Tracheal tug 6. Sweating 7. Cyanosis 8. Paradoxical breathing 9. Noisy breathing (Silent is worse!) 10. Obvious airway obstruction |
|
|
Succesful BVM depends on three conditions. What are those? |
1. A patent airway - use of OPA does help 2. An adequate mask seal - ensure the mask is placed correctly (at the bridge of patient's nose to the chin) 3. Proper ventilation - Appropriate volume, rate and force |
|
|
List the manoeuvres to open the airway: |
1. Head tilt - chin lift - Primary only if cervical spine injury is NOT a concern 2. Jaw thrust - Method of choice if suspected cervical injury |
|
|
How to measure the correct size of OPA and NPA? |
1. OPA - from earlobe to corner of mouth 2. NPA - from nostril to earlobe/angle of the jaw |
|
|
What is the contraindication for NPA insertion? |
Basal skull fracture |
|
|
How to insert guedel? |
In adults; - Insert upside down, then rotate 180 degrees on reaching the oropharynx In children - Insert in functional position as rotation may cause injury to soft palate - Use tongue depressor to hold tongue clear |
|
|
How to insert LMA? LMA - Laryngeal Mask Airway |
Insert the mask into the pharynx with the distal aperture directed caudally in one continuous movement until resistance to further progression is felt. Let go of the tube. Fully inflate thecuff with air (10mL), which secures the airway and will usually allow ventilation unlessairway pressures are high. |
|
|
What is suctioning? |
Suctioning is the use of negative pressure to remove fluids and secretions through a tube. |
|
|
What are some considerations that must be taken care of when doing suction? |
Oropharyngeal method is less traumatic = method of choice Nosopharyngeal method is contraindicated in facial trauma/surgery, nasal bleeding and clotting disorders. |
|
|
List the layer of the blood vessels from innermost to outermost |
Tunica intima --> Tunica media --> Tunica externa |
|
|
List the two most preferred sites for IV cannulation. |
1. Cephalic vein 2. Basilic vein |
|
|
What conditions should be considered when choosing veins? |
1. Select distal, upper extremities as first option 2. Non - dominant side of patient 3. Vein must be easily palpable, soft, full, not obstructed and straight 4. Ask patient what is the best site? 5. Observe for vein bifurcation |
|
|
List some conditions for a vein to be avoided? |
1. Areas of flexion and joints 2. Vein that have been traumatised 3. Veins in lower extremities - risk of thrombus 4. Veins close to arteries 5. Small, superficial but impalpable vein. |
|
|
What are some indications of PIVC? |
- Fluid and electrolyte therapy - Blood transfusion - Delivery of medication - Parenteral nutrition - Diagnostic imaging reagents - Blood drawing |
|
|
What are some contraindications of PIVC? |
- Oedema - Veins of fractured limbs - Sites close to infection source |
|
|
What are some complications of PIVC? |
- INFECTION - Clot formation - Phlebitis (Inflammation of the vein) |
|
|
What are some prevention strategies that may help to prevent complications of PIVC? |
Infection: - Adhere to aseptic hand hygiene technique - Site inspection and care Clot formation and phlebitis - Use correct gauge size - Site inspection and care |
|
|
What are the cannula size guidelines? |
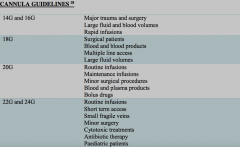
|
|
|
Cannula for fastest flow? |
Short cannula with large diameter - Changing the diameter increases 4x flow - Changing length increases 1x flow |

