![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Subdivide the Nervous System |
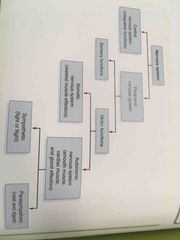
Back (Definition) |
|
|
3 meningeal layers |
P Pia Mater (inner layer) A Arachnoid (middle layer) D Dura mater (outermost layer) level |
|
|
Level of organizations in Humans |
Chemical Cellular Tissue Organ Organ system Organism |
|
|
Characteristics of life |
Absorption Circulation Digestion Excretion Growth Movement Reproduction Respiration Responsiveness |
|
|
Absorption |
The ability to absorb materials through various membranes, such as digestive tract |
|
|
Circulation |
The ability to move substances in the body by way of body fluids |
|
|
Digestion |
The ability to convert food sources to simpler compounds |
|
|
Excretion |
The ability to excrete waste material |
|
|
Growth |
Ability to increase in side |
|
|
Movement |
The ability to move locations, change position, or move internal structures |
|
|
Reproduction |
The ability to create new cells, such as in cellular reproduction,or the ability to create new organisms such as offspring |
|
|
Bilirubin |
Waste product of red blood cell destruction |
|
|
Hering-Breur Reflex |
Protective mechanism that prevents over expansion of the lungs |
|
|
Hepatic Portal System |
From digestive to liver to inferior vena cava |
|
|
Hematocrit |
Percentage of red blood cells in the blood |
|
|
Visceral Pain |
Deep pain triggered by receptors in abdomen, chest, etc Poorly localized
|
|
|
Crenation |
abnormal shrinking of the cell due to exposure to hypertonic environment |
|
|
Lysis |
The swelling and bursting of a cell due to hypotonic environment |
|
|
Isotonic |
Equal concentration of solute and water present on either side of semipermeable membrane |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
Link between endocrine and nervous system -controls BP/HR/TEMP/BGL |
|
|
Pituitary Gland |
Master Gland Anterior- hormones directly into blood stream Posterior- distal ends of hypothalamic neurons, release ADH,OXYTOCIN |
|
|
Thyroid Gland |
Base of neck Metabolism,growth,development |
|
|
Gonads |
Promotes sexual maturation to puberty and fulfill subsequent reproductive needs |
|
|
Pancreas |
Secretes insulin from the islets of langerhorn 1) alpha - produce glucagon 2)beta - produce insulin 3)delta - produce somastatin 4)F Cells - pancreatic peptide |
|
|
Pineal Gland |
Synthesizes and secretes melatonin Effects sleep wake patterns |
|
|
Interstitial Fluids |
Extra cellular fluid outside of lymph, vasculatory system |
|
|
Cranial Nerves |
I. OlfactoryII.OpticIII. OculomotorIV. TrochlearV. TrigeminalVI. AbducensVII. Facial
VIII.VestibulochlearIX. Glossopharyngeal X.VagusXI.AccessoryXII. Hypoglossal |
|
|
Dorsal Respiratory Group |
Located in Medulla, signals the Ventral Respiratory Group (VRG) to alter rhythm and depth of ventilation to restore homeostasis |
|
|
Ventral Respiratory Group |
Network of inspiratory and expiratory motor neurons , responds to the DRG |
|
|
Anabolism |
Building of larger substances from smaller substances I.e. Proteins from amino acids |
|
|
Catabolism |
The breakdown of larger substances to smaller substances |
|
|
A + B -> AB |
Synthesis Reaction |
|
|
AB -> A+B |
Decomposition Reaction |
|
|
AB + CD -> AC + BD |
Exchange Reaction |
|
|
Tidal Volume |
Air in or out in a single breath |
|
|
Inspiratory Reserve Volume |
Air that can be inhaled after normal tidal volume is reached ~3,000ml |
|
|
Expiratory Reserve Volume |
Air that can be exhaled after normal tidal volume is reached ~1,200ml |
|
|
Ventilation |
Mechanical air movement |
|
|
Oxygenation |
The loading of oxygen molecules onto hemoglobin (4) |
|
|
Respiration |
The gas Exchange between cell and surround tissues |
|
|
Vital capacity |
Total volume with maximum inhale and exhale |
|
|
Anatomical Dead Space |
Portion of the respiratory system w.o. Alveoli - little to no gas exchange -i.e. Mouth, trachea |
|
|
Physiological Dead Space |
anatomical dead space + Amount of damaged aveoli that cannot participate in Gas exchange |
|
|
Minute volume |
Respiratory Rate x Tidal Volume |

