![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Solid |
Having relative firmness, coherence of particles, or persistence of form, as matter that is not liquid or gaseous. |
|

Liquid |
Composed of molecules that move freely among themselves but do not tend to separate like those of gases; neither gaseous nor solid. |
|

Gas |
A substance possessing perfect molecular mobility and the property of indefinite expansion, as opposed to a solid or liquid. |
|

Matter |
The substance or substances of which any physical object consists or is composed. |
|
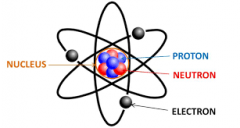
Atom |
The smallest component of an element having the chemical properties of the element, consisting of a nucleus containing combinations of neutrons and protons and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus by electrical attraction. |
|

Physical Properties |
Characteristics that can be observed without changing the substance. |
|
Chemical Properties |
Characteristics that can only be observed by changing the original substance into a new one. |
|

Luster |
The state or quality of shining by reflecting light. |
|

Malleability |
Capable of being shaped or molded. |
|
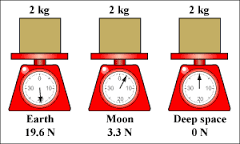
Mass |
The quantity of matter as determined from its weight or from Newton's second law of motion. |
|
Characteristic Properties |
A physical property that doesn't change based on the amount of substance. |
|
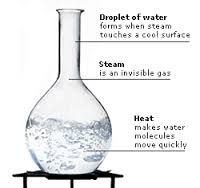
Boiling Point |
The temperature when liquid changes to gas. |
|

Melting Point |
The temperature when solid changes to liquid. |
|

Flammability |
How easily a substance can be lit on fire. |
|

Oxidation |
When a substance chemically reacts to the exposure of oxygen. |
|
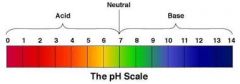
pH |
How acidic or basic a substance is. |
|

Chemical Reaction |
A process that involves changes in the structure and energy content of atoms, molecules, or ions but not their nuclei. |
|

Magnetism |
A substances ability to pull or repel another substance. |
|

Hardness |
The state of being tough and hard to break. |
|

Texture |
How a substance feels. |

