![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
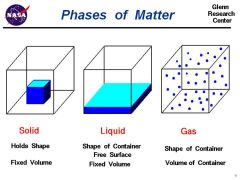
Soild |

Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. |
|
|
Liquid |

having a consistency like that of water or oil, i.e., flowing freely but of constant volume. |
|
|
Gas |

an airlike fluid substance which expands freely to fill any space available, irrespective of its quantity. |
|
|
Matter |
physical substance in general, as distinct from mind and spirit; (in physics) that which occupies space and possesses rest mass, especially as distinct from energy. |
|
|
Atom |
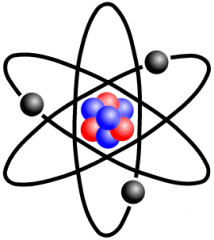
the basic unit of a chemical element. |
|
|
Phyiscal properites |

Physical Properties: Physical properties can be observed or measured without changing the composition of matter. Physical properties are used to observe and describe matter. Physical properties include: appearance, texture, color, odor, melting point, boiling point, density, solubility, polarity, and many others. |
|
|
Chemical properites |
A chemical property is any of a material's properties that becomes evident during, or after, a chemical reaction; that is, any quality that can be established only by changing a substance's chemical identity. |
|
|
Luster |

Lustre or luster is the way light interacts with the surface of a crystal, rock, or mineral. The word traces its origins back to the latin lux, meaning "light", and generally implies radiance, gloss, or brilliance. A range of terms are used to describe lustre, such as earthy, metallic, greasy, and silky. |
|
|
Malleability |

Malleability is the ability of a metal to be hammered into thin sheets. Gold and silver are highly malleable. When a piece of hot iron is hammered it takes the shape of a sheet. The property is not seen in non-metals. |
|
|
Mass |
n physics, mass is a property of a physical body which determines the strength of its mutual gravitational attraction to other bodies, its resistance to being accelerated by a force, and in the theory of relativity gives the mass–energy content of a system. The SI unit ofmass is the kilogram (kg). |
|
|
Characteristic Properties |

A characteristic property is a chemical or physical property that helps identify and classify substances. The characteristic properties of a substance are always the same whether the sample one is observing is large or small. |
|
|
Boiling Point |
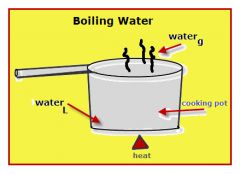
the temperature at which a liquid boils and turns to vapor. |
|
|
Melting Point |

The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a solid is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid at atmospheric pressure. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium |
|
|
Flammability |

Flammability is the ability of a substance to burn or ignite, causing fire or combustion. The degree of difficulty required to cause the combustion of a substance is quantified through fire testing. |
|
|
Oxidation |

Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. |
|
|
pH |
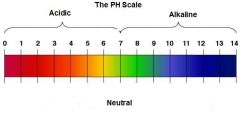
In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. |
|
|
Chemical Reaction |

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. |
|
|
Magnetism |
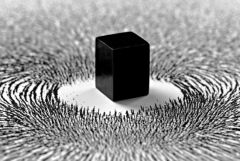
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. |
|
|
Hardness |

the quality or condition of being hard. |
|
|
Texture |

the feel, appearance, or consistency of a surface or a substance |

