![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Standardized Unit |
Definite magnitude of a quantity defined and adopted by law. |
A unit everyone agreed on and understands. |
|
|
International Unit (SI) |
Metric System (m, g, m^3) |
|
|
|
1 Meter comes from? |
1 fraction of the speed of light. |
1/299 792 458 |
|
|
Scientific Notation Multiple or Division steps: |
1) multiple bases 2) add/subtract the powers together 3) make sure the decimal is after first number |
|
|
|
Scientific Notation Addition or Subtraction steps: |
1) convert to same power 2) add or subtract digits |
|
|
|
Order of Magnitude |
An estimate of size or magnitude expressed as a power of 10. |
3E6 same as 8E6 6E8 2 orders larger than 8E6 |
|
|
Richter Scale |
A logarithmic scale to show the magnitude of Earthquakes |
|
|
|
Linear Growthor Decay |
Increases or decreases by a fixed amount during a time interval. |
|
|
|
Exponential Growth/ Decay |
Increases or decreases by a percentage during a time interval. |
|
|
|
Doubling Time |
Time needed for tye quantity to double from initial amount. |
Q=Qo (2)^ t/T |
|
|
Half Life |
Time it takes to decrease to 1/2 of original amount. |
Q=Qo(0.5)^t/T |
|
|
Kinetic vs. Potential Energy |
Kinetic- motion (electricity) Potential- stored energy (nuclear) |
|
|
|
1 Calorie |
4184J. 1kg of water increase by 1°C at 1atm. |
|
|
|
Power |
The rate of energy consumption measured in watts=J/s |
|
|
|
Fossil Fuels |
Fuels that are formed from the decayed remains of the plants and animals. |
coal, natural gas, crude oil |
|
|
Isotope |
Atom with the same number of protons but different neutrons |
|
|
|
Fusion |
Energy released when two nuclei combine together. |
|
|
|
Fission |
When energy is released from the splitting of heavy nucleus into smaller atoms. |
|
|
|
Radioactive Decay |
Process by which the nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting radiation. |
Carbon 14- half life of 5730 years |
|
|
Renewable Energy |
Energy obtained from natural resources that can be replenished or renewed within a human lifespan. |
Solar, Wind, Hydro |
|
|
Alpha Radiation |
A=B+C Poor Penetration- piece of paper |
|
|
|
Beta Radiation |
A=B+e- Penetration- clothing |
|
|
|
Gamma Radiation |
A=A + Gamma Penetration- Concrete |
|
|
|
Radiation Threshold Limit Value |
Level of chemical substance that a worker can be exposed to without adverse effects. |
In Sievets (0.05 Sv) |
|
|
Scientific Method |
Organized process that scientists use to investigate scenarios/problems and to find solutions. |
|
|
|
Independent Variable |
Variable that is changed in a scientific experiment or a variable whose variation does not depend on that of another. |
|
|
|
Dependent Variable |
Variable that is being tested in a scientific experiment or this is what occurs in response to changing independent variable. |
|
|
|
Control Experiment |
Where you dont include the independent variable so you can compare the results. |
|
|
|
Confounding Variable |
Variable your interested in that may affect the dependent variable. |
|
|
|
Positive Control |
Not exposed to the experimental treatment but is exposed to some other treatment that is known to produce the desired effect of the experiment. |
|
|
|
Negative Control |
Not exposed to experimental treatment or any other treatment that is expected to have a desired effect. |
|
|
|
Logic |
The study of reasoning that provides rules and techniques to determine whether an argument is valid. |
|
|
|
Statments: Simple vs Compound |
Simple-single idea Compound- several ideas, includes connectives |
|
|
|
Negation |
Denial of a statement, Not, ~ |
|
|
|
Conjunction |
2 statements connected, AND, A |
|
|
|
Disjunction |
Connected with OR, V |
|
|
|
Conditional |
If... Then -> |
|
|
|
Biconditional |
If and only if, <-> |
|
|
|
Why can C14 not be used to date samples millions of years old? |
After 50000 years the amount left is so small that it would be impossible to measure accurately. |
|
|
|
Half life of C14? |
5730 years |
|
|
|
Contagious Value (P) of 9? |
P=9, One person can infect 9 new people a day. |
|
|
|
Define: Vaccination |
The injection of a dead of disabled pathogen that produces immunity un the body against that pathogen. |
The body will produce antibodies that are able to fight against the disease if the person is infected with the disease again. |
|
|
Minimal Compliance Immunization Rate |
Minimum percent of people needed to be vaccinated to avoid epidemic. |
P=9, 1 infects 9 a day, 100 infects 900 P=1, 1 infects 1, 100 infects 100 Vaccinations =900-100=800 800/900x100%= 88.89% MCIR |
|
|
Transform Boundary |
When 2 plates slide past eachother. |
|
|
|
Divergent Boundary |
2 plates move apart from eachother |
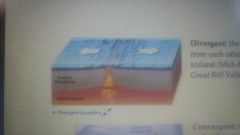
Sea floor spreading, canyons and trenches |
|
|
Convergent Boundary |
2 plates crash into eachother, 1 goes up and one goes down |
Mountain ranges and volcanoes |
|
|
Shield Volcano |
Less Explosive Divergent Boundaries or Hot Spots Runny Magma, Low Silica Content |
|
|
|
Composite Volcano |
Highly Explosive Convergent Boundary(O-C) Thick Viscous Magma, High Silica |
|
|
|
Earthquake Destruction Factors |
1) depth and distance to epicenter 2) population density 3) amount and strength of infastructure 4) ground conditions 5) economic development |
|
|
|
Which waves are used to find the epicenter of an earthquake? |
P waves and S waves |
|
|
|
Infectious Disease |
Disease caused by an infectious agent such as bacteria, virus, protozoa or fungi. |
|
|
|
Infection |
When an infectious agent enters the body and begins to reproduce. |
|
|
|
Vector |
An agent that carries and transmits an infectious disease from one host to another. |
|
|
|
When was first antibiotic discovered? |
Penicillin in 1920 |
|
|
|
Antibiotic Resistance |
Certain antibiotic treatments that used to work, may not work anymore |
|
|
|
Emerging Infectious Disease |
Whose incidence in humans has increased in the past 2 decades or threatens to increase in the near future. |
|
|
|
Re-emerging Infectious Disease |
Disease that was once an issue then declined dramatically but is now rapidly increasing again. |
|
|
|
Pseudoscience |
A claim, practice, belief or study which is presented as scientific, but does not adhere to a valid scientific method. |
|
|
|
Traits of pseudoscience |
Fixed ideas Non peer reviewed Favorable studies only Non-repeatable results Critism=Conspiracy Anecdotal Evidence |
|
|
|
Probability |
Liklihood an event will happen based on possible outcomes. |
Between 0 and 1. Expressed as fraction, decimal or percent. |
|
|
Superbug |
An informal term for a bacteriym that has become resistant to antibioticd that usually used to treat it. |
|
|
|
Zoonoses |
Disease and infections that are naturally transmitted between animals and humans. |
61% of human pathogens are zoonotic. Salomella, Swine Flu, Avian Flu etc. |
|
|
Calculating Epicenter |
Distance= time delay between p and s / (1/km/s of S - 1/km/s of P) 10seconds/( 1/3km- 1/5km) = 75km away. |
Use 3 locations distance to find the epicenter. |
|
|
3 types of Volcanoes |
Active-errupted in history Dormant- have not erupted, but may Extinct- no longer active and no chance of eruptions |
|
|
|
Hypothesis of Continental Drift |
1912- Alfred Wegner Continents were joined in super continent, Pangea, but seperated and spread apart. |
Jigsaw puzzle Fossil matching Mountain ranges |

