![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
standard form |
the number must be 1 or more and less than 10 |
|
|
Pythagoras triples |
3:4:5 and 5:12:13 |
|
|
Area of parallelogram |
A=b×h |
|
|
Area of triangle |
A=b×h/2 |
|
|
Area of Trapezium |
A=(a+b)h/2 |
|
|
Volume of Cubeoid |
V=l×b×h |
|
|
Area of rectangle |
A=l×b |
|
|
Area of square |
A=l² |
|
|
Volume of Cube |
V=l³ |
|
|
1litre |
1000cm³ |
|
|
Length of arc |
(θ/360)×2πr |
|
|
Volume of Prism |
V=c.s.a×l |
|
|
1m |
100cm |
|
|
Area of a circle |
A=πr² |
|
|
Circumference |
C=πd or C=2πr |
|
|
1cm |
10mm |
|
|
1km |
1000m |
|
|
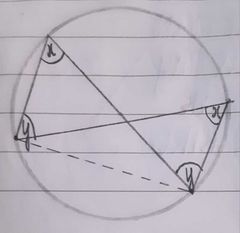
Angles in the same segment are equal. |
|
|
Angles at centre is twice the angle at circumference |
|
|
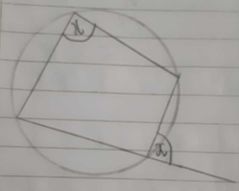
The exterior angle of a cyclic quad is equal to the opposite interior angle. |
|
|
curved surface area of cylinder |
CSA=2πrh |
|
|
Area of sector |
(θ/360)×πr² |
|
|
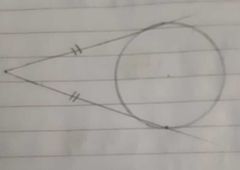
Two tangents to a circle are equal. |
|
|
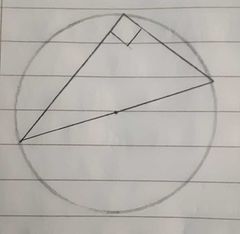
Angles in a semi-circle is equal to 90° |
|
|
Opposite angles in a cycling quad add up to 180° |
|

|
Tangent perpendicular to a radius makes an angle of 90° |
|
|
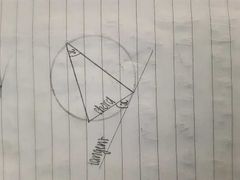
Alternate segment theorem |
|
|
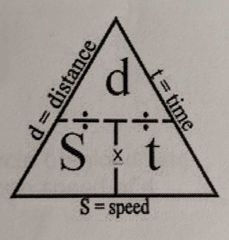
speed formula |
|
|
|
Volume of Cylinder |
V=πr²h |
|
|
average speed formula |
average speed=total distance travelled/total time taken |
|
|
angle of elevation |
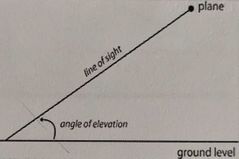
|
|
|
angle of depression |
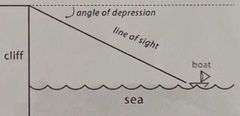
|
|
|
simple interest formula |
I=PTR/100 |
|
|
equation of a line |
y=mx+c m=gradient c=y-intercept |
|
|
gradient formula |
∆y/∆x |
|
|
shape with 3 sides |
triangle |
|
|
shape with 4 sides |
Quadrilateral |
|
|
shape with 5 sides |
Pentagon |
|
|
shape with 6 sides |
Hexagon |
|
|
Shape with 7 sides |
Heptagon |
|
|
Shape with 8 sides |
Octagon |
|
|
sum of exterior angles |
360° |
|
|
one exterior angle |
360°/n |
|
|
sum of interior angles |
(n-2)x180° |
|
|
mode |
the mode is the number that appears most in the set of data. |
|
|
median |
the median is the middle number. Putting all the data points in order and taking the one in the middle. OR if there are two middle numbers, taking them and dividing them by two (taking the mean). |
|
|
range |
Difference between largest and smallest number. |
|
|
mean |
Mean is the average. Mean: all numbers added/number of numbers |
|
|
prime number |
has only two factors (one and itself) |
|
|
Factor |
numbers which divide another number. ex: factors of 12 are 1,2,3,4,6,12 |
|
|
Multiple |
the multiplication table of a number. ex. multiples of 12 are 12,24,36,48,.... |
|
|
HCF |
highest common factor. ex. HCF of 48 and 32 factors of 48: 1,2,3,4,6,(8),12 32: 1,2,4,(8),16 |
|
|
LCM |
Lowest common multiple. ex. LCM of 12 and 15 multiples of 12: 12,24,48,(60),72... 15: 15,30,45,(60),75... |
|
|
Compound Interest |
A=P(1+R/100)^T P-principle e R-rate T-timeR-rateA-amount(final)(principle+interest) A-amount(final)(principle+interest) |
|
|
Area of rectangle |
A=LxB |
|
|
1cm^2 |
100mm^2 |
|
|
1m^2 |
1000cm^2 |
|
|
1km^2 |
1000000m^2 |
|
|
1cm^3 |
1000mm^3 |
|
|
1m^3 |
1000000cm^3 |
|
|
1km^3 |
1000000000m^3 |
|
|
Area of segment |
Area of segment-Area of triangle |
|
|
Discrete data |
Data which can only be measured in whole numbers. ex. no. of siblings, objects, animals |
|
|
continuous data |
Data which can be measured in decimal numbers. ex. height, money, distance, weight, volume, time. |
|
|
percentage error |
%error=error/correct value x100% |
|
|
one Interior angle |
(n-2)x180°/n |
|
|
median formula |
n+1/2 |

