![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Data?
|
Data
Consist of information coming from observations, counts, measurements, or responses. |
|
|
Statistics
|
Statistics
|
|
|
Population
|
The collection of all outcomes, responses, measurements, or counts that are of interest.
|
|
|
Sample
|
A subset of the population
|
|
|
Example: Identifying Data Sets
|
Example: Identifying Data Sets
|
|
|
Solution: Identifying Data Sets
|
The population consists of the responses of all adults in the U.S.
The sample consists of the responses of the 1500 adults in the U.S. in the survey. The sample is a subset of the responses of all adults in the U.S. The data set consists of 855 yes’s and 645 no’s. |
|
|
Parameter
|
A number that describes a population characteristic.
Average age of all people in the United States |
|
|
Statistic
|
A number that describes a sample characteristic.
Average age of people from a sample of three states |
|
|
Descriptive Statistics Involves organizing, summarizing, and displaying data.
e.g. Tables, charts, averages |
Inferential Statistics Involves using sample data to draw conclusions about a population.
|
|
|
Qualitative Data
|
Consists of attributes, labels, or nonnumerical entries.
|
|
|
Consists of attributes, labels, or nonnumerical entries.
|
Consists of attributes, labels, or nonnumerical entries.
|
|
|
Midpoint
|

|
|
|
Relative Frequency
|
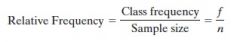
|
|
|
Population Mean
|
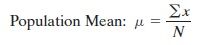
|
|
|
Sample Mean
|
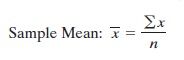
|
|
|
Weighted Mean
|
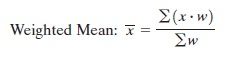
|
|
|
Mean of a Frequency Distribution
|

|
|
|
Range
|

|
|
|
Population Variance
|

|
|
|
Population Standard Deviation
|
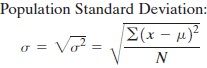
|
|
|
Sample Standard Deviation of a Frequency Distribution
|

|
|
|
Standard Score
|

|
|
|
Sample Variance
|
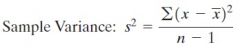
|
|
|
Sample Standard Deviation
|
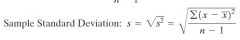
|
|
|
Expirical Rule
|

|
|
|
Chebychev's Theorem
|

|
|
|
Chapter 3
|
Chapter 3
|
|
|
Classical (or Theoretical) Propability
|

|
|
|
Empirical (or Satistical) Probability
|

|
|
|
Probability of a Complement
|

|
|
|
Probability of occurrence of both events A nd B
|
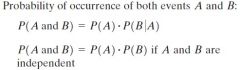
|
|
|
Probability of occurrence of either A or B or both
|

|
|
|
Permutations of n objects taken r at a time
|

|
|
|
Distinguishable Permutations
|

|
|
|
Combination of n objects taken r at a time
|

|
|
|
Frequency distribution
|
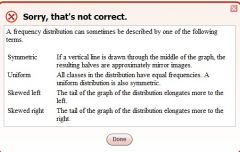
|
|
|
Find Weighted Means Sample
|

|
|
|
Mean of a Frequency Distribution
|

|

