![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
If fetal death occurs at 18-16 weeks and is retained > 6 weeks, the patient is at risk for what condition?
|
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
|
|
|
Name some post-abortion follow-up actions.
|
If mother is Rh negative, give RhoGam.
If near 20 weeks, consider the Keinhauer Betke test to measure fetal cells within mother to assess how much Rhogam to give. If mother is Rubella non-immune, offer rubella immunizations. |
|
|
Name some risk factors for having an ectopic pregnancy.
|
-PID, endometriosis
-Infertility, former ectopic pregnancy -Use of hormonal birth control methods -In vitro fertilization, therapeutic abortions -Past abdominal surgery or DES exposure -Incidence found greater in non-white women and AMA |
|
|
Name at least 2 signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy.
|
Abdominal tenderness
Dark brown vaginal spotting Decreased pregnancy symptoms Referred shoulder pain d/t hemorrhage and irritation of diaphragm NOTE: suspect ectopic pregnancy in a pregnant woman who comes to the clinic with abdominal pain. |
|
|
Name some differences between the different types of abortions.
|
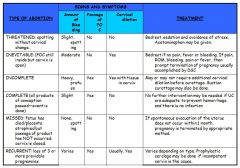
|
|
|
List the criteria for cerclage for incompetent cervix.
|
Membranes intact.
Cervical dilation < 3 cm <50% effaced |
|
|
Name at least 2 signs and symptoms associated with H-mole or GTD.
|
Chronic/acute bleeding
Hyperemesis r/t high levels of hCG Expulsion of grape-like vesicles Rapid enlargement of uterus No FHT or activity Extremely high levels of hCG |
|
|
List 2 complications and risks associated with H-mole.
|
HTN, PIH, ARDS, hyperthyroidism, increased risk of developing cancer.
|
|
|
Describe the treatment for invasive
H-mole. |
Evacuation of uterus (D&C)
After termination: -CXR, CT scan to r/o metastasis -Chemotherapy -Serial hCG weekly for 3 weeks then monthly for 6 weeks. |
|
|
List differences in signs and symptoms of abruptio placenta and placenta previa.
|

|
|
|
Name the 3 classic signs of preeclampsia.
|
hypertension: >140/90 or an increase of 30mmHg or greater in systolic BP, and 15mmHg or greater in diastolic BP.
Edema: manifests as sudden weight gain, sudden onset edema that does not go away. Proteinuria: >2+ protein (urine dipstick) |
|
|
Describe normal BP changes during pregnancy.
|
Early part of pregnancy: at baseline
Middle: slightly low BP Later part of pregnancy: back at baseline. |
|
|
Name at least 3 risk factors for PIH.
|
-Primigravida
A: age (teens, AMA) B: babies more than 1 (multiple gestation) C: chronic illness D: diabetes E: ethnicity (African American) F: family history, fat (obesity) G: gestational trophoblastic disease |
|
|
Name PIH-induced changes in the renal system.
|
Decreased renal blood flow and GFRincreased uric acid, BUN, and creatininedamage to glomerular membranesproteinuria… as it worsens, oliguria and hematuria develop.
|
|
|
Name at least 2 nursing assessments and interventions for severe PIH.
|
-continuous monitoring in a low stimulus environment
-medications: Magnesium Sulfate, antihypertensives, BMZ, -DTRs, clonus, urine dipstick -bedrest -Assess for vision changes, epigastric pain, UO (may be monitored through FC) |
|
|
What are signs and symptoms of magnesium toxicity?
|
Decreased to absent reflexes, decreased respirations, decreased LOC
|
|
|
What is the antidote for Magnesium Sulfate?
|
Calcium Gluconate
|
|
|
What is the therapeutic blood level of Magnesium?
|
4-7 mEq
|
|
|
List nursing actions for a client with eclampsia.
|
Keep client safe.
Do not force anything by mouth. |
|
|
Describe signs and symptoms of HELLP syndrome.
|
HEMOLYSIS: resulting in increase in bilirubin
ELEVATED LIVER ENZYMES: epigastric pain, UOQ tenderness, increase in AST, ALT LOW PLATELETS: <100,000 |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE
There is no increase in risk of congenital fetal abnormalities in pregnant women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM). |
TRUE
Because GDM develops at 20 weeks gestation, organogenesis is complete. |
|
|
List at least 2 prenatal risks caused by GDM.
|
PIH, IUGR, increased risk for infections, yeast infections, UTIs, pyelonephritis, polyhydramnios, SAB, shoulder dystocia, PTL, C/S birth, fetal macrosomia, fetal birth defects
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE
Pregnant women with DM are prohibited from using insulin. They are encouraged to take oral antihyperglyemics. |
FALSE
Many oral hypoglycemic agents are teratogenic. Insulin use is safe during pregnancy as it does not cross the placenta. Note: Glucose crosses the placenta. |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE
Risk for hypoglycemia is greater during the 3rd trimester. |
FALSE
Hypoglycemia: 1st trimester Hyperglycemia: 2nd and 3rd trimester |
|
|
Glucose levels should be maintained at what levels during pregnancy?
|
-May not require insulin for 24-48 hours, usually stabilized within 3 days of delivery
-Breastfeeding is encouraged -BCM: barriers, progestins |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE
DKA occurs in a state of untreated hypoglycemia and ketosis. |
FALSE
DKA occurs in a state of untreated HYPERGLYCEMIA. It is thus more likely to occur during the 2nd and 3rd trimesters. |
|
|
List nursing actions for a woman with GDM.
|
Teach about tight glucose control by diet, exercise, and/or insulin; blood glucose parameters (FBS <90mg/dl, 2hr PPrandial <120mg/dl, Before meals <105 mg/dl)
-Nutritionist referral -Educate of sxs of complications and tight glucose control. |
|
|
List at least 2 PP complications associated with GDM.
|
PP hemorrhage, PIH/eclampsia, infection
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE
Neonatal Hyperglycemia is a common in babies born to diabetic mothers. |
FALSE
Neonatal HYPOglycemia: Maternal hyperglycemia fetal hyperglycemiaoverstimulation of fetal pancreas hyperinsulinemia(after birth) hypoglycemia. |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE
All women who have a blood glucose level >140 after a 1 hour glucose tolerance test are diagnosed with GDM. |
FALSE
1 hour OGTT (usually done in week 24-28 in low risk women) is a screening test. Levels above 140mg/dl indicate need for the diagnostic test (3 hour OGTT) |
|

Fill out the following table about Prolonged Labor Patterns.
|
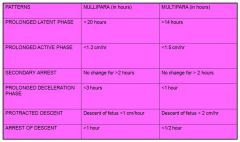
|
|
|
List nursing actions for tetanic contractions for a client who is receiving pitocin for augmentation of labor.
|
Turn off pitocin, turn client to a sidelying position, and administer O2 by facemask.
Note: Also assess UO because oxytocin has an antidiuretic effect which may cause water intoxication. |
|
|
List at least 3 contraindications of using pitocin to augment labor.
|
Known CephaloPelvic Disproportion
Fetal stress Placenta Previa Prior classical incision into uterus Active genital herpes infection Floating fetus Unripe cervix |
|
|
Name 3 assessments that should be monitored continuously if a client is on Oxytocin.
|
FHR
Uterine Resting Tone Contraction frequency, duration, strength NOTE: Duration should be no longer than 90 seconds. |
|
|
At what stage does hypertonic dystocia usually occur as opposed to hypotonic dystocia?
|
HYPERTONIC: USUALLY IN THE LATENT PHASE
HYPOTONIC: USUALLY IN THE ACTIVE PHASE |
|
|
List some possible causes of Hypotonic Dystocia.
|
Overdistended uterus, excessive use of narcotic analgesic, anesthetic or sedative.
|
|
|
List common complications of C-sections.
|
Infection and increase in bleeding.
Bladder or ureter damage. Pain Bowel Dysfunction Complications associated with anesthesia |
|
|
Name at least 4 indications for C-sections.
|
Labor dystocia
Repeat C/S, previous uterine surgery, uterine abnormalities Placenta Previa, Placenta Abruptio, prolapsed cord Active herpes, Severe PIH, multiple gestation Fetal distress, malpresentation, congenital abnormality |
|
|
Name at least 2 complications of shoulder dystocia to the newborn.
|
Fractured clavicle
Brachial plexus injury cephalhematoma death |
|
|
What station should the fetus be at in order for Vaccuum Extraction to be considered?
|
2+ or greater
|
|
|
Define Preterm Labor.
|
Preterm Labor:
True labor that occurs between 20-37 wks |
|
|
What do we instruct clients to do when sign and symptoms occur?
|
Empty Bladder
Lay Down on Left Side Drink 2-3 glasses of fluids If greater than 1hour, call MD. |
|
|
List at lest 4 tests to be done when a pregnant woman comes in with suspected PTL.
|
Fetal Fibronectin
Salivary estriol test Transvaginal sonogram Tests for ROM (fern test, nitrazine swab) Cervical cultures, wet mount, CBC, C&S Amniocentesis to determine fetal lung maturity |
|
|
List the criteria for PTL suppression
|
<3 cm dilated, <50% effaced
|
|
|
List at least 2 side effects of Terbutaline Sulfate.
|
MATERNAL:
Tachycardia, CP, Pulmonary Edema, Hyperglycemia, FETAL: Tachcardia, Hypoglycemia, hyper insulinemia. |
|
|
Name the medication that can be used to suppress labor aside from Terbutaline, Magnesium Sulfate, and Nifedipine.
|
Indomethacin
(prostaglandin Inhibitor) -side effect: premature closure of the ductus arteriosus. |
|
|
List some strategies to PREVENT PTB for women with no PTL signs and symptoms
|
Assess prior reproductive history, lifestyle, etc
Encourage changes in risk behavior Teach signs and symptoms to identify early PTL Modify work situation Maintain adequate hydration and empty bladder frequently Restrict number of embryos in IVF |
|
|
Describe the characteristics of an infant who has the best chance of survival in PTB.
|
Neonates over 2000 g (4.5lbs) or 32 weeks gestation have best chance of survival
|
|
|
List some predisposing factors to PTL.
|
DM, cardiac disease, preeclampsia, placenta previa
Infection, especially UTI Overdistention of the uterus due to multiple gestation, hydramnios, LGA baby Psychosocial stresses |
|
|
What signs and symptoms should alert the nurse to hold the next dose of Magnesium Sulfate?
|
RR< 12/min
UO < 100cc/4 hrs Absent DTRs Magnesium Sulfate Level >8mg |
|
|
True or false,
Podofilox is safe to use during pregnancy |
FALSE
|
|
|
What important instruction should you provide a woman on Flagyl?
|
“Do not take alcohol with this medication”
|
|
|
MYSTERY VAGINAL DISCHARGE:
Discharge has a fishy odor, yellow, creamy, gray |
DISCHARGE 101
Bacterial Vaginosis- fishy odor, creamy yellow, white or gray VVC: odorless, cottage cheese like Trichomonas: greenish, yellowish mucopurulent, odorous |
|
|
Which STD’s can cause opthalmia neonatorium?
|
Gonorrhea and Chlamydia
|
|
|
True or False
A pregnant woman who is non-immune to Rubella should receive a vaccine. |
FALSE
|
|
|
True or False
Painful genital lesions are associated with syphillis |
FALSE
Chancre: syphilis: painless lesions HSV: painful lesions HSV I: facial lesions HSV 2: genital lesions + shedding and recurrence on nerves |
|
|
How is toxoplasmosis transmitted and prevented?
|
Toxoplasmosis is a protozoal infection transmitted by handling or eating anything contaminated with infected cat feces or eating or handling raw meat.
Prevention includes avoiding the handling of cat litter, soil, or raw meat. |
|
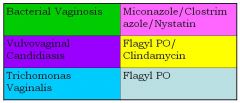
Match the correct treatment to the correct vaginosis
|
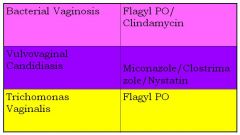
|
|
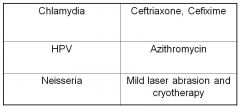
Match the following dz to the tx
|
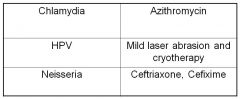
|

