![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The quantity of mass diffusing through and perpendicular to a unit cross-sectional area of material per unit time.
|
Diffusion
|
|
|
What quantities are materials dependent values (depends on which material you are discussing)?
|
Pre-exponential coefficiant
Activation Energy for diffusion |
|
|
γ-iron (FCC) at 900°C has a larger diffusion coefficient, for the self-diffusion of iron, than α-iron (BCC) at 900°C.
|
False. The atomic packing factor is greater for FCC FE meaning that there are more interstitial spaces available in the BCC FE. Therefore, motion of interstitial atoms moves more easily.
|
|
|
What do we call the energy required to initiate a reaction such as diffusion?
|
Activation energy.
|
|
|
What do we call the diffusion mechanism wherein net atomic migration is from a lattice site to an adjacent vacancy.
|
Vacancy Diffusion
|
|
|
On the basis of diffusion, why are integrated circuits typically made of aluminum (compared to Au, Ag & Cu)?
|
Less interconnect aluminum atoms diffuse into the silicon.
|
|
|
Gold and silver form a substitutional FCC alloy. The mechanism by which silver diffuses within gold is called:
|
Vacancy diffusion
|
|
|
What is the driving force for diffusion?
|
Concentration Gradient
|
|
|
Interstitial diffusion is normally more rapid than vacancy diffusion because:
|
(1) interstitial atoms, being smaller, are more mobile; (2) the probability of an empty adjacent interstitial site is greater than for a vacancy adjacent to a host atom.
|
|
|
What do we call the impetus behind a reaction, such as diffusion, grain growth, or a phase transformation.
|
Driving Force
|
|
|
A diffusion mechanism whereby atomic motion is from interstitial site to interstitial site
|
Interstitial Diffusion
|
|
|
What is the term used for defining mass flow through and perpendicular to a unit cross sectional area of solid per unit time?
|
Diffusion Flux
|
|
|
What is the diffusion condition for which there is no net accumulation or depletion of diffusion species (where the diffusion flux is independent of time).
|
Steady-state diffusion
|
|
|
What is the process by which the surface carbon concentration of a ferrous alloy is increased by diffusion from the surrounding environment.
|
Carburizing
|
|
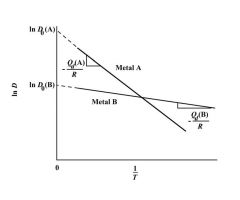
True or False: Metal A has a greater activation energy?
|
True
|
|
|
True or False: the activation energy for diffusion depends on temperature?
|
False
|
|
|
What is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform before fracturing.
|
Toughness
|
|
|
True or False: Elastic deformation is permanent and non-recoverable.
|
False
|
|
|
True or False:
Plastic deformation is non-permanent and recoverable. |
False
|
|
|
True or False: At the atomic level, during elastic deformation, bonds are breaking?
|
False
|
|
|
True or False
Brittle metals are normally tougher than ductile ones. |
False
|
|
|
Dislocation motion occurs within a crystalline material during during what type of deformation?
|
Plastic
|
|
|
True or False:
Poisson's ratio is defined as the ratio of the lateral and axial strains. |
True
|
|
|
Hooke's law applies to which region of the stress strain curve?
|
Elastic
|
|
|
True or False:
Ductility is a measure of the degree to which a material will plastically deform by the time fracture occurs. |
True
|
|
|
True or False:
Yield strength is the stress at the maximum on the engineering stress-strain curve. |
False
|
|
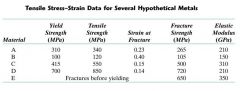
Which hypothetical material is the stiffest?
|
E
|
|
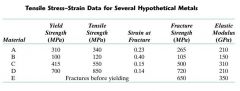
Which hypothetical material exhibits the greatest ductility?
|
B
|
|
|
True or False:
Toughness is the capacity of a material to absorb energy when it is deformed elastically and then, upon loading, to have this energy recovered. |
False
|
|
|
What are three factors that should be considered in designing a test to assess the mechanical characteristics of materials for
|
Environmental conditions, load duration, and the nature of the applied load (tension, compressional, shear)
|
|
|
What does a material that undergoes ductile fracture show?
|
necking
|
|
|
True or False:True stress is defined as the instantaneous applied load divided by the instantaneous cross-sectional area.
|
True
|
|
|
True or False:To strengthen an alloy, dislocation motion must be impeded (assuming the material has defects).
|
True
|
|
|
True or False:Recrystallization can happen to a metal or an alloy that has been plastically deformed and then heated.
|
True
|
|
|
Would you expect it to be possible for ceramic materials to experience recrystallization?
|
No
|
|
|
True or False:Metals such as lead and tin do not strain harden at room temperature.
|
True
|
|
|
For a metal or alloy that has been plastically deformed and then annealed what happens to ductility, grain size, tensile strength, and total number of grains?
|
Ductility? Increase; Tensile strength? Decreases; Grain Size? Increases; Total number of grains? Decreases
|
|
|
What does a slip system consist of?
|
A slip system consists of a crystallographic plane, and, within that plane, a direction along which dislocation motion (or slip) occurs.
|
|
|
What is the primary slip system for a BCC crystal?
|
110 plane in the -111 direction
|
|
|
True or False: Most metals strain harden at room temperature?
|
True
|
|
|
What is the Hall-Petch Equation used for?
|
Used to determine Yield strength from the average grain size.
|
|
|
True or False:
The critical resolved shear stress is the value of resolved shear stress at which yielding begins; it is a property of the material. |
True
|
|
|
True or False:
Addition of substitutional components into a metal will weaken the metal (this is called solid-solution strengthening). |
False
|
|
|
True or False:The hardness measured from an indentation that is positioned close to a preexisting indentation will be higher than if it were positioned further away.
|
True
|
|
|
True or False: Defects in a crystal can slow dislocation motion; this is how strain hardening weakens an alloy.
|
False
|
|
|
True or False:
It is possible for two screw dislocations of opposite sign to annihilate one another if their dislocation lines are parallel. |
True
|
|
|
True or False:Cold working, work hardening and strain hardening all refer to the phenomena by which a ductile metal becomes harder as it is plastically deformed.
|
True
|
|
|
True or False:
In general, the ways to strengthen an alloy relies on increasing the ease with which slip occurs in the alloy. |
False
|
|
|
Can a cold-worked metal can regain its mechanical properties through heat treatment?
|
Yes
|
|
|
True or False:
In general, for metals, as grain size increases the yield strength increases. |
False
|
|
|
True or False:
Defects in a crystal can slow dislocation motion; this is how strain hardening strengthens an alloy. |
True
|
|
|
True or False:
Edge, screw and mixed dislocations move (slip) in response to tensile stresses applied along a slip plane and in a slip direction. |
False
|
|
|
Can a cold worked metal ever regain its mechanical properties?
|
Yes
|
|
|
Can recrystallization happen to a metal or an alloy that has been elastically deformed and then heated.
|
No
|
|
|
True or False: Cold working, work hardening and strain hardening all refer to the phenomena by which a ceramic becomes harder as it is plastically deformed.
|
False
|
|
|
True or False:
Edge, screw and mixed dislocations move (slip) in response to shear stresses applied along a slip plane and in a slip direction. |
True
|
|
|
True or False:
Addition of substitutional components into a metal will strengthen the metal (this is called solid-solution strengthening). |
True
|
|
|
Slip is where elastic deformation occurs within a plane.
|
False
|
|
|
Would you expect a crystalline ceramic material to strain harden at room temperature?
|
No; because ceramics are brittle and cannot plastically deform.
|
|
|
Factors that may lead to scatter in fatigue life data include:
|
Variation in mean stress, specimen fabrication and surface preparation, specimen alignment and test apparatus, metallurgic variables, variation in test cycle frequency.
|
|
|
The type of fracture where crack propagation is along grain boundaries is termed:
|
Intergranular
|
|
|
True or False:
Creep results from cyclic loading |
False
|
|
|
True or False:A material’s tendency to exhibit creep decreases with increasing temperature.
|
False
|
|
|
The type of fracture where the crack passes through the grains, is termed:
|
Transgranular
|
|
|
When designing structures (that are subject to stresses) sharp corners should be avoided because they act as points of stress concentration, or "stress raises."
|
True
|
|
|
For metal alloys, select three metallurgical/processing techniques that enhance creep resistance:
|
dispersion strengthening by using insoluble second phase, solid solution alloying, increasing the grain sized or producing a grain structure with preferred orientation.
|
|
|
True or false:
A material’s tendency to exhibit creep increases with increasing temperature. |
True
|
|
|
Fatigue results from cyclic loading?
|
True
|
|
|
The term that describes brittle crack propagation corresponding to the successive and repeated breaking of atomic bonds along specific crystallographic planes.
|
Cleavage
|
|
|
True or False:
Inset square edges are places that can initiate creep cracks. |
False
|
|
|
Fatigue strength and fatigue life are parameters used to characterize the fatigue behavior of metals and alloys.
|
True
|
|
|
Some low strength steel alloys have a ductile-to-brittle transition which suggests:
|
The alloy changes to a brittle behavior with decreasing temperature.
|
|
|
Cup and Cone fractures are usually associated with what type of fracture?
|
Ductile
|

