![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Thermoplastics |
A polymer that softens when heated or reheated and gardens when cooled. |
|
|
Thermosetting |
A polymer that once cured by chemical reaction will not soften when reheated. |
|
|
What are the four kinds of polymer structures? |
Linear, branched, crosslinked, network |
|
|
Linear Polymer |

A polymer produced from bifunctional monomers consisting of repeated units joined end to end in a chain. |
|
|
Branched Polymer |

A polymer having a molecular structure of secondary chains extended from the primary chains |
|
|
Crosslinked Polymer |
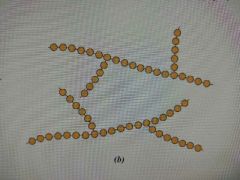
A polymer in which adjacent linear molecular chains are joined together |
|
|
Network Polymer |
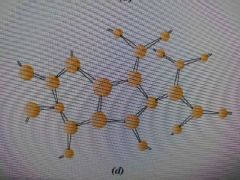
A polymer with multifunctional monomers having three or more bonds to for a 3D molecule |
|
|
Three types of stereoisomerism |
Isotactic, Syndiotactic, atactic |
|
|
Isotactic Configuration |
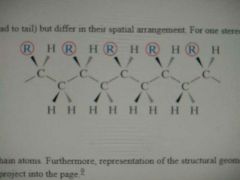
Polymer chain in which all side groups are positioned on the same side of the chain molecule |
|
|
Syndiotactic Configuration |
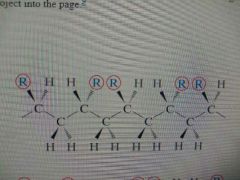
Polymer chain configuration where side groups alternate position. |
|
|
Atactic Configuration |
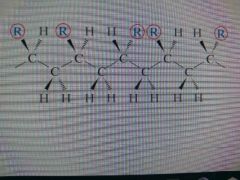
A polymer chain configuration where the side groups are randomly positioned |
|
|
Viscoelasticity |
A type of deformation exhibiting the mechanical characteristics of viscous flow and elastic deformation. The deformation is NOT instantaneous |
|
|
What effect does porosity have on ceramics? |
The higher the porosity volume fraction the weaker the ceramic becomes. |
|
|
Fatigue Limit |
The maximum stress amplitude level below which the material can endure essentially and infinite number of cycles. |
|
|
Composite |
A structural material that consists of two or more materials combined at the macroscopic level and are not soluble to one another. |
|
|
Name the types of composites |
Partial reinforced, fiber reinforced, structural, metal matrix, ceramic matrix, and polymer matrix. |
|
|
Metal Matrix Composite |
A composite where the matrix phase is metal and the reinforced phase are fibers, whiskers, or particles. High cost Used in aircraft and rocket engines |
|
|
Ceramic Matrix Composite |
A composite where both the matrix and reinforced phase are ceramics Used as diskbrakes and to reinforce ceramics. |
|
|
Polymer Matrix Composite |
A composite where the matrix is a polymer resin and fibers are dispersed particles High specific strength Corossive resistant Makes fiverglass or kevlar |
|
|
Corrosion |
Deterioration of properties due to a reaction with the environment |
|
|
Name the types of corrosion |
Uniform Attack Stress Corrosion Erosion Corrosion Pitting Crevice Galvanic Intergranular Selective Leaching |
|
|
Uniform Attack Corrosion |
Oxidation and reduction occurs uniformally over the surface (rust) |
|
|
Stress Corrosion |
When stress and corrosion work together at a crack tip |
|
|
Erosion Corrosion |
Breakdown of participating later by erosion (pipe elbows) |
|
|
Pitting Corrosion |
Downward propagation of small pits or holes |
|
|
Crevice Corrosion |
Corrosion between two pieces of the same metal |
|
|
Galvanic Corrosion |
Dissimilar metals are joined together and the more anodic one corrodes |
|
|
Intergranular Corrosion |
Corrosion along grain boundaries |
|
|
Selective Leaching |
Preferred corrosion of one element |
|
|
List factors of corrosion |
Electrolyte Electron Path Cathode Anode |
|
|
List ways to combat corrosion |
Proper naterial selection Coating Cathodic protection Inhibitiors Proper Design |
|
|
What makes metals good conductors? |
They have a high number of free electrons and allow for easy electron flow |

