![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
When a person expires with great force, the expiratory airflow reaches a maximum flow beyond which the flow cannot be increased any more even with greatly increased additional force. This is the _______ ______ _____.
|
maximum expiratory flow
|
|
|
Constricted lung diseases include fibrotic diseases of the lung itself, such as ___________, and diseases that constrict the chest cage, such as _____________-.
|
fibrotic dx: tuberculosis and silicosis
constrictive chest cage dx: kyphosis, scoliosis, and fibrotic pleurisy |
|
|
The classic disease that causes severe airway obstruction is ______. Serious airway obstruction also occurs in some stages of _________.
|
asthma
emphysema |
|
|
Comment on volume differences of constrictive lung disease vs obstructive lung disease
|
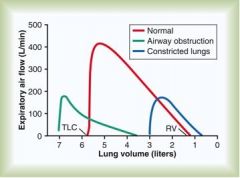
.
|
|
|
pulmonary artery pressures:
a) systolic b) diastolic c) mean d) capillary |
a) 25 mmHg
b) 8 mmHg c) 15 mmHg d) 7 mm Hg |
|
|
Main drainage of the lungs is into _________ ____ duct. Extends around terminal bronchioles.
|
right lymphatic
|
|
|
Thde normal blood volume in the lungs
|
~500ml
|
|
|
In the normal person (see Figure 42–3A), the percentage of the FVC that is expired in the first second divided by the total FVC (FEV1/FVC%) is _?_ per cent.
|
80
|
|
|
with airway obstruction, this value decreased to only _?_ per cent.
|
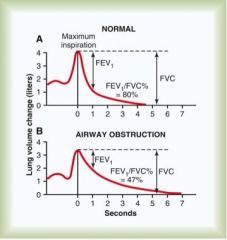
47
In serious airway obstruction, as often occurs in acute asthma, this can decrease to less than 20 per cent. |
|
|
What is the reserve volume of the lungs?
|
250ml
|
|
|
What is the stroke volume of the heart?
|
~70 to 80 ml
|
|
|
Why do shifts in blood volume distribution between the pulmonary and systemic circuits have a greater effect on the pulmonary circuit?
How is this idea significant from a clinical perspective???? |
The systemic circuit can absorb more volume.
|
|
|
The blood volume of the lungs is about 450 milliliters, about __?__ per cent of the total blood volume of the entire circulatory system.
|
9
|
|
|
Approximately how much of pulmonary blood volume is in the pulmonary capillaries?
(and the remainder is divided about equally between the pulmonary arteries and the veins.) |
70 milliliters
|
|
|
When the concentration of oxygen in the air of the alveoli decreases below normal—especially when it falls below 70 per cent of normal (below 73 mm Hg Po2)—the adjacent blood vessels constrict or dilate?
|
constrict
This is opposite to the effect observed in systemic vessels, which dilate rather than constrict in response to low oxygen. |
|
|
Gravity effects lung blood vessel pressure…. How?
|
in the standing position at rest, there is little flow in the top of the lung but about five times as much flow in the bottom.
the pulmonary arterial pressure in the uppermost portion of the lung of a standing person is about 15 mm Hg less than the pulmonary arterial pressure at the level of the heart, and the pressure in the lowest portion of the lungs is about 8 mm Hg greater |
|
|
Which zone?
No blood flow during all portions of the cardiac cycle because the local alveolar capillary pressure in that area of the lung never rises higher than the alveolar air pressure during any part of the cardiac cycle |
Zone 1:
|
|
|
Which zone?
Intermittent blood flow only during the pulmonary arterial pressure peaks because the systolic pressure is then greater than the alveolar air pressure, but the diastolic pressure is less than the alveolar air pressure |
Zone 2:
|
|
|
Which zone?
Continuous blood flow because the alveolar capillary pressure remains greater than alveolar air pressure during the entire cardiac cycle |
Zone 3:
|

