![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a proposition (or statement)? |
A statement that can only be either true or false |
|
|
What disqualifies something from being a proposition? |
An opinion or an equation by itself doesnt constitute a proposition |
|
|
How are propositions represented? |
They are assigned to variables like p, q and r and the proposition they are assigned to are put in parentheses Ex. p = (1 + 2 = 3) |
|
|
What are logical operators? |
Symbols that create new propositions, called compound propositions, from existing propositions. |
|
|
What is a truth table? |
A list of each truth value the output has for each combinatuon of input propositions. |
|
|
What are the common logical operators? |
Negation, conjunction, disjunctuon, exclusive disjunction, conditional and biconditional. |
|
|
What is the symbol and translation of the negation operator? |

Not |
|
|
What is the symbol and translation of the conjunction operator? |
Symbol: ^ Translation: and |
|
|
What is the symbol and translation of the conjunction symbol? |

(Inclusive) or |
|
|
What is the translation and symbol of the exclusice disjunction symbol? |

Exclusive or, xor |
|
|
What is the symbol and translation of the conditional operator? |
If...then, ... implies Symbol: -> |
|
|
What is the translation and symbol of the biconditional operator? |
If and only if, iff Symbol: <-> |
|
|
When is a conditional true? |
Going by: if p, then q. A conditional is true when both p and q are true or when p is false. |
|
|
What is p in the condition: p -> q? |
The premise |
|
|
What is q in the conditional: p -> q? |
The conclusion |
|
|
True or false: in conditional statements whatever comes first or second determines what is the condition and what is the premise |
False |
|
|
What happens in a conditional statement if the premise is false? |
The overall statement IS NOT evaluated to false |
|
|
How is "p is necessary for q" illustrated? |
p -> q |
|
|
How is "p is sufficient for q" illustrated? |
p -> q |
|
|
How is "p is necessary and sufficient for q" illustrated? |
p <-> q |
|
|
What does it mean for something to be sufficient? |
It means it GUARANTEES an outcome |
|
|
What does it mean for something to be necessary? |
It means its required but DOES NOT GUARANTEE the outcome |
|
|
What does "only if" mean? |
It means that something is a requirement but there might be other requirements that need satisfying |
|
|
What does "unless" mean? |
Going by "p unless q" it means that if q doesnt happen then p is guaranteed |
|
|
What is the converse if "p -> q"? |
q -> p |
|
|
What is the inverse of p -> q? |
(Not) p -> (not) q |
|
|
What is the contrapositive of p -> q? |
(Not) q -> (not) p |
|
|
When is an order of operation needed? |
When there are compound statements that involve 2 or more logical operators |
|
|
What is the order of operation? |
1. Negation 2. Conjunctuon 3. Disjunction 4. Conditional 5. Biconditional |
|
|
What do you do if there is more than one chain of conjunctions or disjunctions? |
It evaluates the same whether you do it from right to left or left to right |
|
|
What do you do in the case of multiple conditional statements? |
There is no convention so a local convention must be given in order to evaluate it properly |
|
|
What is a tautology? |
A compound proposition that is always true, no matter what the truth values involved are |
|
|
What is a contradiction? |
A compound proposition that is always false, no matter what truth values involved are. |
|
|
What is a contingency? |
A compound statement is isnt a tautology or a contradiction |
|
|
What does it mean for two compound statment to be "logically equivalent"? |
If they always share the same truth value |
|
|
What symbol is used to show logical equivalence? |
|
|
|
What is the formal definition of logical equivalence? |
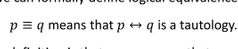
|
|
|
What is the difference between "equivalent" and "equal"? |
"Equal applies to two quantities that are the same , "equivalence" applies to two statements that are the same. |
|
|
How does the De Morgan laws explain the interaction between conjunction and disjunction? |
Negating (disjunction) a statment involving a conjunction means that only one statement has to be false in order for the negation to be valid |
|
|
What happens when you negate a conditional? |
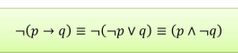
It inverts the truth table of the original conditional |
|
|
How does logical equivalences involving conjunction, disjunction and negation affect commutative, associative, distributive and identity laws? |
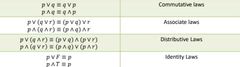
|
|
|
How do logical equivalences involving conjunction, disjunction and negation affect domination, idempotent, double negation and absorption laws? |
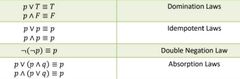
|
|
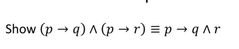
|
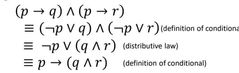
|
|
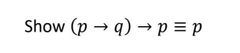
|

|
|
|
What is a conditional equivalent to? |
Its contrapositive |
|
|
What is a conditional not equivalent to? |
Its inverse or converse |
|
|
What do conditionals describe? |
Correlation |
|
|
What do conditionals NOT describe? |
Causality or temporal sequence |

