![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
116 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Steps or stages in Marketing Process: |
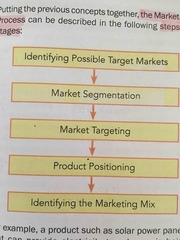
1. OPERATIONS
2. MARKETING 3. FINANCE |
|
|
Involves the creation of goods and services |
OPERATIONS |
|
|
refers to the totality of activities involved in the transfer of products from the producers/seller to the customer/buyer, including advertising, promotion, and selling, for the aim of obtaining customer satisfaction. |
MARKETING |
|
|
Deals with the management of revenues and money resources. |
FINANCE |
|
|
Is defined as the creation of goods and services. These goods and services are what a business sells to its market, which consists of customers. Involves a series of processes that convert a raw material into something useful. |
PRODUCTION |
|
|
Three Stages in Production: |
1. Assembly 2. Finishing 3. Inspection |
|
|
Means putting parts together to form a final product |
ASSEMBLY |
|
|
Involves processes such as painting, varnishing, polishing, trimming, cleaning, glazing etc. |
FINISHING |
|
|
It happens when an operation is checked to see if it has been done well, according to the specified quantity or quality. It can be done by verifying with the five senses or with the use of equipment. |
INSPECTION |
|
|
Is involved with the management of system and processes that create goods and/or provide services. It involved the planning, implementation, and control of production processes to ensure smooth and efficient production. |
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT |
|
|
What are the 6M's? |
1. MEN 2. MONEY 3. MACHINES 4. MATERIALS 5. METHODS 6. MARKETS |
|
|
Which are manufactures or created or done, are either goods or services. |
PRODUCTS |
|
|
What are the Characteristics of A Good? |
• It is a tangible product • Consistent product definition • Production is usually separated from consumption • Good can be inventoried • Low customer interaction |
|
|
What are the characteristics of service? |
• Intangible product • Produced and consumed at same time • Often unique • High customer interaction • Inconsistent product definition • Often knowledge-based |
|
|
What are the characteristics of service? |
• Intangible product • Produced and consumed at same time • Often unique • High customer interaction • Inconsistent product definition • Often knowledge-based |
|
|
What are the Ten Critical Areas of Operation Management? |
1. Service and product design 2. Quality management 3. Process and capacity design 4. Location 5. Layout design 6. Human resources and job design 7. Supply-chain management 8. Inventory management 9. Scheduling 10. Maintenance |
|
|
This means that it is something material that can be perceived by the senses-touched, tasted, held, smelled, and handled. |
IT IS TANGIBLE PRODUCT |
|
|
a good is usually easily defined and describes, because one good is usually the same as another good of its kind. |
CONSISTENCE PRODUCT DEFINITION |
|
|
The production of the good takes place at a place and time that is different from the place and time that the good is consumed or used. |
PRODUCTION IS USUALLY SEPARATED FROM CONSUMPTIONS. |
|
|
To be inventoried means that the good can be stored in either a storage room or warehouse, for a certain period of time |
GOOD CAN BE INVENTORIED |
|
|
During the production of the good and sale of good, there is minimal, low, or few instances of contact between the producers of good and customers who purchased and consume them. |
LOW CUSTOMER INTERACTION |
|
|
A service is not a material object that can be touched, held , tasted, or otherwise perceived by the senses in the usual way. |
INTANGIBLE PRODUCT |
|
|
As a service is being done, it is also consumed or used. |
PRODUCED AND CONSUMED AT SAME TIME |
|
|
Usually each service is different from another service, due to particular circumstances or conditions that accompany each service or due to the needs of the customer |
OFTEN UNIQUE |
|
|
As the service is being done, a high degree of interaction occurs between the service provider and the customers. |
HIGH CUSTOMER INTERACTION |
|
|
As the service is being done, a high degree of interaction occurs between the service provider and the customers. |
HIGH CUSTOMER INTERACTION |
|
|
It is usually difficult to define or describe the service because it may vary a bit each time. |
INCONSISTENT PRODUCT DEFINITION |
|
|
A service is often based on the knowledge and skills that the service provider has or possesses. |
OFTEN KNOWLEDGE-BASED |
|
|
Involves deciding whether to offer a good or a service or both, which goods or services to offer, and how a good or service is to be designed, composed, and created |
SERVICE AND PRODUCT DESIGN |
|
|
Means deciding who is responsible for quality. It also means trying to define quality in good or service, and how to build in the quality and ensure that the product and/or service meets the quality standards or requirements |
QUALITY MANAGEMENT |
|
|
Means deciding who is responsible for quality. It also means trying to define quality in good or service, and how to build in the quality and ensure that the product and/or service meets the quality standards or requirements |
QUALITY MANAGEMENT |
|
|
Involves deciding which processes or operations will be used in order to make the products. It means determining the order in which these various processes will be arranged. |
PROCESS AND CAPACITY DESIGN |
|
|
Means deciding who is responsible for quality. It also means trying to define quality in good or service, and how to build in the quality and ensure that the product and/or service meets the quality standards or requirements |
QUALITY MANAGEMENT |
|
|
Involves deciding which processes or operations will be used in order to make the products. It means determining the order in which these various processes will be arranged. |
PROCESS AND CAPACITY DESIGN |
|
|
Means deciding where the best place is to have factory or facility. |
LOCATION |
|
|
Means deciding who is responsible for quality. It also means trying to define quality in good or service, and how to build in the quality and ensure that the product and/or service meets the quality standards or requirements |
QUALITY MANAGEMENT |
|
|
Involves deciding which processes or operations will be used in order to make the products. It means determining the order in which these various processes will be arranged. |
PROCESS AND CAPACITY DESIGN |
|
|
Means deciding where the best place is to have factory or facility. |
LOCATION |
|
|
Refers to finding the best size for the facility or factor and determining the best layout or arrangement of rooms and various areas within the facility that maximizes their usage and meets the requirements of the various processes that will take place within the facility. |
LAYOUT DESIGN |
|
|
Means deciding who is responsible for quality. It also means trying to define quality in good or service, and how to build in the quality and ensure that the product and/or service meets the quality standards or requirements |
QUALITY MANAGEMENT |
|
|
Involves deciding which processes or operations will be used in order to make the products. It means determining the order in which these various processes will be arranged. |
PROCESS AND CAPACITY DESIGN |
|
|
Means deciding where the best place is to have factory or facility. |
LOCATION |
|
|
Refers to finding the best size for the facility or factor and determining the best layout or arrangement of rooms and various areas within the facility that maximizes their usage and meets the requirements of the various processes that will take place within the facility. |
LAYOUT DESIGN |
|
|
Involves determining how much the employees and workers can be expected to produce so that standards can be made. |
HUMAN RESOURCES AND JOB DESIGN |
|
|
Means deciding who is responsible for quality. It also means trying to define quality in good or service, and how to build in the quality and ensure that the product and/or service meets the quality standards or requirements |
QUALITY MANAGEMENT |
|
|
Involves deciding which processes or operations will be used in order to make the products. It means determining the order in which these various processes will be arranged. |
PROCESS AND CAPACITY DESIGN |
|
|
Means deciding where the best place is to have factory or facility. |
LOCATION |
|
|
Refers to finding the best size for the facility or factor and determining the best layout or arrangement of rooms and various areas within the facility that maximizes their usage and meets the requirements of the various processes that will take place within the facility. |
LAYOUT DESIGN |
|
|
Involves determining how much the employees and workers can be expected to produce so that standards can be made. |
HUMAN RESOURCES AND JOB DESIGN |
|
|
Involves determining who and how many should the suppliers, who provide the raw materials, be. It means maintaining good working relationships with them. It also refer to determining whether a business will make some of its spare parts or materials, or buy them from suppliers. |
SUPPLY-CHAIN MANAGEMENT |
|
|
Means deciding who is responsible for quality. It also means trying to define quality in good or service, and how to build in the quality and ensure that the product and/or service meets the quality standards or requirements |
QUALITY MANAGEMENT |
|
|
Involves deciding which processes or operations will be used in order to make the products. It means determining the order in which these various processes will be arranged. |
PROCESS AND CAPACITY DESIGN |
|
|
Means deciding where the best place is to have factory or facility. |
LOCATION |
|
|
Refers to finding the best size for the facility or factor and determining the best layout or arrangement of rooms and various areas within the facility that maximizes their usage and meets the requirements of the various processes that will take place within the facility. |
LAYOUT DESIGN |
|
|
Involves determining how much the employees and workers can be expected to produce so that standards can be made. |
HUMAN RESOURCES AND JOB DESIGN |
|
|
Involves determining who and how many should the suppliers, who provide the raw materials, be. It means maintaining good working relationships with them. It also refer to determining whether a business will make some of its spare parts or materials, or buy them from suppliers. |
SUPPLY-CHAIN MANAGEMENT |
|
|
Involves determining how much inventory or stocks of materials a business should keep or maintain in its storage area, stock room, or warehouse |
INVENTORY MANAGEMENT |
|
|
Means deciding who is responsible for quality. It also means trying to define quality in good or service, and how to build in the quality and ensure that the product and/or service meets the quality standards or requirements |
QUALITY MANAGEMENT |
|
|
Involves deciding which processes or operations will be used in order to make the products. It means determining the order in which these various processes will be arranged. |
PROCESS AND CAPACITY DESIGN |
|
|
Means deciding where the best place is to have factory or facility. |
LOCATION |
|
|
Refers to finding the best size for the facility or factor and determining the best layout or arrangement of rooms and various areas within the facility that maximizes their usage and meets the requirements of the various processes that will take place within the facility. |
LAYOUT DESIGN |
|
|
Involves determining how much the employees and workers can be expected to produce so that standards can be made. |
HUMAN RESOURCES AND JOB DESIGN |
|
|
Involves determining who and how many should the suppliers, who provide the raw materials, be. It means maintaining good working relationships with them. It also refer to determining whether a business will make some of its spare parts or materials, or buy them from suppliers. |
SUPPLY-CHAIN MANAGEMENT |
|
|
Involves determining how much inventory or stocks of materials a business should keep or maintain in its storage area, stock room, or warehouse |
INVENTORY MANAGEMENT |
|
|
Involves keeping machines, equipment, and facilities in good working order. |
MAINTENANCE |
|
|
Has been defined as the processing of planning and executing the conception, promotion, and distribution of goods and services to create exchange that will satisfy individual and organizational objectives. |
MARKETING |
|
|
Has been defined as the processing of planning and executing the conception, promotion, and distribution of goods and services to create exchange that will satisfy individual and organizational objectives. |
MARKETING |
|
|
Refers to what has been called the four Ps |
MARKETING MIX |
|
|
Has been defined as the processing of planning and executing the conception, promotion, and distribution of goods and services to create exchange that will satisfy individual and organizational objectives. |
MARKETING |
|
|
Refers to what has been called the four Ps |
MARKETING MIX |
|
|
What are the four Ps? |
1. Price 2. Product 3. Promotion 4. Placement/Distribution |
|
|
Has been defined as the processing of planning and executing the conception, promotion, and distribution of goods and services to create exchange that will satisfy individual and organizational objectives. |
MARKETING |
|
|
Refers to what has been called the four Ps |
MARKETING MIX |
|
|
What are the four Ps? |
1. Price 2. Product 3. Promotion 4. Placement/Distribution |
|
|
Is defined as an item that satisfies a consumer want or need. It may be tangible good such as a laptop or an intangible service such as a haircut. |
PRODUCT |
|
|
Has been defined as the processing of planning and executing the conception, promotion, and distribution of goods and services to create exchange that will satisfy individual and organizational objectives. |
MARKETING |
|
|
Refers to what has been called the four Ps |
MARKETING MIX |
|
|
What are the four Ps? |
1. Price 2. Product 3. Promotion 4. Placement/Distribution |
|
|
Is defined as an item that satisfies a consumer want or need. It may be tangible good such as a laptop or an intangible service such as a haircut. |
PRODUCT |
|
|
Is the amount a customer pays for the product. It is very important as it determines the company's profit and hence, survival. It is consisting of a percentage mark-up of the cost. |
PRICE |
|
|
Has been defined as the processing of planning and executing the conception, promotion, and distribution of goods and services to create exchange that will satisfy individual and organizational objectives. |
MARKETING |
|
|
Refers to what has been called the four Ps |
MARKETING MIX |
|
|
What are the four Ps? |
1. Price 2. Product 3. Promotion 4. Placement/Distribution |
|
|
Is defined as an item that satisfies a consumer want or need. It may be tangible good such as a laptop or an intangible service such as a haircut. |
PRODUCT |
|
|
Is the amount a customer pays for the product. It is very important as it determines the company's profit and hence, survival. It is consisting of a percentage mark-up of the cost. |
PRICE |
|
|
Refers to all the methods of communication that a marketer may use to provide information to different parties about the product. |
PROMOTION |
|
|
Has been defined as the processing of planning and executing the conception, promotion, and distribution of goods and services to create exchange that will satisfy individual and organizational objectives. |
MARKETING |
|
|
Refers to what has been called the four Ps |
MARKETING MIX |
|
|
What are the four Ps? |
1. Price 2. Product 3. Promotion 4. Placement/Distribution |
|
|
Is defined as an item that satisfies a consumer want or need. It may be tangible good such as a laptop or an intangible service such as a haircut. |
PRODUCT |
|
|
Is the amount a customer pays for the product. It is very important as it determines the company's profit and hence, survival. It is consisting of a percentage mark-up of the cost. |
PRICE |
|
|
Refers to all the methods of communication that a marketer may use to provide information to different parties about the product. |
PROMOTION |
|
|
Refers to providing the product a place which is convenient for consumers to access or buy. It bridges the gap between manufacturer and consumer. |
PLACEMENT/DISTRIBUTION |
|
|
What are the 3 Ps? |
1. PHYSICAL EVIDENCE 2. PEOPLE 3. PROCESS |
|
|
What are the 3 Ps? |
1. PHYSICAL EVIDENCE 2. PEOPLE 3. PROCESS |
|
|
It show that a service was actually performed, such as the delivery packaging for the item delivered by a delivery service. |
PHYSICAL EVIDENCE |
|
|
What are the 3 Ps? |
1. PHYSICAL EVIDENCE 2. PEOPLE 3. PROCESS |
|
|
It show that a service was actually performed, such as the delivery packaging for the item delivered by a delivery service. |
PHYSICAL EVIDENCE |
|
|
Refers to employees who execute the service, as well as the manner in which they delivered the service. |
PEOPLE |
|
|
What are the 3 Ps? |
1. PHYSICAL EVIDENCE 2. PEOPLE 3. PROCESS |
|
|
It show that a service was actually performed, such as the delivery packaging for the item delivered by a delivery service. |
PHYSICAL EVIDENCE |
|
|
Refers to employees who execute the service, as well as the manner in which they delivered the service. |
PEOPLE |
|
|
Means the processes and systems within the oraganization that affect the execution of its service, such as the scheduling of jobs or attending to customer complaints |
PROCESS |
|
|
He proposed the four Cs classification in 1990 which is a more consumer-oriented version of the four Ps |
ROBERT F. LAUTERBORN |
|
|
Mean dividing a heterogeneous market into several homogeneous groups. This means dividing a market composed of people with very different kinds of characteristics. |
MARKET SEGMENTATION |
|
|
Mean dividing a heterogeneous market into several homogeneous groups. This means dividing a market composed of people with very different kinds of characteristics. |
MARKET SEGMENTATION |
|
|
What are the basis of market segmentation? |
1. Geographical 2. Demographic 3. Psychographics 4. Behavioral |
|
|
Customers can be segmented according to location, population, density, and climate |
GEOGRAPHICAL |
|
|
Customers can be segmented according to age, gender, civil status, income, education, profession, family organization, and religion. |
DEMOGRAPHIC |
|
|
Customers may be segmented according to social issues, such as religion, politics or work, or according to personal interest such as family life, food, health, friends, and shopping. |
PSYCHOGRAPHICS |
|
|
Customers may be segmented according to how often they buy, user status, user rate, user loyalty, and readiness to buy. |
BEHAVIORAL |
|
|
Means evaluating potential and commercial attractiveness of the market segments. |
MARKET TARGETING |
|
|
Means evaluating potential and commercial attractiveness of the market segments. |
MARKET TARGETING |
|
|
What are the factors of market targeting: |
1. Segment size and growth 2. Segment attractiveness 3. Company objectives and resources |
|
|
Means communicating a product's image in comparison to competitors in the market. |
PRODUCT POSITIONING |
|
|
Three main functions exist in every organization: |
1. OPERATIONS 2. MARKETING 3. FINANCE |

