![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The Role of Promotion |
Communications by marketers that informs, persuades, and reminds potential buyers of a product in order to influence an opinion or elicit a response. |
|
|
Communication Process |
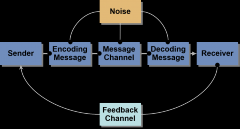
|
|
|
Components of promotion mix |
Advertising Public Relations Sales Promotion Personal Selling |
|
|
AIDA |
Attention Interest |
|
|
Promotional Goals |
Informing Persuading Reminding |
|
|
factors affecting the promo mix |
nature of the product stage in PLC target market factors type of buying decision promotion funds push or pull strategy |
|
|
Integrated Marketing Communications |
coordination of all promotional messages to assure the consistency of messages at every contact point where a company meets the consumer |
|
|
S-Curve |
compares return and money spent |
|
|
Major types of Advertising |
Institutional: corporate identity, advocacy Product: pioneering, competitive, comparative |
|
|
DAGMAR |
Define target audience Define desired percentage change Define the time for change |
|
|
Creative Decisions |
Identify product benefits Develop and evaluate advert. appeals execute the message eval. the campaign's effectiveness |
|
|
Media Scheduling |
Continuous Flighted Pulsing (cont.+flighted) Seasonal |
|
|
Media Decisions in Advertising |
Monitored media Unmonitored media: direct mail, coupons, catalogs |
|
|
Personal Relations |
Consumer Education Crisis Management |
|
|
Marketing |
activity, set of instructions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners and society at large. |
|
|
Consumer sales promotions vs. trade sales promotions |
Pull vs. push and directed toward marketing channel |
|
|
Objectives of sales promotion |
Loyal customers Competitor's customers Brand switchers Price buyers |
|
|
Tools for consumer sales promotion |
Coupon's and Rebates Premiums Loyalty Marketing Programs Contests and Sweepstakes Sampling Point-of-Purchase Promotion |
|
|
Trade Sales Promotion |
Trade Allowances/Discounts Push Money Training Free Merchandise Conventions and Trade Shows |
|
|
Personal Selling |
F (features) A (advantage) B (benefits) |
|
|
Relationship Selling |
similar to being a consultant |
|
|
Steps in the selling process |
Generate leads Qualify leads Probe customer needs Develop/propose solutions Handle objections Close the sale Follow up |
|
|
Importance of price |
Seller-price is revenue consumer-price is cost profit=revenue-expenses |
|
|
What increases or decreases price? |
Flood of new products Increased availability of bargain-priced private and generic brands Price cutting as a strategy to maintain or regain market share Internet used for comparison shopping |
|
|
Pricing Objectives |
Profit-oriented (long-term, profit max, satisfactory products, ROI) Sales oriented (volume, market share, sales max) Stauts quo (passive, easy) |
|
|
The demand determinant of price |
price dependent of the demand for the good or service and cost to the seller for that good or servie |
|
|
Demand |
Quantity of a product that will be offered to the market by a supplier or suppliers at various prices for a specifies period |
|
|
Supply |
the quantity of a product that will be offered to the market by a supplier or suppliers at various prices for a specified period |
|
|
Elasticity |
Elastic-consumers buy more or less of a product when the price changes Inelastic-no significantly affect demand Factors that affect elasticity of demand availability of substitutes price relative to purchasing power product durability a product's other assets rate of inflation |
|
|
Determinants of price |
Product life cycle competition distribution strategy promotion strategy perceived quality |
|
|
How to set a price on a good or service |
price skimming price penetration status quo |
|
|
Legality and Ethics of price setting |
Unfair trade practices Price fixing Price Discrimination Predatory Pricing |
|
|
Tactics for fine-tuning the base price |
Discounts Geographic pricing Special pricing tactics |
|
|
Value-based pricing |
Quality discounts Cash discounts Functional discounts Seasonal discounts promotional allowances rebates zero percent financing value-based pricing |
|
|
Geographic pricing |
FOB origin pricing uniform delivered pricing zone pricing freight absorption pricing basing-point pricing |
|
|
other tactics |
Single-price tactics Flexible pricing professional services pricing Price lining Leader pricing Bait pricing Odd-even pricing Price bundling Two-part pricing |
|
|
Product line pricing |
primary goal is to achieve maximum profits for the entire line |
|
|
relationship among products |
complementary substitutes neutral |
|
|
pricing during recessions |
cost-oriented tactics (high volume sales with low profit margin, eliminating product to reduce economies of scale) Delayed-quotation pricing Escalator pricing Added fees Demand oriented tactics (price shading) build market share(value based pricing, (un)bundle) negotiating with suppliers (offer help, reduce costs, cut number of suppliers) |

