![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
161 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Marketing |
The process by which companies createvalue for customers and build strongcustomer relationships in order to capturevalue from customers in return. |
|
|
Needs |
States of felt deprivation. |
|
|
Wants |
The form human needs take as theyare shaped by culture and individualpersonality. |
|
|
Demands |
Human wants that are backed by buyingpower. |
|
|
Market offerings |
Some combination of products, services,information, or experiences offered to amarket to satisfy a need or want. |
|
|
Marketing myopia |
The mistake of paying more attention tothe specific products a company offersthan to the benefits and experiencesproduced by these products. |
|
|
Exchange |
The act of obtaining a desired object fromsomeone by offering something in return. |
|
|
Market |
The set of all actual and potential buyersof a product or service. |
|
|
Marketing managment |
The art and science of choosingtarget markets and building profitablerelationships with them. |
|
|
Production Concept |
The idea that consumers will favorproducts that are available and highlyaffordable; therefore, the organizationshould focus on improving productionand distribution efficiency. |
|
|
Production Concept |
The idea that consumers will favorproducts that offer the most quality,performance, and features; therefore,the organization should devote itsenergy to making continuous productimprovements. |
|
|
Selling Concept |
The idea that consumers will not buyenough of the firm’s products unless the promotion effort. |
|
|
Marketing concept |
A philosophy in which achievingorganizational goals depends on knowingthe needs and wants of target marketsand delivering the desired satisfactionsbetter than competitors do. |
|
|
Societal marketing concept |
The idea that a company’s marketingdecisions should consider consumers’wants, the company’s requirements, |
|
|
Customer relationship management |
The overall process of building andmaintaining profitable customerrelationships by delivering superiorcustomer value and satisfaction. |
|
|
Customer-perceuved value |
The customer’s evaluation of thedifference between all the benefits and allthe costs of a marketing offer relative tothose of competing offers. |
|
|
Customer satisfaction |
The extent to which a product’s perceivedperformance matches a buyer’sexpectations. |
|
|
Customer-managed relationships |
Marketing relationships in whichcustomers, empowered by today’snew digital technologies, interact withcompanies and with each other to shapetheir relationships with brands. |
|
|
Consumer-generated marketing |
Brand exchanges created by consumersthemselves—both invited and uninvited—by which consumers are playing anincreasing role in shaping their ownbrand experiences and those of otherconsumers. |
|
|
Partner relationship management |
Working closely with partners in othercompany departments and outside thecompany to jointly bring greater value tocustomers. |
|
|
Customer lifetime value |
The value of the entire stream ofpurchases a customer makes over alifetime of patronage. |
|
|
Share of customer |
The portion of the customer’s purchasingthat a company gets in its productcategories. |
|
|
Customer equity |
The total combined customer lifetimevalues of all of the company’s customers. |
|
|
Internet |
A vast public web of computer networksthat connects users of all types allaround the world to each other and to anamazingly large information repository. |
|
|
Strategic planning |
The process of developing andmaintaining a strategic fit between theorganization’s goals and capabilities andits changing marketing opportunities. |
|
|
Mission statement |
A statement of the organization’spurpose—what it wants to accomplish inthe larger environment. |
|
|
Business portfolio |
The collection of businesses andproducts that make up the company. |
|
|
Portfolio analysis |
The process by which managementevaluates the products and businessesthat make up the company. |
|
|
Growth-share matrix |
A portfolio-planning method that evaluates a company’s SBUs in terms ofmarket growth rate and relative marketshare. |
|
|
Product/market expanison grid |
A portfolio-planning tool for identifying company growth opportunities throughmarket penetration, market development,product development, or diversification. |
|
|
Market penetration |
Company growth by increasing salesof current products to current marketsegments without changing the product. |
|
|
Market development |
Company growth by identifying anddeveloping new market segments forcurrent company products. |
|
|
Product development |
Company growth by offering modifiedor new products to current marketsegments. |
|
|
Diversication |
Company growth through starting upor acquiring businesses outside thecompany’s current products and markets. |
|
|
Value Chain |
The series of internal departments that design, produce, market, deliver, andsupport a firm’s products. |
|
|
Value delivery network |
The network made up of the company, itssuppliers, its distributors, and, ultimately,its customers who partner with eachother to improve the performance of theentire system. |
|
|
Marketing strategy |
The marketing logic by which thecompany hopes to create customervalue and achieve profitable customerrelationships. |
|
|
Market segmentation |
Dividing a market into distinct groupsof buyers who have different needs,characteristics, or behaviors, and whomight require separate products ormarketing programs. |
|
|
Market segment |
A group of consumers who respond ina similar way to a given set of marketingefforts. |
|
|
Market targeting |
The process of evaluating each marketsegment’s attractiveness and selectingone or more segments to enter. |
|
|
Differentiation |
Actually differentiating the market offeringto create superior customer value. |
|
|
Marketing mix |
The set of tactical marketing tools—product, price, place, and promotion—that the firm blends to produce theresponse it wants in the target market. |
|
|
SWOT analysis |
An overall evaluation of the company’sstrengths (S), weaknesses (W),opportunities (O), and threats (T). |
|
|
Market implementation |
Turning marketing strategies and plansinto marketing actions to accomplishstrategic marketing objectives. |
|
|
Marketing control |
Measuring and evaluating the resultsof marketing strategies and plans andtaking corrective action to ensure that theobjectives are achieved. |
|
|
Return on marketing investment |
The net return from a marketinginvestment divided by the costs of themarketing investment. |
|
|
Marketing environment |
The actors and forces outside marketingthat affect marketing management’sability to build and maintain successfulrelationships with target customers. |
|
|
Microenvironment |
The actors close to the company thataffect its ability to serve its customers—the company, suppliers, marketingintermediaries, customer markets,competitors, and publics. |
|
|
Macroenvironment |
The larger societal forces that affectthe microenvironment—demographic,economic, natural, technological, political,and cultural forces. |
|
|
Marketing intermediaries |
Firms that help the company to promote,sell, and distribute its goods to finalbuyers. |
|
|
Public |
Any group that has an actual or potentialinterest in or impact on an organization’sability to achieve its objectives. |
|
|
Demography |
The study of human populations in termsof size, density, location, age, gender,race, occupation, and other statistics. |
|
|
Baby boomers |
The 78 million people born during theyears following World War II and lastinguntil 1964. |
|
|
Generation X |
The 49 million people born between 1965and 1976 in the “birth dearth” followingthe baby boom. |
|
|
Millenials (Generation Y) |
The 83 million children of the babyboomers born between 1977 and 2000. |
|
|
Economic environment |
Economic factors that affect consumerpurchasing power and spending patterns. |
|
|
Natural environment |
The physical environment and the naturalresources that are needed as inputsby marketers or that are affected bymarketing activities. |
|
|
Environmental sustainability |
Developing strategies and practices thatcreate a world economy that the planetcan support indefinitely. |
|
|
Technical environment |
Forces that create new technologies,creating new product and marketopportunities. |
|
|
Political environment |
Laws, government agencies, andpressure groups that influence and limitvarious organizations and individuals in agiven society. |
|
|
Cultural environment |
Institutions and other forces that affectsociety’s basic values, perceptions,preferences, and behaviors. |
|
|
Internal Databases |
Electronic collections of consumer andmarket information obtained from datasources within the company network. |
|
|
Competitive marketing inteligence |
The systematic collection and analysisof publicly available informationabout consumers, competitors,and developments in the marketingenvironment. |
|
|
Marketing research |
The systematic design, collection,analysis, and reporting of data relevant toa specific marketing situation facing anorganization. |
|
|
Exploratory research |
Marketing research to gather preliminaryinformation that will help define problemsand suggest hypotheses. |
|
|
Descriptive research |
Marketing research to better describemarketing problems, situations,or markets, such as the market potentialfor a product or the demographics andattitudes of consumers. |
|
|
casual research |
Marketing research to test hypotheses about cause and effect relationship |
|
|
Secondary Data |
Information that already existssomewhere, having been collected foranother purpose. |
|
|
Primary Data |
Information collected for the specificpurpose at hand. |
|
|
Observational research |
Gathering primary data by observingrelevant people, actions, and situations. |
|
|
Ethnographic research |
A form of observational research thatinvolves sending trained observers towatch and interact with consumers intheir “natural environments.” |
|
|
Survey Research |
Gathering primary data by asking peoplequestions about their knowledge,attitudes, preferences, and buyingbehavior. |
|
|
Experimental Research |
Gathering primary data by selectingmatched groups of subjects, giving themdifferent treatments, controlling relatedfactors, and checking for differences ingroup responses. |
|
|
Focus group interviewing |
Personal interviewing that involves inviting6 to 10 people to gather for a few hourswith a trained interviewer to talk abouta product, service, or organization. The interviewer “focuses” the groupdiscussion on important issues. |
|
|
Online focus groups |
Gathering a small group of people onlinewith a trained moderator to chat abouta product, service, or organization andgain qualitative insights about consumerattitudes and behavior. |
|
|
Sample |
A segment of the population selectedfor marketing research to represent thepopulation as a whole. |
|
|
Customer realtionship management |
Managing detailed information aboutindividual customers and carefullymanaging customer touch points tomaximize customer loyalty. |
|
|
Consumer buyer behavior |
The buying behavior of final consumers—individuals and households that buygoods and services for personalconsumption. |
|
|
Consumer market |
All the individuals and households thatbuy or acquire goods and services forpersonal consumption. |
|
|
Culture |
The set of basic values, perceptions,wants, and behaviors learned by amember of society from family and otherimportant institutions. |
|
|
Subculture
|
A group of people with shared valuesystems based on common lifeexperiences and situations. |
|
|
Social Class
|
Relatively permanent and ordereddivisions in a society whose membersshare similar values, interests, andbehaviors. |
|
|
Group
|
Two or more people who interact toaccomplish individual or mutual goals. |
|
|
Word-of mouth influence |
The impact of the personal words andrecommendations of trusted friends,associates, and other consumers onbuying behavior. |
|
|
Opinion leader |
A person within a reference group who,because of special skills, knowledge,personality, or other characteristics,exerts social influence on others. |
|
|
Online social networks |
Online social communities—blogs, socialnetworking Web sites, and other onlinecommunities—where people socialize orexchange information and opinions. |
|
|
Lifestyle |
A person’s pattern of living as expressedin his or her activities, interests, andopinions. |
|
|
Personality |
The unique psychological characteristicsthat distinguish a person or group. |
|
|
Motive |
A need that is sufficiently pressing todirect the person to seek satisfaction ofthe need. |
|
|
Perception |
The process by which people select,organize, and interpret information toform a meaningful picture of the world |
|
|
Learning |
Changes in an individual’s behaviorarising from experience. |
|
|
Belief
|
A descriptive thought that a person holdsabout something. |
|
|
Complex buying behaviour |
Consumer buying behavior in situationscharacterized by high consumerinvolvement in a purchase and significantperceived differences among brands. |
|
|
Dissonance-reducing buying behavior |
Consumer buying behavior in situationscharacterized by high involvement butfew perceived differences among brands. |
|
|
Habitual buying behavior |
Consumer buying behavior in situationscharacterized by low consumerinvolvement and few significant perceivedbrand differences. |
|
|
Variety-seeking buying behavior |
Consumer buying behavior in situationscharacterized by low consumerinvolvement but significant perceivedbrand differences. |
|
|
Need recognition |
The first stage of the buyer decisionprocess, in which the consumerrecognizes a problem or need. |
|
|
Information search |
The stage of the buyer decision processin which the consumer is motivated tosearch for more information. |
|
|
Alternative evaluation |
The stage of the buyer decision processin which the consumer uses informationto evaluate alternative brands in thechoice set. |
|
|
Purchase decision |
The buyer’s decision about which brandto purchase. |
|
|
Postpurchase behavior |
The stage of the buyer decision processin which consumers take further actionafter purchase, based on their satisfactionor dissatisfaction. |
|
|
Cognitive dissonance |
Buyer discomfort caused bypostpurchase conflict. |
|
|
new Product |
A good, service, or idea that is perceivedby some potential customers as new. |
|
|
Adoption process |
The mental process through which anindividual passes from first hearing aboutan innovation to final adoption. |
|
|
Business buyer behavior |
The buying behavior of organizationsthat buy goods and services for use inthe production of other products andservices that are sold, rented, or suppliedto others. |
|
|
Business buying process |
The decision process by which businessbuyers determine which products andservices their organizations need topurchase and then find, evaluate, andchoose among alternative suppliers andbrands. |
|
|
Derived demand |
Business demand that ultimately comesfrom (derives from) the demand forconsumer goods. |
|
|
Supplier development |
Systematic development of networks appropriate and dependable supply ofproducts and materials for use in makingproducts or reselling them to others. |
|
|
Straight rebuy
|
A business buying situation in whichthe buyer routinely reorders somethingwithout any modifications. |
|
|
Modified rebuy
|
A business buying situation in whichthe buyer wants to modify productspecifications, prices, terms, or suppliers. |
|
|
New Task |
A business buying situation in which thebuyer purchases a product or service forthe first time. |
|
|
Systems selling (or solutions selling
|
Buying a packaged solution to a problemfrom a single seller, thus avoiding all theseparate decisions involved in a complexbuying situation. |
|
|
Ding Dong where's my Ping pong? |
In the garage |
|
|
Buying center |
All the individuals and units that play arole in the purchase decision-makingprocess. |
|
|
users |
Members of the buying organization whowill actually use the purchased productor service. |
|
|
Influencers
|
People in an organization’s buyingcenter who affect the buying decision;they often help define specifications andalso provide information for evaluatingalternatives. |
|
|
Buyers
|
People in an organization’s buying centerwho make an actual purchase. |
|
|
Deciders
|
People in an organization’s buying centerwho have formal or informal power toselect or approve the final suppliers. |
|
|
Gatekeepers
|
People in an organization’s buying centerwho control the flow of information toothers. |
|
|
Problem recognition
|
The stage of the business buying processin which the company recognizes aproblem or need that can be met byacquiring a good or a service. |
|
|
General need description |
The stage in the business buyingprocess in which a buyer describes thegeneral characteristics and quantity of aneeded item. |
|
|
Product specification
|
The stage of the business buying processin which the buying organization decideson and specifies the best technicalproduct characteristics for a needed item. |
|
|
Supplier search
|
The stage of the business buying processin which the buyer tries to find the bestvendors. |
|
|
Proposal solicitation
|
The stage of the business buying processin which the buyer invites qualifiedsuppliers to submit proposals. |
|
|
Supplier selection |
The stage of the business buying processin which the buyer reviews proposals andselects a supplier or suppliers. |
|
|
Order-routine specification
|
The stage of the business buying processin which the buyer writes the final orderwith the chosen supplier(s), listing thetechnical specifications, quantity needed,expected time of delivery, return policies,and warranties. |
|
|
Performance review |
The stage of the business buyingprocess in which the buyer assessesthe performance of the supplier anddecides to continue, modify, or drop thearrangement. |
|
|
E-procurement
|
Purchasing through electronicconnections between buyers andsellers—usually online. |
|
|
Institutinal market
|
Schools, hospitals, nursing homes,prisons, and other institutions thatprovide goods and services to people intheir care. |
|
|
Goverment market
|
Governmental units—federal, state,and local—that purchase or rent goodsand services for carrying out the mainfunctions of government. |
|
|
Market segmentation |
Dividing a market into smaller segments of buyers with distinct needs, characteristics, or behaviours that might require separate marketing strategies or mixes |
|
|
Market targeting |
Evaluating each market segment's attractivness and selecting on or more segments to enter |
|
|
Differntiation |
Differntiating the market offering to create superior customer value. |
|
|
Positioning |
Arranging for a market offering to occupy a clear, distinctive and desirable place realtive to competing products in the minds of target consumers. |
|
|
Geographic segmentation |
Dividing a market into different geographical units, such as nations states regions counties cities or even neighborhoods |
|
|
Demographic segmentation |
Dividing the market into segments based on variables such as age life cycle stage gender income occupation education religion ethnicity and generation |
|
|
Age and life cycles segmentation |
Dividing a market into differnt age and life cycle groups |
|
|
Gender segmentation |
Dividng a market into different segments based on gender |
|
|
income segmentation |
Dividing a market into differnt income segment |
|
|
Psychographic segmentation |
Dividing a market into different segments based on social class lifestyle or personality characteristics |
|
|
behavioral segmentation |
dividing market into segments based on consumer knwledge atttudes, uses or respnses to a product |
|
|
Occasion segmentation |
Dividng the market into segments according to aoccasions when buyers get the idea to guy actually make their purchase or use the purchased item |
|
|
Benefit segmentation |
Dividing the market into segments according to the different benefits that consumser seek from the product |
|
|
Intermarket (cross-market) segmentation |
Forming segments of consumers who have similar needs and buying behaviours even though they are located in different countries |
|
|
Target market |
A set of buyers sharing common needs or characteristics that the company decides to serve |
|
|
Undifferentiated marketing
|
A market coverage stragey in which a firm decides to ignore market sgment differnecs and go after the whole market with one offer |
|
|
Target market |
A set of buyers sharing common needs or characteristics that the company decides to serve |
|
|
Undifferntiaded (mass) marketing |
A merket-coverage strategy in which a firm decides to ignore market segment differnces and go after the whole market with one offer |
|
|
Differntiated (segmented) marketing |
A market coverage strategy in which a firm decides to target several market segments and designs seperate offers for each
|
|
|
Concentrated (niche) marketing |
A market-coverage strategy in which a firm goes after a large share of one or a few segments or niches |
|
|
Micromarketing |
Tailoring procuts and marketing programs to the needs and wants of specific individuals and local customer segments> It includes local marketing and individual marketing |
|
|
Local marketing |
tailoring brands and marketing to the needs anwants of local customer segments: Cities neighborhoods and even specific stores! Like Groupon |
|
|
individual Marketing |
Tailoring products and marketing programs to the needs and preferences of individual customers. (Nike shoe creator) |
|
|
Product position
|
The way a product is defined by consumers on important attributes the place the product occupies in consumers minds relative to competing products. Honest tea -> positions itself as honest tea |
|
|
Competitive advantage |
an advantage over competitors gained by offering greater customer value either by having lower prices or providing more benefits that justify higher prices. |
|
|
Value proposition |
The full positioning of a brand - the full mix of benefits on which is positioned |
|
|
Positioning Statement |
A statement that summaries company or brand positioning using this form: To (target segment and need) our (brand) is (concept) that (point of difference) |
|
|
Possible value propositions |
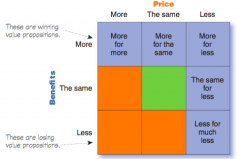
|
|
|
Postioning Map: large Luxery SUV's |
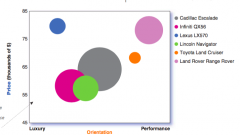
|
|
|
Designing a customer driven marketing strategy |
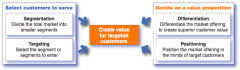
|
|
|
Homy where you at? |
At the gas station
|

